Why hasn’t #MachineLearning conquered SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19 (P.S., SARS-CoV-2 is the name of the #virus, while COVID-19 is the name of the disease)? One of the possible answers is that the virus “learns” faster than machines through “mutations”.
That causes us thinking: If mutation is such an efficient weapon (for virus), can we learn something from it and then apply our understanding to #DeepLearning to create “fast-mutating” #DeepLearning models capable of helping us to fight intractable crisis like a #pandemic?
https://bit.ly/3c9GE5s
Virus Mutation https://bit.ly/35xVvUQ
#COVID19 #AI #technology #innovation #NeuralNetworks
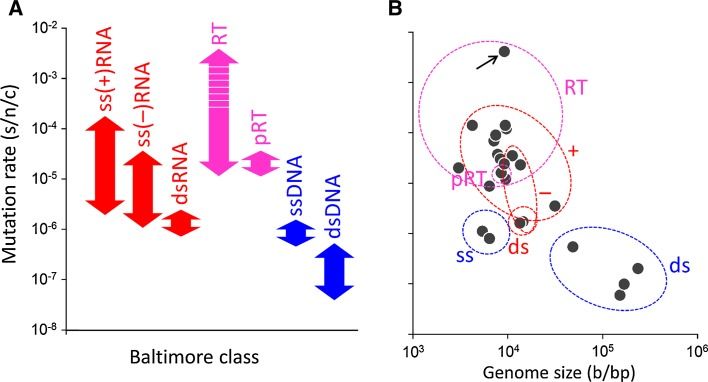
The remarkable capacity of some viruses to adapt to new hosts and environments is highly dependent on their ability to generate de novo diversity in a short period of time. Rates of spontaneous mutation vary amply among viruses. RNA viruses mutate faster than DNA viruses, single-stranded viruses mutate faster than double-strand virus, and genome size appears to correlate negatively with mutation rate. Viral mutation rates are modulated at different levels, including polymerase fidelity, sequence context, template secondary structure, cellular microenvironment, replication mechanisms, proofreading, and access to post-replicative repair. Additionally, massive numbers of mutations can be introduced by some virus-encoded diversity-generating elements, as well as by host-encoded cytidine/adenine deaminases. Our current knowledge of viral mutation rates indicates that viral genetic diversity is determined by multiple virus- and host-dependent processes, and that viral mutation rates can evolve in response to specific selective pressures.
The mutation rate of an organism is defined as the probability that a change in genetic information is passed to the next generation. In viruses, a generation is often defined as a cell infection cycle, which includes attachment to the cell surface, entry, gene expression, replication, encapsidation, and release of infectious particles. Mutations are not restricted to replication since they can also result from editing of the genetic material, or spontaneous nucleic acid damage. The mutation rate should not be confused with the frequency at which mutations are found in a given viral population. The latter is a measure of genetic variation that depends on a number of other processes such as natural selection, random genetic drift, recombination, and so on (Fig. 1 a). Higher mutation rates lead to higher genetic diversity but, except in special cases, it is not possible to infer mutation rates directly from observed population mutation frequencies [1].