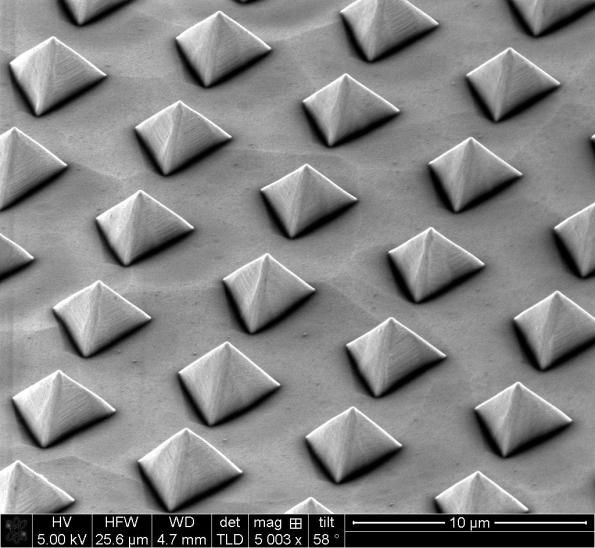
Researchers from the Tyndall National Institute in Cork have created micro-structures shaped like small pyramids that can create entangled photons. Does this mean that quantum computers are closer than we realize?
Quantum computers have been the stuff of science fiction for the past few decades. In recent times, quantum computers have slowly become more of a reality with some machines successfully solving real world problems such as games and path finding algorithms.
But why are quantum computers so desired by tech firms and why is there so much research into the field? Silicon has been incredibly loyal to the tech world for the past 50 years, giving us the point contact transistor in 1947. Now, silicon is at the center of technology with computers, tablets, smartphones, the IoT, and even everyday items. In fact, you cannot walk down a city street without being in range of some Wi-Fi network or influence from a small silicon device.