Imagine having your government declare fast internet a basic human right.
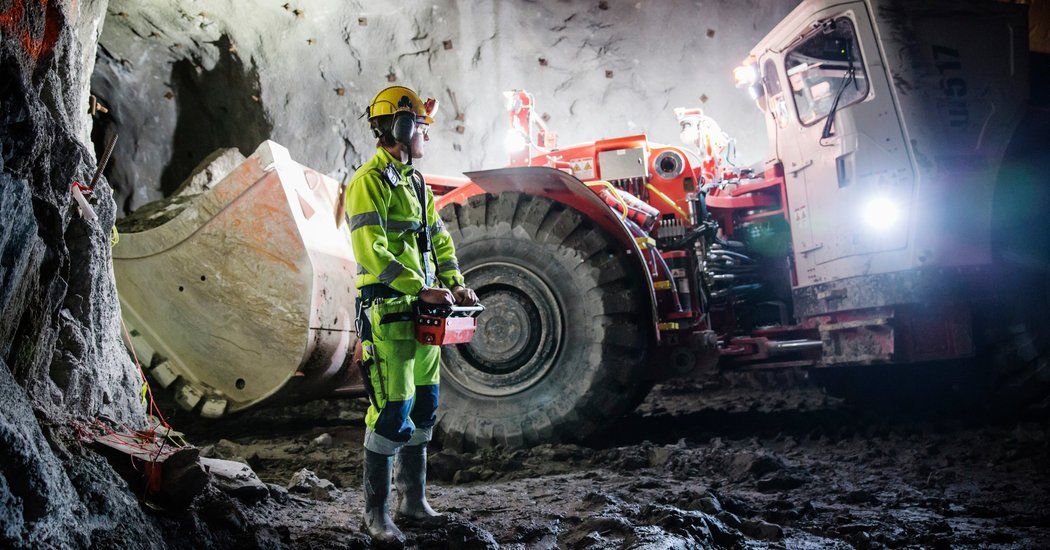



But such talk has little currency in Sweden or its Scandinavian neighbors, where unions are powerful, government support is abundant, and trust between employers and employees runs deep. Here, robots are just another way to make companies more efficient. As employers prosper, workers have consistently gained a proportionate slice of the spoils — a stark contrast to the United States and Britain, where wages have stagnated even while corporate profits have soared.
In a world full of anxiety about the potential job-destroying rise of automation, Sweden is well placed to embrace technology while limiting human costs.
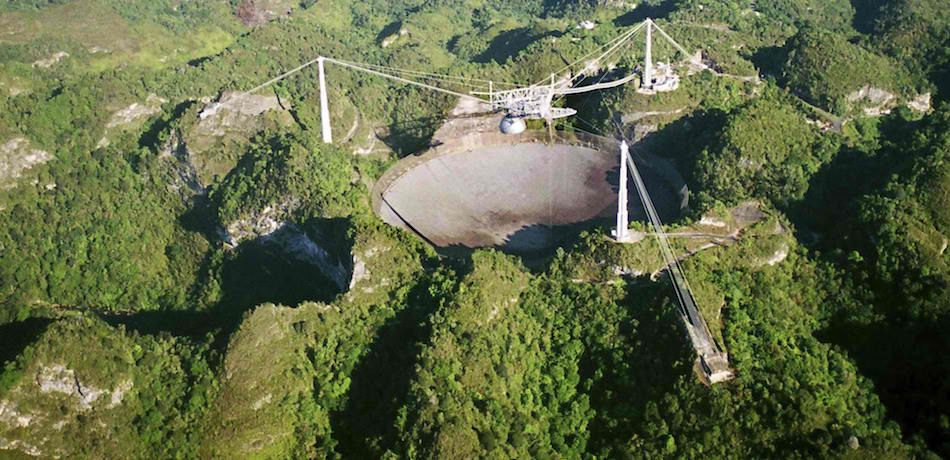

Despite being battered by Hurricane Maria, and facing a decrease in funding from the U.S. government, the Arecibo radio telescope in Puerto Rico is still going strong, and is now up and running again, following a series of repairs. And with the near-Earth asteroid 3200 Phaethon having just flown by our planet, Arecibo has just sent back images that are supposed to represent the highest-resolution photos of the asteroid, which help reveal some important details about the object.
According to a press release from NASA, the radar images were taken by the Arecibo Observatory Planet Radar last Saturday, December 16, and generated the day after, as asteroid Phaethon 3200 had its close encounter with Earth. At the time of its closest approach, the object was only 1.1 million miles away from Earth, or less than five times the distance separating our planet from the moon. The images have resolutions estimated at about 250 feet per pixel, making them the best-quality photos of the asteroid that are currently available, Phys.org added.
Based on Arecibo’s radar images, scientists believe that 3200 Phaethon is substantially larger than once estimated, with a diameter of approximately 3.6 miles, or 0.6 miles larger than what previous studies had suggested. That also makes Phaethon the second largest near-Earth object classified as a “potentially hazardous asteroid,” or a comparatively large asteroid that orbits much closer to Earth than most others do. The images also suggest Phaethon has a spheroidal shape, with a number of peculiar physical features that scientists are still trying to understand in full. These features include a concave area believed to be several hundred meters wide, and a dark, crater-like area located near one of its poles.
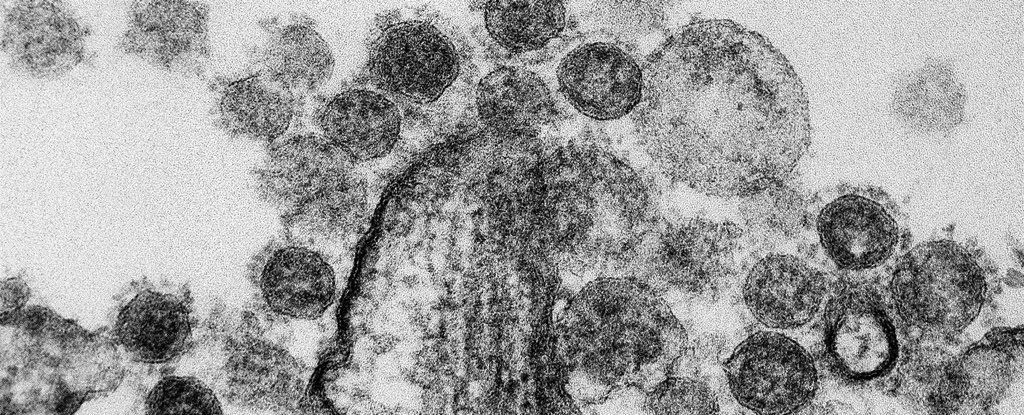
The US federal government has lifted an enforced moratorium on funding research into how to make viruses deadlier and more transmissible.
The moratorium, which was imposed three years ago, froze funding for what’s called “gain of function” research: controversial experiments seeking to alter pathogens and make them even more dangerous. Now, the money is back on the table, giving those trials the green light once more.
The director of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Francis S. Collins, announced the lifting of the moratorium on Tuesday, saying gain of function (GOF) research with viruses like influenza, MERS, and SARS could help us “identify, understand, and develop strategies and effective countermeasures against rapidly evolving pathogens that pose a threat to public health”.
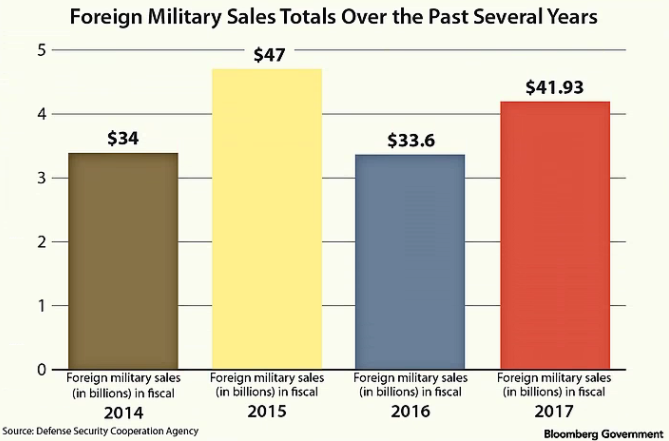
“The top five government contracts disputes that could be be decided this upcoming year concern:”
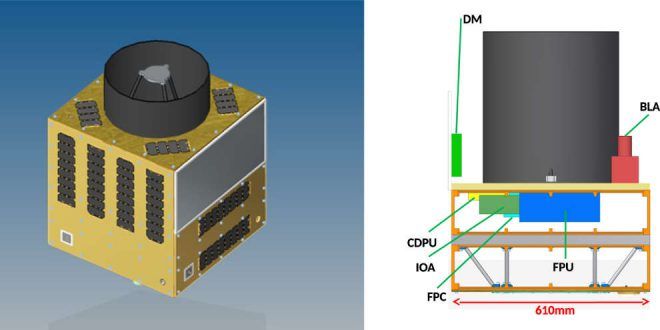
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) has awarded $1.85M contract to the University of Waterloo for the Quantum Encryption and Science Satellite (QEYSSat) mission.
The QEYSSat mission was one of two projects cited in the 2017 budget when it was unveiled in March of this year. In April, the government sent Innovation Science and Economic Development (ISED) Minister Navdeep Bains to the CSA’s headquarters to formally announce the funding for the QEYSSat mission along with funding for a radar instrument that will be developed for a future orbiter mission to Mars and to announce the Canadian CubeSat Project. The $80.9M of funding would be over five years.
A short history of the QEYSSat mission.

The internet may be an international system of interconnecting networks sharing a rough global consensus about the technical details of communicating through them – but each country manages its own internet environment independently. As the U.S. debate about the role of government in overseeing and regulating the internet continues, it’s worth looking at how other countries handle the issue.
As the U.S. weakens its protections for internet users, it risks falling behind the rest of the world.

Bitcoin has many characteristics of a currency. It is portable, fungible, divisible, resistant to forgery, and it clearly has value. Today, that value came close to $20,000 per coin. Whether it has ‘intrinsic value’ is somewhat of a moot question, because the US dollar hasn’t exhibited this trait since 1972. Today, economists don’t even recognize the intrinsic value of gold—beyond a robust, international, supply-demand network.
Lately, Bitcoin is failing as a viable currency, at least for everyday consumer transactions. The settlement of each transaction is bogged down with long delays and a very high cost. The situation has become critical because of squabbling between miners, users and developers over how to offer speed transactions or lower the cost of settlement. Bitcoin forks and altcoins such as Dash and Bitcoin Cash demonstrate that these technical issues have solutions. Since Bitcoin is adaptable, I believe that these issues are temporary.
But an interesting question is not whether Bitcoin will eventually become a consumer currency. it is whether Bitcoin can distinguish itself as a store of value, rather than just an instrument for payment or debt settlement. After all, a Visa credit card, a traveler’s check and an Amazon gift card can all be used in retail payments, but none of them have value unless backed by someone or something. US Dollars on the other hand are perceived as inherently valuable. They carry the clout and gravitas of institutions and populations, without users questioning from where value arises. (This is changing, but bear with me)…
What about Bitcoin? Does owning some bitcoin represent a store of value? Yes: It absolutely does!
Bitcoin is a rapidly maturing two-sided network. Despite a meteoric rise in exchange value and wild fluctuations during the ride, it is the epitome of a stored value commodity. Regardless of government regulation, adoption as a consumer payment instrument, or the cost and speed of transactions, it has demonstrated stored value since May 22 2010, when Laszlo, a Bitcoin code developer, persuaded a restaurant to accept 10,000 BTC for 2 pizzas.
The “currency” accepted by the pizza parlor wasn’t a gift card. It was not backed by a government, a prior deposit, dollars, gold, the promise of redemption, or by threat of force or blackmail. When a large community of individuals value, exchange, and can easily authenticate something that has none of those underpinnings, that thing clearly has stored value.
In this case, value arises from its scarcity and a robust supply-demand-network. Because its value is not tied to a government or to other commodities, its exchange rate with other things will be bumpy, at first. But as it is recognized, traded and adopted as a stored value token, the wild spikes will smooth out.
A tipping point will precipitate rapid adoption when…
 Bitcoin is clearly a store of value, and it is beginning to displace gold and the US dollar as the recognized reserve currency (it is gradually becoming the new gold standard). But before Bitcoin can serve as a widely adopted everyday currency (i.e. as a payment instrument—with or without the stored value of a currency unto itself), it must first incorporate technical improvements that speed transactions and lower cost.
Bitcoin is clearly a store of value, and it is beginning to displace gold and the US dollar as the recognized reserve currency (it is gradually becoming the new gold standard). But before Bitcoin can serve as a widely adopted everyday currency (i.e. as a payment instrument—with or without the stored value of a currency unto itself), it must first incorporate technical improvements that speed transactions and lower cost.
This is taking longer than many enthusiasts would have liked. But, that’s OK with anyone who keeps their eye on the big picture. Democracy is sometimes very sloppy.
Philip Raymond co-chairs CRYPSA, publishes A Wild Duck and hosts the New York Bitcoin Event. Last month, he kicked off the Cryptocurrency Expo in Dubai. Click Here to inquire about a live presentation or consulting engagement.

In an April 2014 article, I demonstrated how one might approach a fair Bitcoin valuation.
My methodology was based on the demand that Bitcoin would generate if it displaced a small fraction of cash and credit used for retail and commercial payments around the world. At the time, Bitcoin had a value of USD $450. I estimated that if it captured 5% of global payments, it would have a fair value of about $10,000/BTC (I didn’t complete the calculation—I left that up to the reader. That’s because I was concerned that publishing such a prediction would cause me to lose credibility as an economist and blogger. For what it is worth, I also predicted that a rise to $10,000 would take 5~8 years.
As you might imagine, my friends and family urged me to unload my BTC investment. The April 2014 price of $450/BTC seemed very high to most armchair analysts. After all, thirteen months earlier, it had been just $45.
Yet, now, just 2½ years later, Bitcoin has reached $18,000 per coin. Last week, on Dec 7, 2017, it climbed 40% in just 40 hours, and 120% in less than 2 months. Naturally, this leaves everyone asking if Bitcoin’s rapid rise in value represents an investment “bubble”.
…And so it is time to update the calculation of a fair value for Bitcoin. I can’t do better than point to a terrific prediction model described by Divyanth Jayaraj. His answer to a question at Quora presents a sound basis for valuation—much better than my original valuation method. How so?…

Bitcoin is rapidly demonstrating viability as a reserve rather than a daily transaction currency. Few people believe that Bitcoin will replace national currencies throughout the world, but it very well may replace gold for government and interbank settlement, and for large intercontinental purchases of commodities, such as oil, grain or airplanes.
Sure! When developers and miners get a handle on transaction cost and delays, it may also become a de facto instrument for retail payments and debt settlement even among consumers. But, even if Bitcoin never achieves this status, Divyanth’s excellent analysis is still valid.
I won’t steal the author’s thunder. Click the link and learn what is very likely to be a fair future value for Bitcoin. Prepare to digest a very large number. I didn’t think of this valuation methodology, but I agree that it represents a realistic peek into the future.
For a few other methods of determining Bitcoin’s inherent value, check out the links at the bottom of my original article. But that was then and this is now. Give extra weight to this newer analysis. The methodology is more accurate given what we know now.
Philip Raymond co-chairs CRYPSA, publishes A Wild Duck and hosts the Bitcoin Event. He was keynote at Cryptocurrency Expo in Dubai. Click Here to inquire about a presentation or consulting engagement.
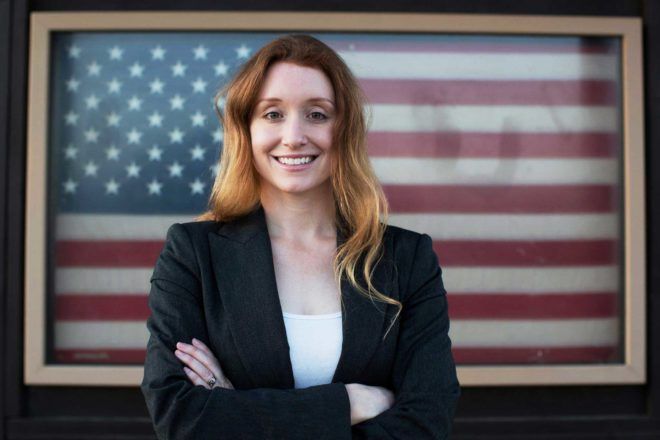

Vulcanologist Jess Phoenix never expected to be involved in politics. Until recently her life revolved around science—traveling the world to study different volcanoes and running an educational nonprofit. But the environmental record of the Trump administration has motivated her to run for Congress.
“These guys are basically gutting every environmental protection that existed,” Phoenix says in Episode 284 of the Geek’s Guide to the Galaxy podcast. “It’s a trend we have to stop now. We can’t let this continue.”