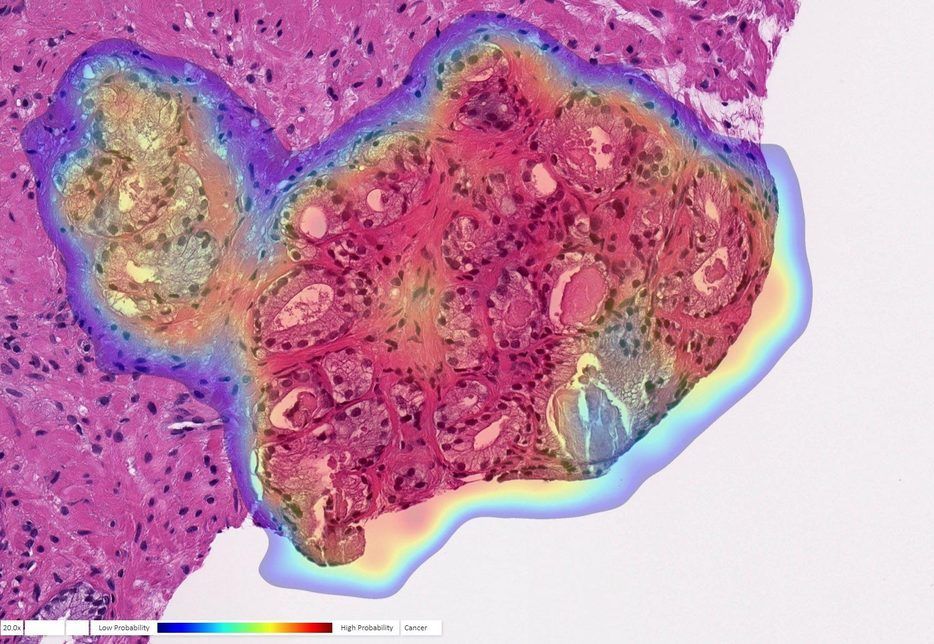
A study published today (July 27, 2020) in The Lancet Digital Health by UPMC and University of Pittsburgh researchers demonstrates the highest accuracy to date in recognizing and characterizing prostate cancer using an artificial intelligence (AI) program.
“Humans are good at recognizing anomalies, but they have their own biases or past experience,” said senior author Rajiv Dhir, M.D., M.B.A., chief pathologist and vice chair of pathology at UPMC Shadyside and professor of biomedical informatics at Pitt. “Machines are detached from the whole story. There’s definitely an element of standardizing care.”
To train the AI to recognize prostate cancer, Dhir and his colleagues provided images from more than a million parts of stained tissue slides taken from patient biopsies. Each image was labeled by expert pathologists to teach the AI how to discriminate between healthy and abnormal tissue. The algorithm was then tested on a separate set of 1,600 slides taken from 100 consecutive patients seen at UPMC for suspected prostate cancer.