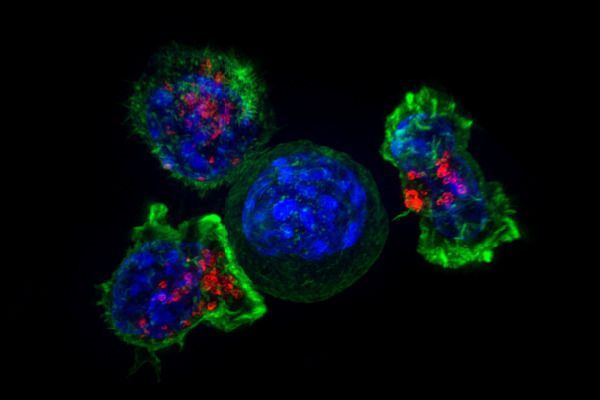
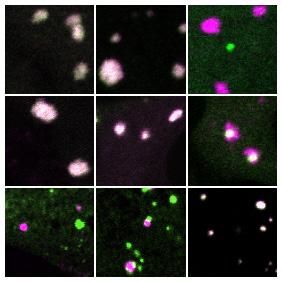
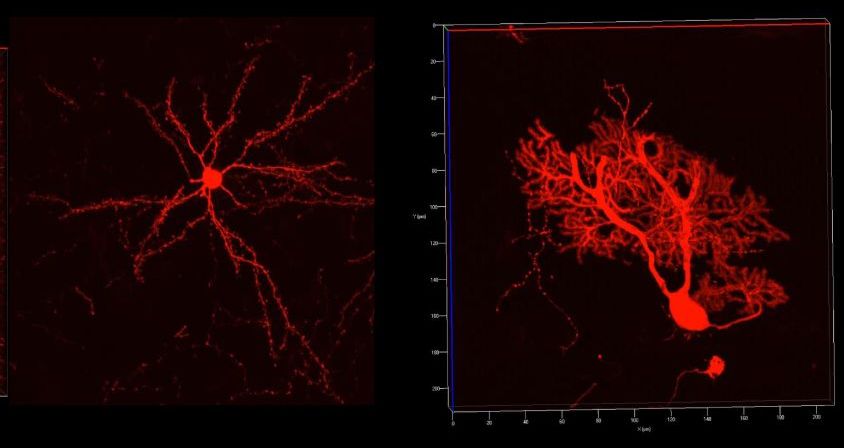
UC San Francisco researchers have discovered how a mutation in a gene regulator called the TERT promoter—the third most common mutation among all human cancers and the most common mutation in the deadly brain cancer glioblastoma—confers “immortality” on tumor cells, enabling the unchecked cell division that powers their aggressive growth.
The research, published September 10, 2018 in Cancer Cell, found that patient-derived glioblastoma cells with TERT promoter mutations depend on a particular form of a protein called GABP for their survival. GABP is critical to the workings of most cells, but the researchers discovered that the specific component of this protein that activates mutated TERT promoters, a subunit called GABP-ß1L, appears to be dispensable in normal cells: Eliminating this subunit using CRISPR-based gene editing dramatically slowed the growth of the human cancer cells in lab dishes and when they were transplanted into mice, but removing GABP-ß1L from healthy cells had no discernable effect.
“These findings suggest that the ß1L subunit is a promising new drug target for aggressive glioblastoma and potentially the many other cancers with TERT promoter mutations,” said study senior author Joseph Costello, Ph.D., a leading UCSF neuro-oncology researcher.