Researchers have shown that a type of magnetic resonance imaging—called neuromelanin-sensitive MRI (NM-MRI)—is a potential biomarker for psychosis. NM-MRI signal was found to be a marker of dopamine function in people with schizophrenia and an indicator of the severity of psychotic symptoms in people with this mental illness. The study, funded by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), part of the National Institutes of Health, appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science.
“Disturbances affecting the neurotransmitter dopamine are associated with a host of mental and neurological disorders, such as schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease,” said Joshua A. Gordon, M.D., Ph.D., director of NIMH. “Because of the role dopamine plays in these disorders, the ability to measure dopamine activity is critical for furthering our understanding of these disorders, including how to best diagnose and treat them.”
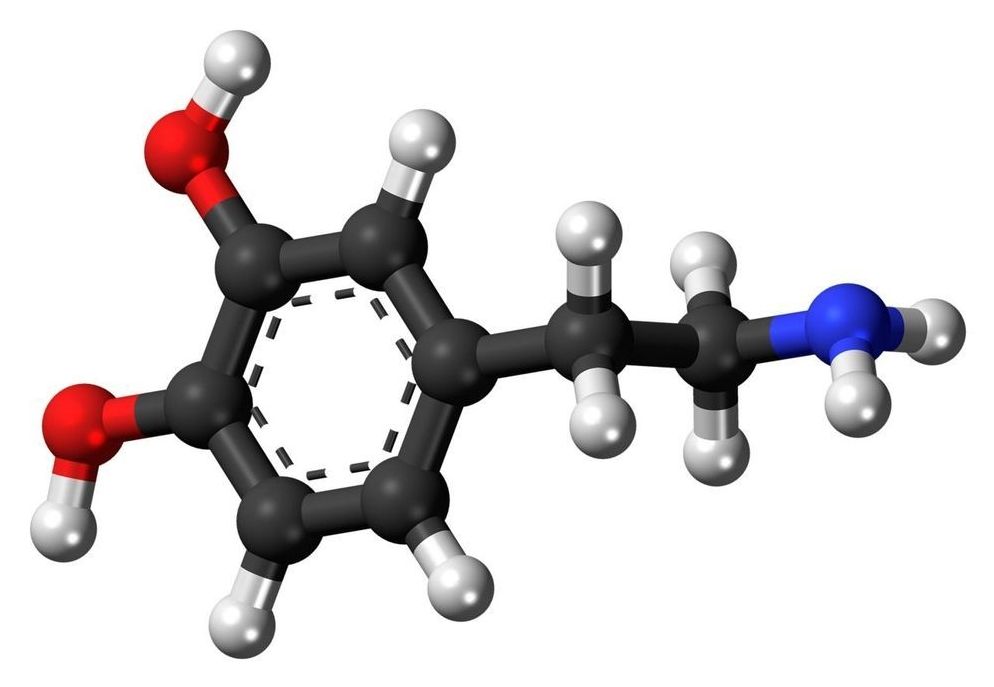
Neuromelanin is a dark pigment created within dopamine neurons of the midbrain—particularly in the substantia nigra, a brain area that plays a role in reward and movement. Neuromelanin accumulates over the lifespan and is only cleared away from cells following cell death, as occurs in neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease. Researchers have found that NM-MRI signal is lower in the substantia nigra of people with Parkinson’s disease, reflecting the cell death that occurs in these patients.
Read more