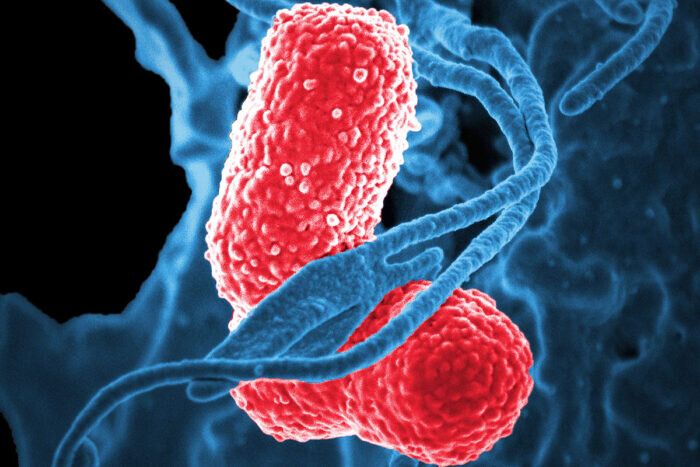
Scientists have produced and tested, in mice, a vaccine that protects against a worrisome superbug: a hypervirulent form of the bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae. And they’ve done so by genetically manipulating a harmless form of E. coli, report researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and VaxNewMo, a St. Louis-based startup.
Klebsiella pneumoniae causes a variety of infections including rare but life-threatening liver, respiratory tract, bloodstream and other infections. Little is known about how exactly people become infected, and the bacteria are unusually adept at acquiring resistance to antibiotics. The prototype vaccine, details of which are published online Aug. 27 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, may offer a way to protect people against a lethal infection that is hard to prevent and treat.
“For a long time, Klebsiella was primarily an issue in the hospital setting, so even though drug resistance was a real problem in treating these infections, the impact on the public was limited,” said co-author David A. Rosen, MD, Ph.D., an assistant professor of pediatrics and of molecular microbiology at Washington University. “But now we’re seeing Klebsiella strains that are virulent enough to cause death or severe disease in healthy people in the community. And in the past five years, the really resistant bugs and the really virulent bugs have begun to merge so we’re beginning to see drug-resistant, hypervirulent strains. And that’s very scary.”