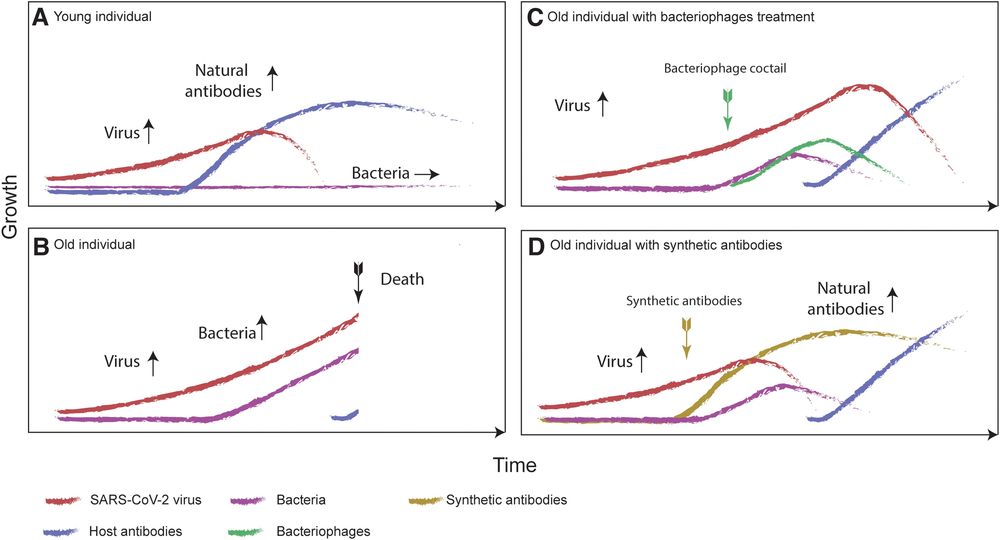
Bacteriophage can reduce bacterial growth in the lungs, limiting fluid build-up. This could decrease the mortality of patients affected by COVID-19, according to the peer-reviewed journal PHAGE: Therapy, Applications, and Research.
“The bacterial growth rate could potentially be reduced by the aerosol application of natural bacteriophages. These prey on the main species of bacteria known to cause respiratory failure,” says Marcin Wojewodzic, PhD, University of Birmingham (U.K.). Decreasing bacterial growth would also give the body more time to produce protective antibodies against the disease-causing coronavirus.
Used correctly, phages have an advantage here of being able to very specifically target the bacteria that cause secondary infections. They would remove the problematic bacterium but leave an otherwise fragile microbiome intact.” Martha Clokie, PhD, Editor-in-Chief of PHAGE and Professor of Microbiology, University of Leicester (U.K.)
The pandemic of the coronavirus disease (Covid-19) has caused the death of at least 270,000 people as of the 8th of May 2020. This work stresses the potential role of bacteriophages to decrease the mortality rate of patients infected by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus. The indirect cause of mortality in Covid-19 is miscommunication between the innate and adaptive immune systems, resulting in a failure to produce effective antibodies against the virus on time. Although further research is urgently needed, secondary bacterial infections in the respiratory system could potentially contribute to the high mortality rate observed among the elderly due to Covid-19. If bacterial growth, together with delayed production of antibodies, is a significant contributing factor to Covid-19’s mortality rate, then the additional time needed for the human body’s adaptive immune system to produce specific antibodies could be gained by reducing the bacterial growth rate in the respiratory system of a patient. Independently of that, the administration of synthetic antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 viruses could potentially decrease the viral load. The decrease of bacterial growth and the covalent binding of synthetic antibodies to viruses should further diminish the production of inflammatory fluids in the lungs of patients (the indirect cause of death). Although the first goal could potentially be achieved by antibiotics, I argue that other methods may be more effective or could be used together with antibiotics to decrease the growth rate of bacteria, and that respective clinical trials should be launched.
Both goals can be achieved by bacteriophages. The bacterial growth rate could potentially be reduced by the aerosol application of natural bacteriophages that prey on the main species of bacteria known to cause respiratory failure and should be harmless to a patient. Independently of that, synthetically changed bacteriophages could be used to quickly manufacture specific antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. This can be done via a Nobel Prize awarded technique called “phage display.” If it works, the patient is given extra time to produce their own specific antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 virus and stop the damage caused by an excessive immunological reaction.
The coronavirus pandemic has caused the death of more than 270,000 people, as reported by 8th May 2020 by the World Health Organization (WHO). The crisis we observe is the joint effect of globalization and the properties of the new virus (SARS-CoV-2), which causes the disease, Covid-19. SARS-CoV-2 stands for “Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome COronaVirus 2” describing one of the most dangerous symptoms in Covid-19. Although there have been past warnings of the threat that respiratory targeting viruses pose,1 the SARS-CoV-2 virus has spread at an unprecedented rate and it is devastating our health and economy globally. We urgently need multiple approaches to tackle this crisis.