Summary: Will gene drive wipe out malaria-causing mosquitoes, or will the genetic technology that ‘spreads like wildfire’ cause a catastrophe? Gene drive raises hopes and fears as a team of scientists funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation are using it to wipe out the mosquitoes that carry malaria, to eradicate the disease. [This article first appeared on LongevityFacts. Follow us on Reddit | Google+ | Facebook. Author: Brady Hartman.]
In a basement lab at the Imperial College London (ICL), a group of researchers led by Andrew Hammond are on a mission to wipe out malaria. The scientists are funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and are using a technology called gene drive – a souped-up form of genetic engineering designed to wipe out the mosquitoes that carry the disease.
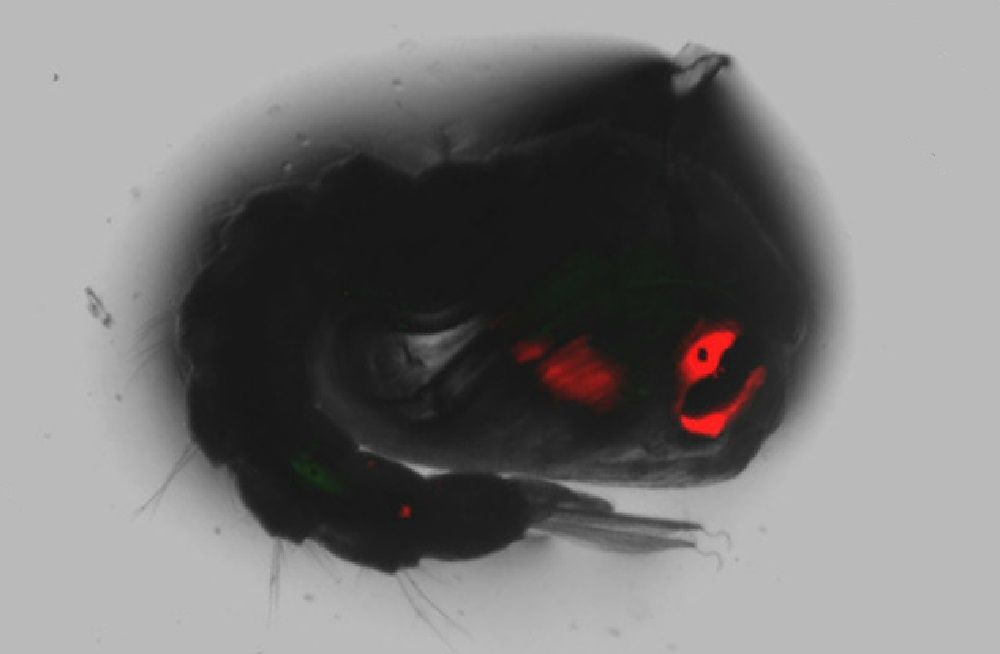
The lab contains cages of mosquitoes modified with the gene drive, along with an additional gene that makes their eyes and other body parts glow red under laser light.