We strongly believe that only digital health can bring healthcare into the 21st century and make patients the point-of-care.



Smartphones aren’t just for selfies anymore. A novel cell phone imaging algorithm can now analyze assays typically evaluated via spectroscopy, a powerful device used in scientific research. Researchers analyzed more than 10,000 images and found that their method consistently outperformed existing algorithms under a wide range of operating field conditions. This technique reduces the need for bulky equipment and increases the precision of quantitative results.
Accessible, connected, and computationally powerful, smartphones aren’t just for “selfies” anymore. They have emerged as powerful evaluation tools capable of diagnosing medical conditions in point-of-care settings. Smartphones also are a viable solution for health care in the developing world because they allow untrained users to collect and transmit data to medical professionals.
Although smartphone camera technology today offers a wide range of medical applications such as microscopy and cytometric analysis, in practice, cell phone image tests have limitations that severely restrict their utility. Addressing these limitations requires external smartphone hardware to obtain quantitative results – imposing a design tradeoff between accessibility and accuracy.

This HPV cure comes at a time when cervical cancer cases are quickly becoming the leading cause for death among female cancer patients around the world, the World Health Organisation (WHO) said in a statement.
The researchers specialise in early detection and photodynamic therapy to fight HPV and have succeeded in winning the ultimate battle — a 100 percent cure — after twenty years of tweaking the treatment.
Tech2 is now on WhatsApp. For all the buzz on the latest tech and science, sign up for our WhatsApp services. Just go to Tech2.com/Whatsapp and hit the Subscribe button.
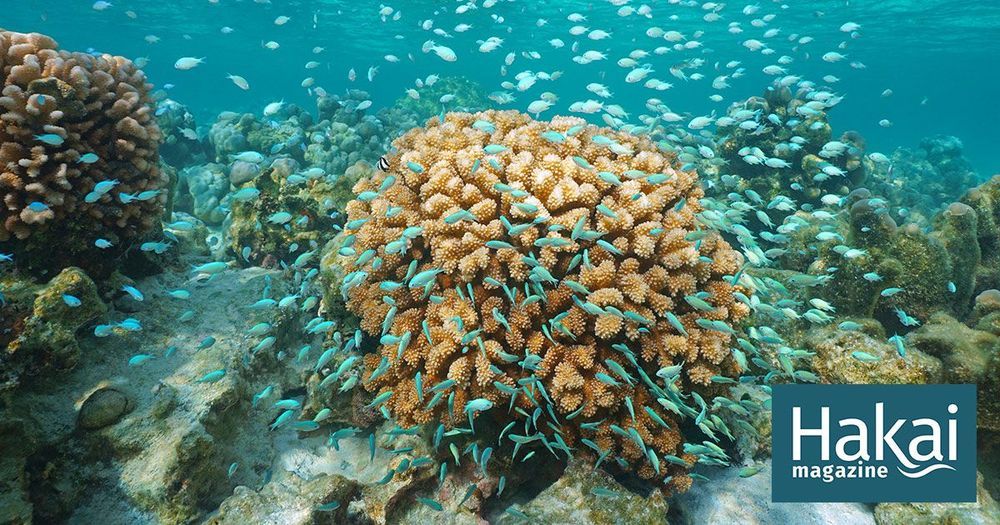

While testing of the probiotic supplements is currently confined to the lab, Peixoto envisions the treatment being administered on wild reefs. The probiotics could be sprayed from a plane, similar to how pesticides are spread over fields, or dropped like little bacterial bombs to target areas more specifically. Peixoto acknowledges the risk of trying to deliberately manipulate microbial ecosystems in the oceans, but believes the probiotics could be a viable long-term solution to coral reefs’ declining health.
When faced with high heat and disease, coral treated with microbial supplements fared better.

Go into your backyard about 20:30 p.m. EST or thereabouts this weekend and you can see the most incredible thing – the Andromeda Galaxy – one of the farthest objects visible to the naked eye. If you know where to look. Locating the ‘other ’ major galaxy in our Local Group is an exercise in stargazing on a grand scale, and the beginning of fall is absolutely the best time to take a look at it.
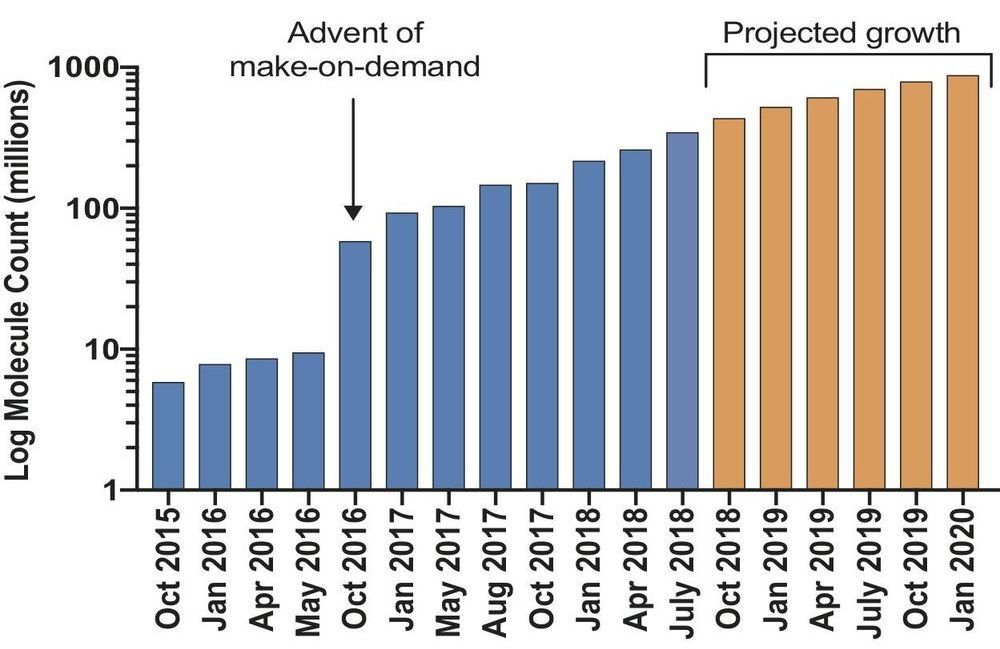
Researchers have launched an ultra-large virtual docking library expected to grow to more than 1 billion molecules by next year. It will expand by 1000-fold the number of such “make-on-demand” compounds readily available to scientists for chemical biology and drug discovery. The larger the library, the better its odds of weeding out inactive “decoy” molecules that could otherwise lead researchers down blind alleys. The project is funded by the National Institutes of Health.
“To improve medications for mental illnesses, we need to screen huge numbers of potentially therapeutic molecules,” explained Joshua A. Gordon, M.D., Ph.D., director of NIH’s National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), which co-funded the research. “Unbiased computational modeling allows us to do this in a computer, vastly expediting the process of discovering new treatments. It enables researchers to virtually “see” a molecule docking with its receptor protein—like a ship in its harbor berth or a key in its lock—and predict its pharmacological properties, based on how the molecular structures are predicted to interact. Only those relatively few candidate molecules that best match the target profile on the computer need to be physically made and tested in a wet lab.”
Bryan Roth, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of North Carolina (UNC) Chapel Hill, Brian Shoichet, Ph.D., and John Irwin, Ph.D., of the University of California San Francisco, and colleagues, report on their findings Feb. 6, 2019 in the journal Nature. The study was supported, in part, by grants from NIMH, National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS), the NIH Common Fund, and National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS).

Perfectionism often develops in childhood, is impacted by parenting and can lead to mental health struggles in later life. Credit: Shutterstock We recently conducted one of the largest-ever studies on perfectionism. We learned that perfectionism has increased substantially over the past 25 years and that it affects men and women equally.
We also learned that perfectionists become more neurotic and less conscientious as time passes.
Perfectionism involves striving for flawlessness and requiring perfection of oneself and others. Extremely negative reactions to mistakes, harsh self-criticism, nagging doubt about performance abilities and a strong sense that others are critical and demanding also define the trait.
Very excited to have interviewed Dr. Michael Lustgarten in my role as longevity / aging ambassador for the ideaXme Show — Mike has been at the forefront of studying the 100 trillion organisms present in the human microbiome, their effect on human health and wellness, as well as a major proponent of metabolomics and biologic age tracking — A true future thinker in the area of extending human lifespan and healthspan