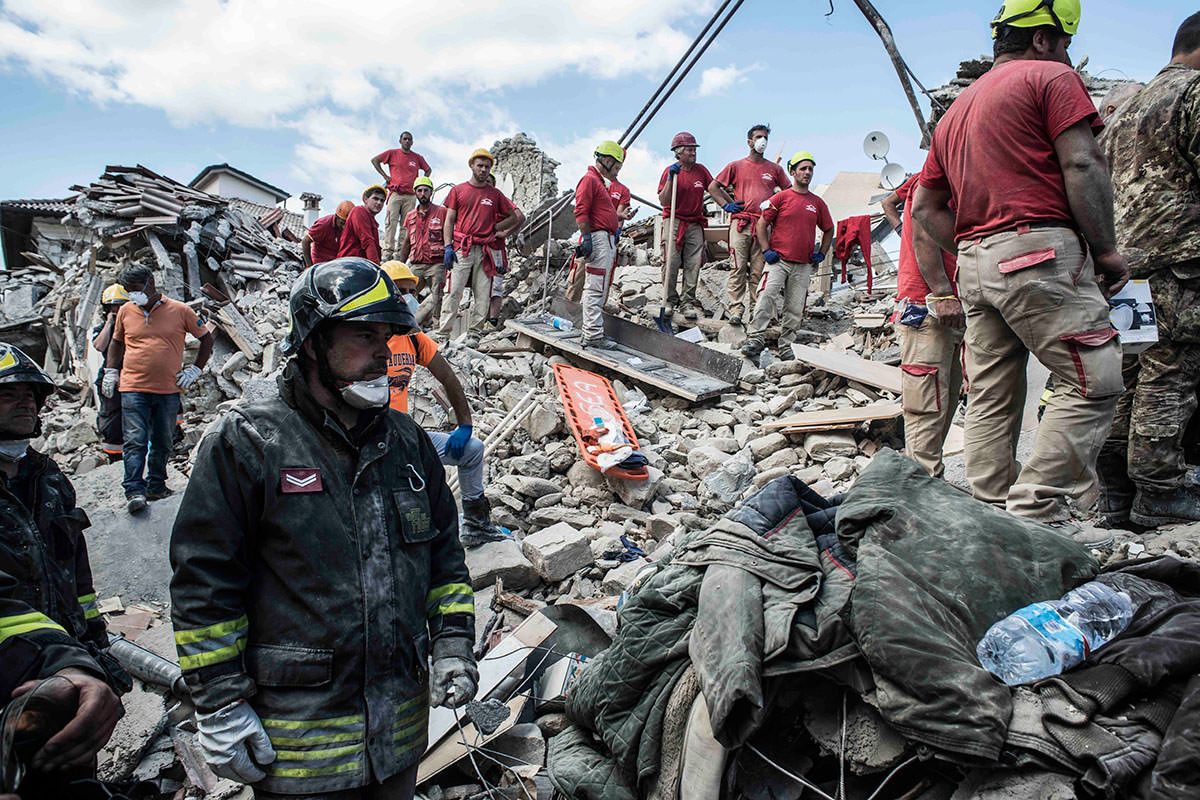
A national earthquake forecasting system combined with data on building vulnerability may help communicate risk of shocks happening – but uncertainties remain.


Beginning with a twitch in his fingers about six months ago, a Canadian man has successfully re-animated his paralyzed hand after undergoing a nerve transfer surgery.
Tim Raglin regularly dove, headfirst, into the water at his family’s lake house. The 45-year old Canadian man had done so thousands of times without incident. In 2007, though Raglin hit his head on a rock in the shallow water, shattering a vertebra in his cervical spine.
His family pulled him to safety, saving him from drowning. However, for nine years, both his hands and feet were left paralyzed.
Good; glad they are hearing us. Because it is a huge issue for sure especially with some of the things that I seen some of the researchers proposing to use CRISPR, 3D Printers, etc. to create some bizarre creatures. Example, in March to scientists in the UK wanted to use CRISPR to create a dragon; personally I didn’t expect it to be successful. However, the scientists didn’t consider the fallout to the public if they had actually succeeded.
For a few hundred dollars, anyone can start doing genetic editing in the comfort of their own home.

The first stage launches the rocket off of the pad and continues firing for about four minutes. Once the first stage is out of fuel, it separates, and if it’s a SpaceX Falcon 9, flies back home to be reused. If it’s anything else, including the Atlas V, the first stage crash lands in the ocean and sinks. Meanwhile, the second stage fires up its own engine (or engines) to boost the payload the rest of the way into orbit. On the Atlas V, the second stage is called Centaur. Once Centaur gets its payload where it needs to go, it separates, and then suicides down into Earth’s atmosphere.
Getting a payload into space is so expensive because you have to build up this huge and complicated rocket, with engines and guidance systems and fuel tanks and stuff, and then you basically use it for like 15 minutes and throw it all away. This is why SpaceX is trying so hard to recover the first stage of the Falcon 9. But what about the second stage? You’ve got a whole bunch of hardware that made it to orbit, and when getting stuff to orbit costs something like $2,500 per kilogram, you then tell it to go it burn itself up in the atmosphere, because otherwise it’s just useless space junk.
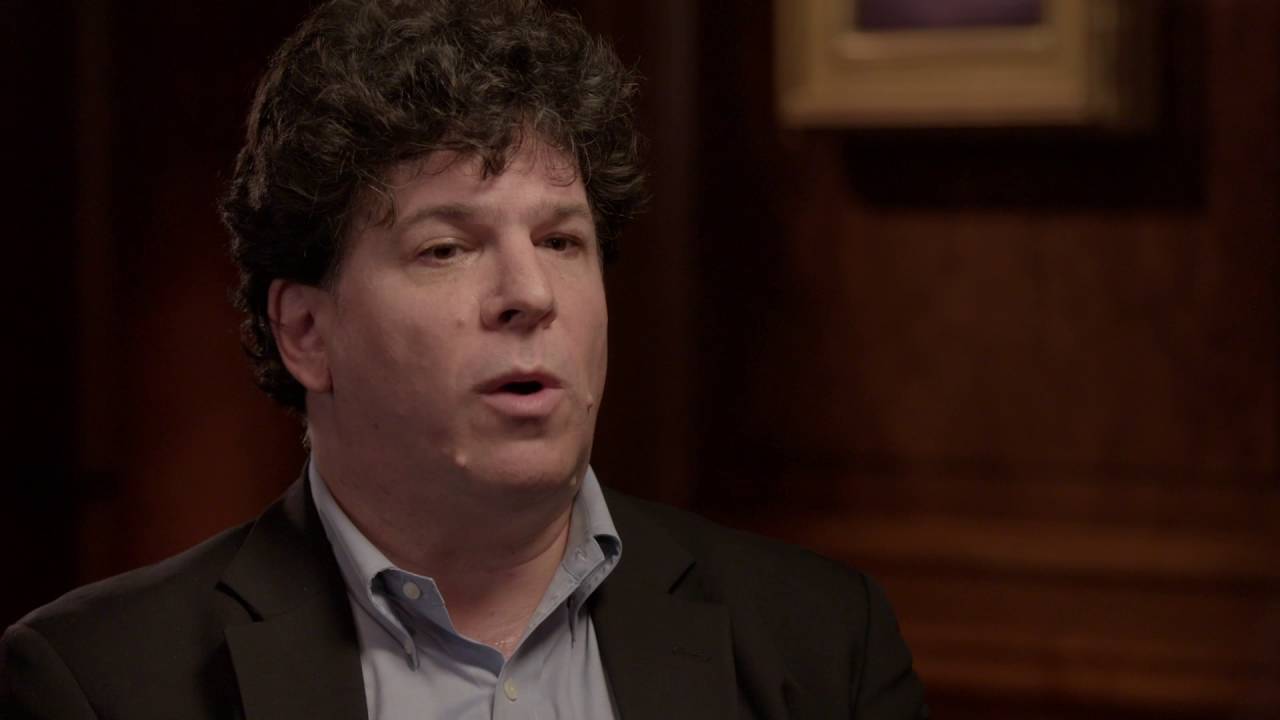

Is Market Capitalism simply an accident of certain factors that came together in the 19th and 20th centuries? Does the innovation of economics require a new economics of innovation? Is the study of economics deeply affected by the incentive structures faced by economists themselves, necessitating a study of the “economics of economics”? In this broad ranging interview INET Senior Economist Pia Malaney sits down with Eric Weinstein — mathematician, economist, Managing Director of Thiel Capital (as well as her co-author and husband) to discuss these and other issues.
Underlying the seismic shifts in the economy in the last ten years, Dr. Weinstein sees not just a temporary recession brought on by a housing crisis, but rather deep and fundamental shifts in the very factors that made market capitalism the driving force of economic growth for the past two centuries. The most profound of these shifts as Dr. Weinstein sees it, is an end to 20th century style capitalism brought about not by a competing ideology, as many had once feared, but instead by changing technology. As production is driven increasingly by bits rather than atoms, he sees the importance of private goods give way to public goods, undermining a basic requirement of market models. In a different line of thinking, as software becomes increasingly sophisticated it takes on the ability to replace humans not only in low level repetitive tasks but also, with the use of deep learning algorithms, in arbitrarily complex repetitive tasks such as medical diagnosis.
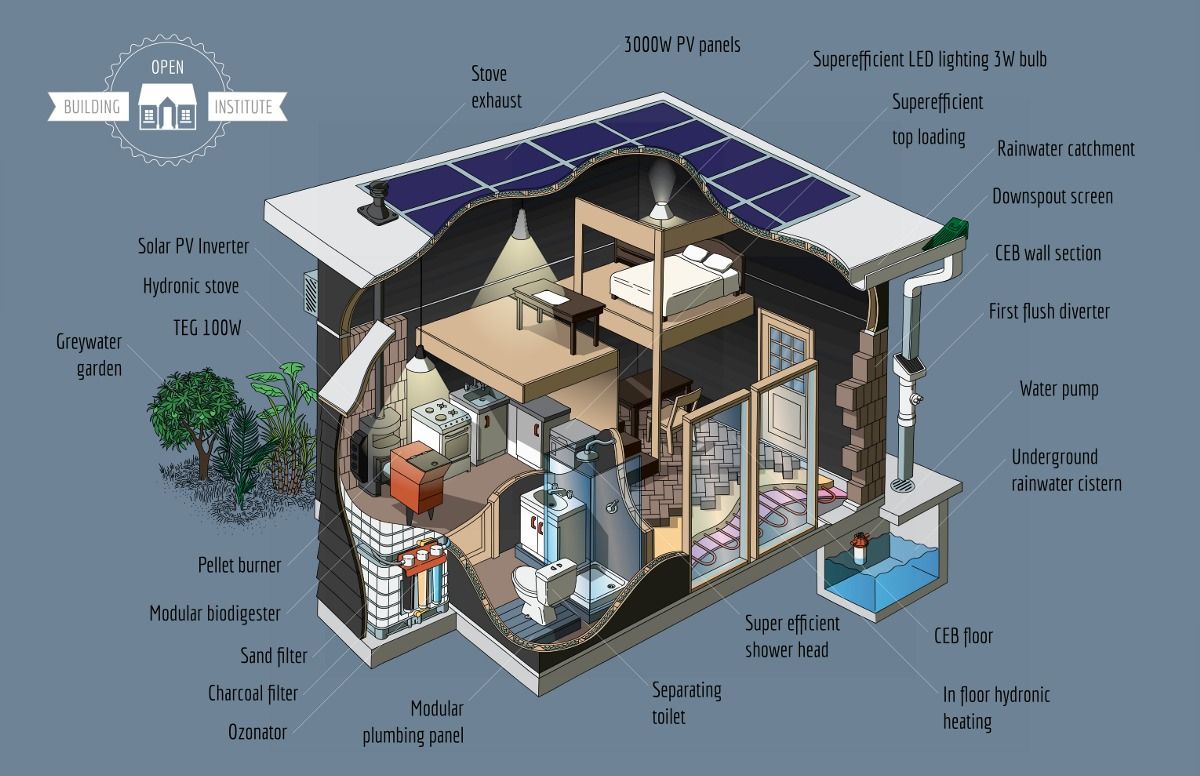
If you’re interested in one day creating your own eco-house using open source tech, this kit is great place to start:
Picture this: you own a small piece of land. Nothing fancy — just a small plot. A group of people shows up, sets up a workshop in your shed, and within five days, using materials available at your local hardware store or made from the raw resources of your land, builds you a small starter house kitted out with state-of-the-art eco features for less than $25,000.
Sound crazy? Well, open source advocate and maker Catarina Mota and inventor Marcin Jakubowski (see their TED Talks, “Play with smart materials” and “Open-sourced blueprints for civilization,” respectively), are making the dream of accessible, affordable eco-housing come true with their Open Building Institute Eco-Building Toolkit. They’ve already built several prototypes and tested the concept through a series of educational builds.
As they close out a successful Kickstarter campaign to raise funds to take the idea to the next stage of development, Marcin and Catarina give the lowdown on barn-raising, open source style. Here’s how it works:
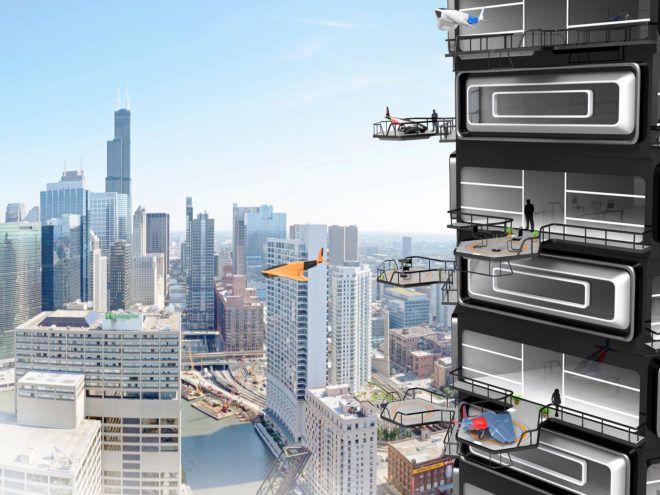

Make no mistake: Drones are coming, and they’re going to change a lot of things about how we shape our lives. So why shouldn’t we change how we shape our buildings to get ready for them?
Early adopters will probably buy personal flying vehicles in the not too distant future. Some models are being developed as we speak. Maybe an innovative architectural firm will even pitch the idea of building a ‘drone-ready’ condo tower in Japan or Dubai in the coming months—and maybe it will sell faster than we think.

Last month, NASA announced the winner of its 3D Printed Habitat Challenge, a competition in which entrants were tasked to develop architectural concepts. These concepts were to implement 3D printing techniques for the construction of habitats on Mars, using materials that could be sourced from the Red Planet itself.
The 3D Printed Habitat Challenge received 165 submissions, with the thirty highest scoring entries being displayed at the New York Maker Faire on September 27th. The overall winner and recipient of the $25,000 grand prize was Team Space Exploration Architecture and Clouds Architecture Office with their Mars Ice House design. The runners up were Team Gamma, who received $15,000, whilst third place was awarded to Team LavaHive.
“The creativity and depth of the designs we’ve seen have impressed us,” said Centennial Challenges Program Manager Monsi Roman. “These teams were not only imaginative and artistic with their entries, but they also really took into account the life-dependent functionality our future space explorers will need in an off-Earth habitat.”
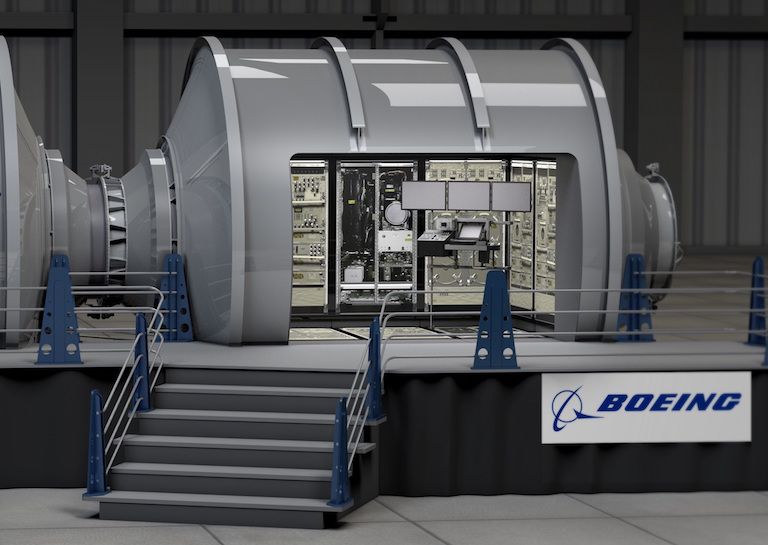

Continuing on with NASA’s trend of contracting work out to private companies, they have just started accepting bids and designs to create space habitats. The habitat selected will eventually house astronauts in future space missions, and possibly those that go to Mars. In their initial announcement, NASA has shown 6 different companies along with each’s design. This is all part of the NextSTEP-3 program.
DARPA has just launched the Engineering Living Materials program, with a vision to create building materials that grow on-site. The materials would be used to construct buildings that repair themselves and adapt to the environment.
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) has certainly had its hand in making the gizmos and gadgets we enjoy into a reality. The agency is still hard at work blazing the trail for the tech of the future, issuing challenges for the creation of the most advanced things on this Earth.
It has issued a new challenges, this time in the field of construction. DARPA has just announced the Engineering Living Materials program, a program to develop building materials that grow on site, repair themselves, and even adapt to the environment. “The vision of the ELM program is to grow materials on demand where they are needed,” said ELM program manager, Justin Gallivan, in a press release. “Imagine that instead of shipping finished materials, we can ship precursors and rapidly grow them on site using local resources.”