2013 saw the release of one of the most important papers in aging research and one that saw renewed interest and support for the concept of SENS.
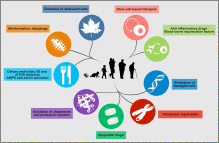
Aging is characterized by a progressive loss of physiological integrity, leading to impaired function and increased vulnerability to death. This deterioration is the primary risk factor for major human pathologies, including cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Aging research has experienced an unprecedented advance over recent years, particularly with the discovery that the rate of aging is controlled, at least to some extent, by genetic pathways and biochemical processes conserved in evolution. This Review enumerates nine tentative hallmarks that represent common denominators of aging in different organisms, with special emphasis on mammalian aging. These hallmarks are: genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, deregulated nutrient sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, and altered intercellular communication. A major challenge is to dissect the interconnectedness between the candidate hallmarks and their relative contributions to aging, with the final goal of identifying pharmaceutical targets to improve human health during aging, with minimal side effects.