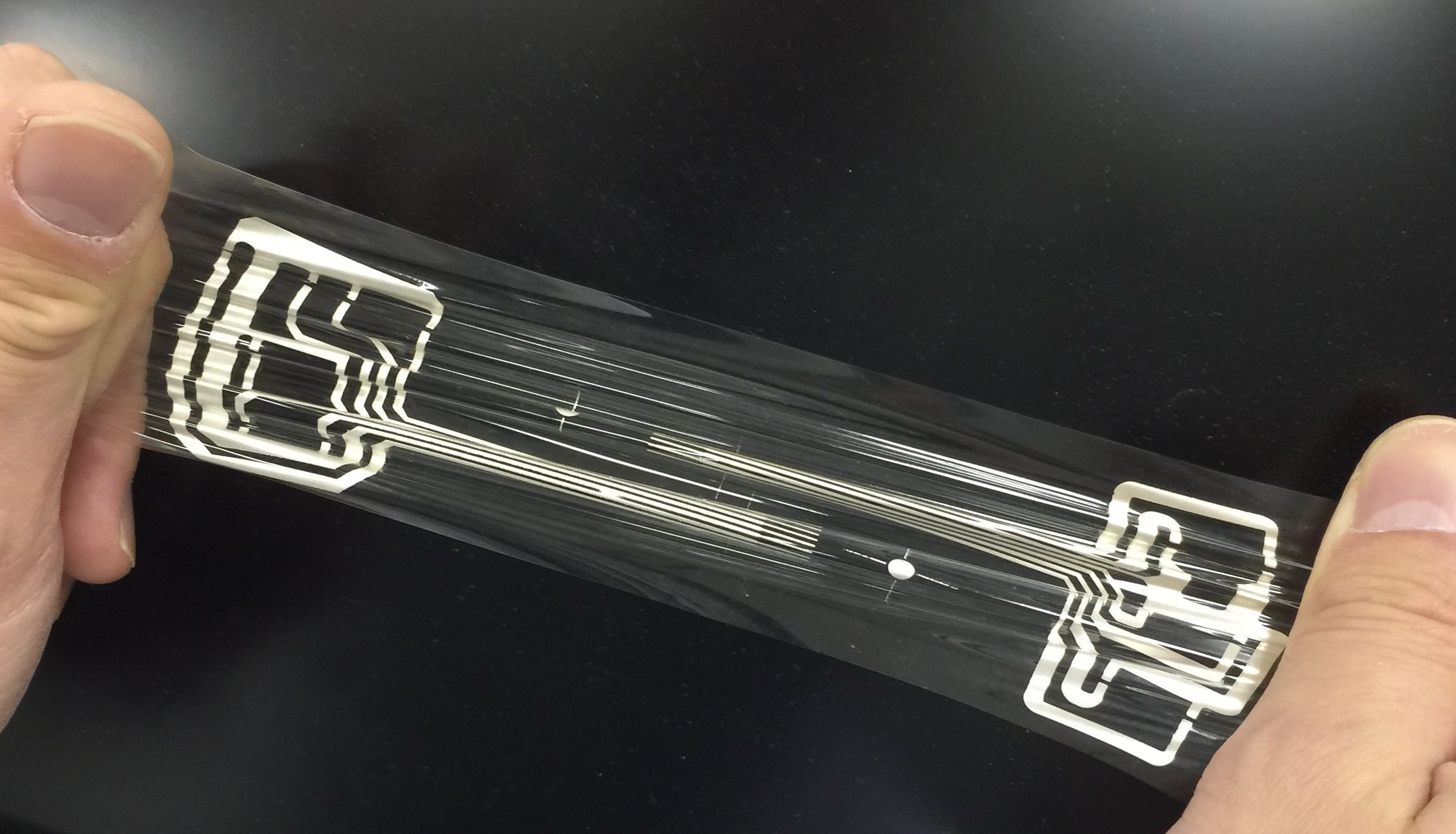
Last week at CES, South San Francisco based Profusa showed off an upcoming injectable sensor that can be used to continuously monitor oxygen levels in tissue. Measuring only five millimeters long and a tiny 250 microns in diameter, the biosensor can be injected into tissue with just a hypodermic needle. It consists of a soft hydrogel scaffold that allows it to be biologically compatible with the surrounding tissue without any foreign body response. The sensor also contains a special chemical marker that changes fluorescence depending on the amount of oxygen that reacts with it. An optical reader placed on the skin measures the fluorescence and relays the data to a smartphone. The biosensor can last as long as two years (at which point the chemical marker begins to lose its potency), and because it contains no electronics and is completely biocompatible there’s no need to remove it.
Last week at CES, South San Francisco based Profusa showed off an upcoming injectable sensor that can be used to continuously monitor oxygen levels in tissue. Measuring only five millimeters long and a tiny 250 microns in diameter, the biosensor can be injected into tissue with just a hypodermic needle. It consists of a soft hydrogel scaffold that allows it to be biologically compatible with the surrounding tissue without any foreign body response. The sensor also contains a special chemical marker that changes fluorescence depending on the amount of oxygen that reacts with it. An optical reader placed on the skin measures the fluorescence and relays the data to a smartphone. The biosensor can last as long as two years (at which point the chemical marker begins to lose its potency), and because it contains no electronics and is completely biocompatible there’s no need to remove it.
On stage at the CES Digital Health Summit, Profusa CEO Dr. Ben Hwang gave a live demonstration of how the sensor works in action. As two of his colleagues with the sensors implanted and using a blood pressure cuffs performed stretches to simulate changes in blood flow, a graph displayed the live view of the changing tissue oxygen levels at the site of the sensors.
We had the opportunity to talk to Dr. Hwang after his talk, and he shared that the first application of the sensor is the Lumee Oxygen Sensing System, which is designed to monitor oxygen levels during the wound healing process. Sufficient oxygen flow through a wound is vital to the healing process, and Lumee can detect low oxygen levels early in the healing process and even before treatment or surgery begins.