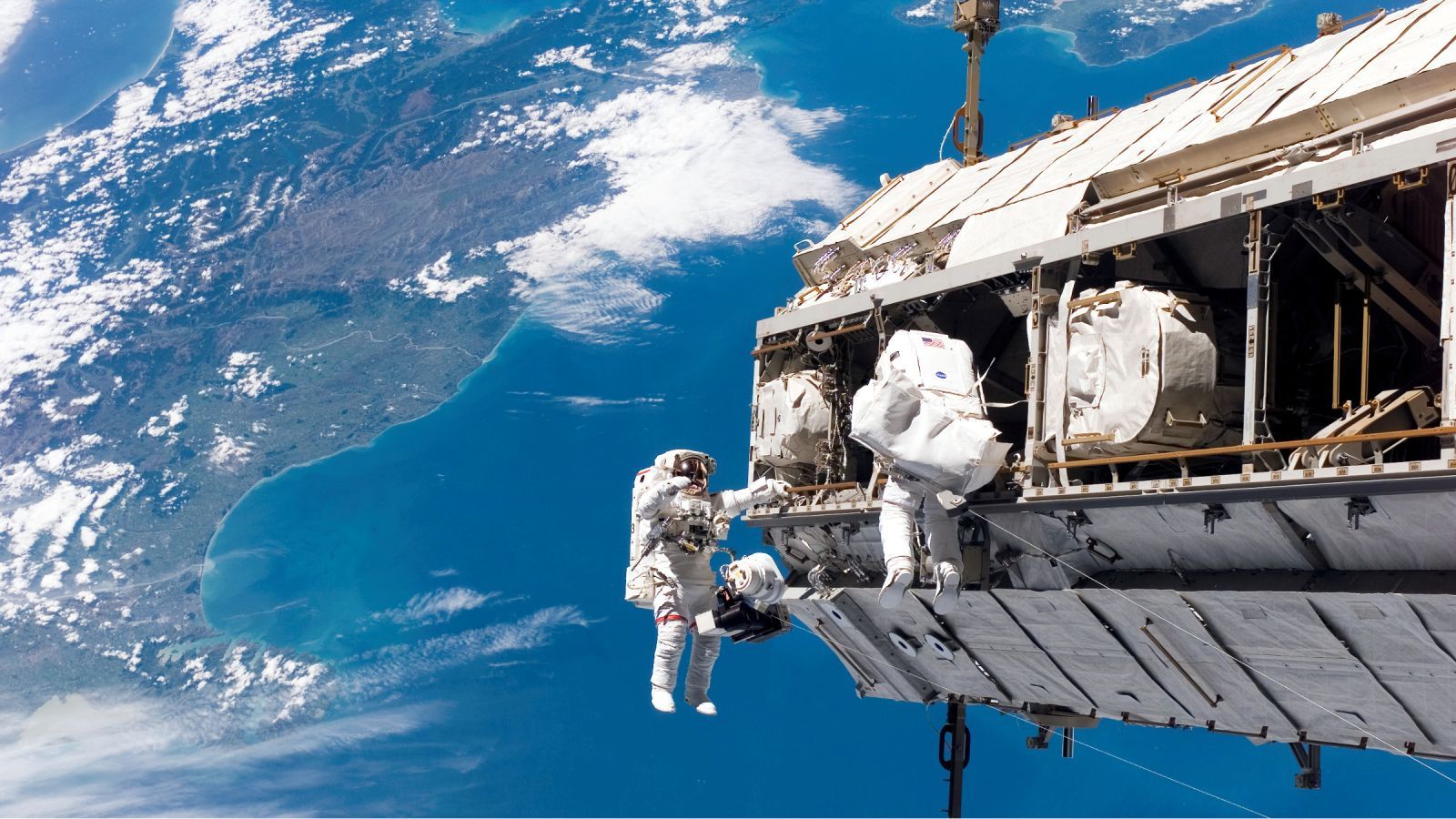
In one corner, we have an international, orbital laboratory that cost over $150 billion to build and operate. In the other, a $23 billion and growing program to develop a huge new deep-space rocket and spacecraft to carry humans to the moon and beyond. Now, they will face off in a Darwinian struggle for survival, unless US lawmakers can find a third way.
“About half of the current [NASA] budget is allocated to low-Earth orbit endeavors which consist of the International Space Station, commercial cargo, and commercial crew,” a former NASA and Lockheed Martin executive, A. Thomas Young, told US lawmakers in February. “The other half of the budget is for human exploration which includes [the Space Launch System rocket] and Orion [spacecraft]. A $4.5 billion annual budget is clearly inadequate for a credible human exploration program. A choice must be made and made soon between [low-Earth orbit] and exploration.”
The decision won’t be made this year. Though there was an astronaut in the oval office as a beaming president Donald Trump signed a bill March 21 to fund NASA through 2018, it didn’t bring the government any closer to launching humans to the ISS, much less to distant planets.
Read more