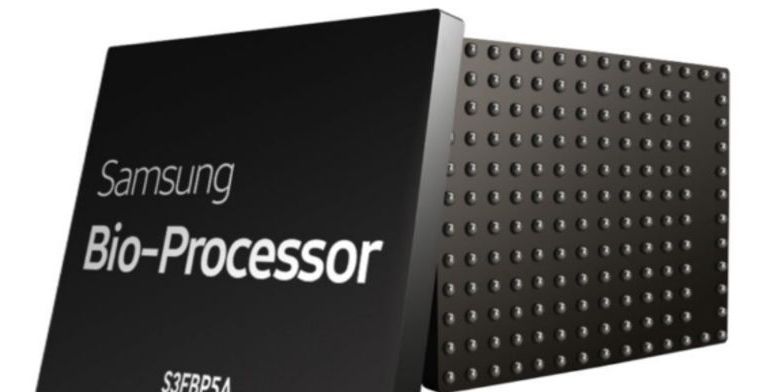
Samsung’s already wide product family is getting even bigger thanks to its new chip dubbed the “Samsung Bio-Processor.” As the company tells it, it’s already in mass production and is “specifically designed to allow accelerated development of innovative wearable products for consumers who are increasingly monitoring their health and fitness on a daily basis.” Phew. The announcement post goes on to say that the processor is the first all-in-one health solution chip and that since it’s packing a number of different control and sensor units (like a quintet of Analog Front Ends, a microcontroller unit, digital signal processor and eFlash memory) it can do all these tricks without the need for external processing.
The idea behind the silicon is to be the one-stop wearable fitness resource. Those five AFEs? One keeps track of bioelectrical impedance analysis, while the others focus on volumetric measurements of organs, an electrocardiogram and skin temperature, among other things. Bear in mind that Samsung’s latest smartwatch, the Gear S2, only tracks your heart rate. Same goes for the Apple Watch. Considering how err… interesting Samsung wearables tend to be, a possible scenario here is that the tech giant won’t keep the Bio-Processor all to itself. Nope, the real money here lies in potentially licensing it out to other folks, as it’s wont to do with its other self-made parts.
We won’t have to wait too long to see these in the wild, either: Samsung promises it’ll be packed into devices available early next year. If you’re wondering where, the inevitable follow-up to the aforementioned Gear S2 successor is a pretty likely bet. Whether that shows its face at CES or Mobile World Congress is the real question, though.
Read more