Mutations are a part of life. Every time a virus replicates, there is a chance that its genetic code won’t be copied accurately. These typos travel inside new virus particles as they leave one body and move on to infect the next. Some of these mutations die out; others survive and circulate widely. Some mutations are harmless; others increase infectivity or allow a virus to better escape the immune system—that’s when public health bodies might deem that strain a variant of concern.
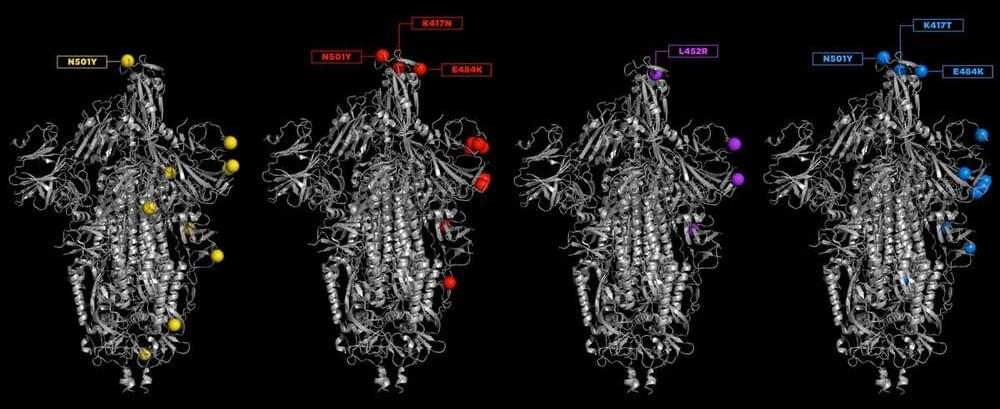
Swaps or deletions of single amino acids can change the shapes of different proteins. Mutations can happen in any of the proteins of SARS-CoV-2, and these may change the virus’s properties. Many of the worrisome mutations are found on the spike protein, as it is the target of antibody treatments and is mimicked by the currently authorized COVID-19 vaccines. Researchers are especially troubled when typos occur in two parts of the spike protein—the N-terminal domain, which is at the beginning of the protein and which some antibodies target, and the receptor-binding domain (RBD), which grabs hold of ACE2 receptors on human cells and starts the process of infection.
To understand how specific mutations affect the structure and function of the spike protein and what those changes mean for treatments and vaccines, C&EN talked to Priyamvada Acharya, Rory Henderson, and Sophie Gobeil at Duke University. With colleagues, these researchers have combined biochemical assays, cryo-electron microscopy, and modeling to show how the mutations seen in the variants of concern work together to change the stability of the spike protein. The spike is a trimer of three identical protein strands folded and interwoven together. Before the virus has infected a cell, the spike takes on two conformations: a down state, in which the RBD is hidden, and an up state, in which the RBD faces out, ready to bind to ACE2. The team found that different mutations can increase binding in different ways. This process, in which similar features are arrived at independently, is called convergent evolution.
SARS-CoV-2 variants are emerging and gaining traction around the world. What does that mean for our vaccines and treatments for COVID-19?