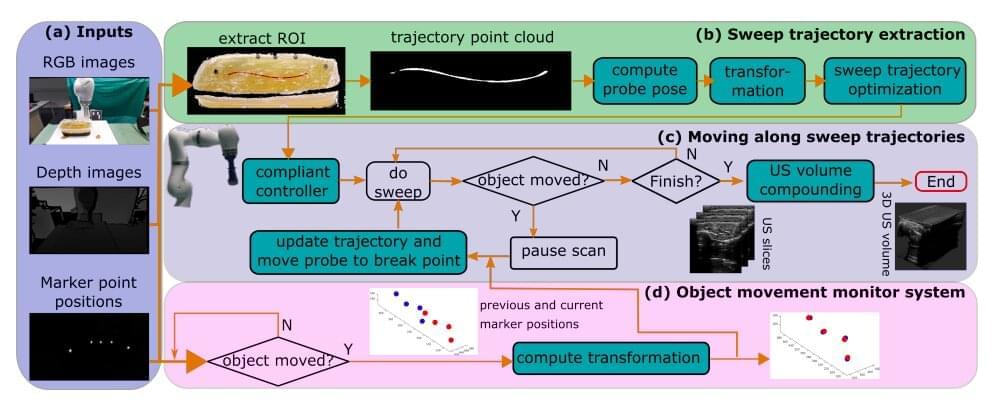
Ultrasound imaging techniques have proved to be highly valuable tools for diagnosing a variety of health conditions, including peripheral artery disease (PAD). PAD, one of the most common diseases among the elderly, entails the blocking or narrowing of peripheral blood vessels, which limits the supply of blood to specific areas of the body.
Ultrasound imaging methods are among the most popular means of diagnosing PAD, due to their many advantageous characteristics. In fact, unlike other imaging methods, such as computed tomography angiography and magnetic resonance angiography, ultrasound imaging is non-invasive, low-cost and radiation-free.
Most existing ultrasound imaging techniques are designed to capture two-dimensional images in real time. While this can be helpful in some cases, their inability to collect three-dimensional information reduces the reliability of the data they gather, increasing their sensitivity to variations in how individual physicians used a given technique.