Today, when a deadly virus explodes out of nowhere, geneticists are indispensable players in the international game of whodunit. Here’s how they help.
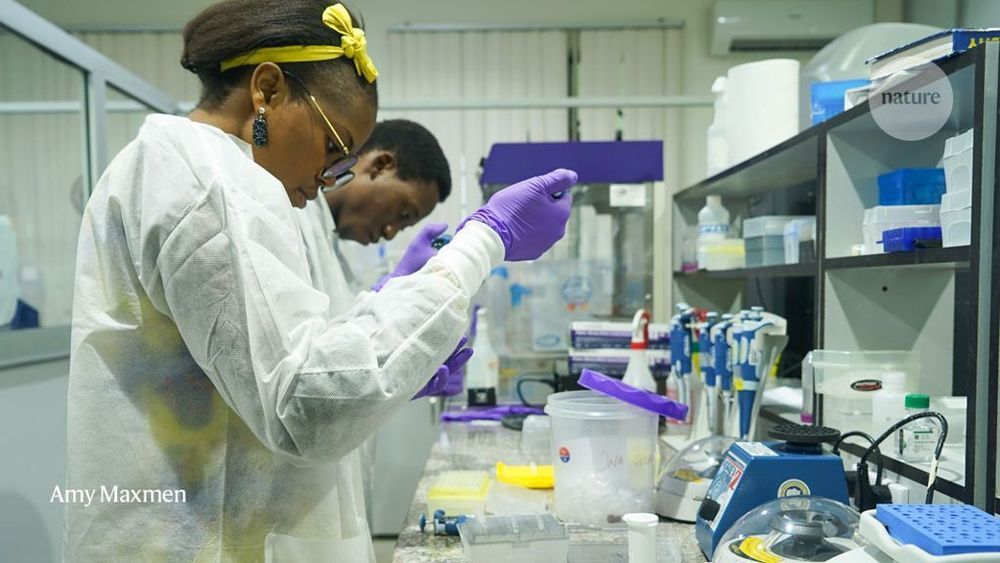


The rest of the world is interested, too. Africa contains much more genetic diversity than any other continent because humans originated there. This diversity can provide insights into human evolution and common diseases. Yet fewer than 2% of the genomes that have been analysed come from Africans. A dearth of molecular-biology research on the continent also means that people of African descent might not benefit from drugs tailored to unique genetic variations. Infectious-disease surveillance also falls short, meaning that dangerous pathogens could evade detection until an outbreak is too big to contain easily.
Nigeria is poised to become a hub for genetics research, but a few stubborn challenges block the way.

For three years, anthropologist Alan Rogers has attempted to solve an evolutionary puzzle. His research untangles millions of years of human evolution by analyzing DNA strands from ancient human species known as hominins. Like many evolutionary geneticists, Rogers compares hominin genomes looking for genetic patterns such as mutations and shared genes. He develops statistical methods that infer the history of ancient human populations.
In 2017, Rogers led a study which found that two lineages of ancient humans, Neanderthals and Denisovans, separated much earlier than previously thought and proposed a bottleneck population size. It caused some controversy—anthropologists Mafessoni and Prüfer argued that their method for analyzing the DNA produced different results. Rogers agreed, but realized that neither method explained the genetic data very well.
“Both of our methods under discussion were missing something, but what?” asked Rogers, professor of anthropology at the University of Utah.
In this data article, we provide five datasets of mantis mitochondrial genomes: PCG123: nucleotide sequences of 13 protein-coding genes including all codon positions; PCG123R: nucleotide sequences of two rRNAs and 13 protein-coding genes including all codon positions; PCG12: nucleotide sequences of 13 protein-coding genes without third codon positions; PCG12R: nucleotide sequences of two rRNAs and 13 protein-coding genes without third codon positions, and PCGAA: amino acid sequences of 13 protein-coding genes. These were used to construct phylogenetic relationships within Mantodea and the phylogenetic trees inferred from Bayesian analysis using two data sets (PCG12R, PCGAA) and Maximum Likelihood analysis using four data sets (PCG123, PCG12, PCG12R and PCGAA). We also provide initiation codon, termination codon, amino acid length and nucleotide diversity (Pi) of protein-coding genes among 27 mantises. The whole mitochondrial genomes of 27 praying mantises were submitted to GenBank with the accession numbers KY689112 – KY689138.
Had a very frank discussion with Greg Mustreader about transhumanism, learned helplessness of society in the face of aging and death, insufficient sense of urgency among researchers of aging, epigenetic rejuvenation, cryonics, and so on. No filter! 😁.
My blog on Medium: https://medium.com/@mustreader
My Twitter: https://twitter.com/mustreader
My Instagram: https://instagram.com/mustreader
Support me on Patreon: https://patreon.com/mustreader
Yuri Deigin: https://facebook.com/ydeigin
Yuri’s YouTube channel: https://youtube.com/channel/UCCSl1bSVzHRfIBeVZPnP4Vw
Yuri’s blog on Medium: https://medium.com/@yurideigin


In some biology classes, teachers will place vials of spit into a funny looking contraption and let it spin around the samples until the stringy DNA separates from the rest of the saliva. It’s a pretty rudimentary experiment, but it quickly gets to the heart of not only your own genetic material, but also how centrifugal force works: Spinning really fast in a circle creates a force strong enough to push a moving object out and away from the center of its path.
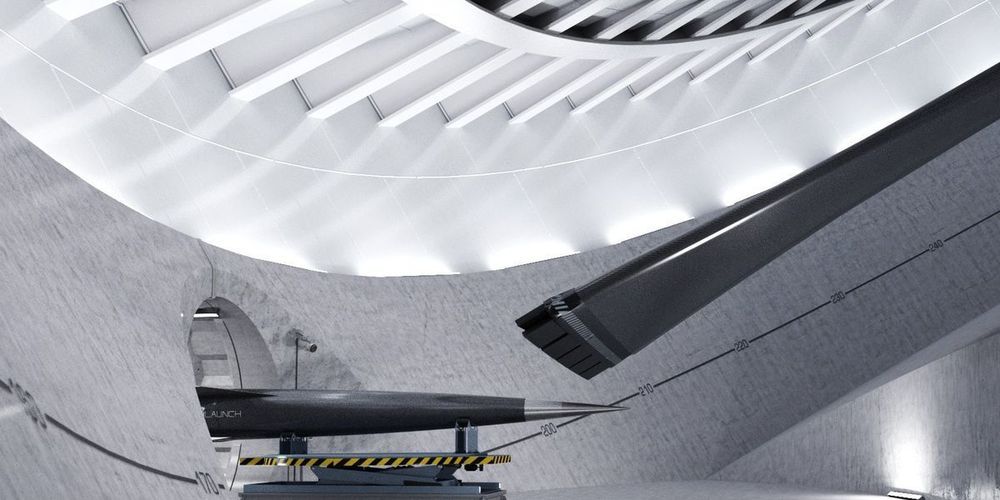
But what happens when that moving object is a rocket that weighs thousands of pounds? We might find out as soon as this year, when a cryptic startup called SpinLaunch starts suborbital test flights of a rocket that is launched using an enormous centrifuge.
Here’s the gist: A centrifuge the size of a football field will spin a rocket around in circles for about an hour until its speed eventually exceeds 5,000 miles per hour. At that point, the rocket and its payload will feel forces 10,000 times stronger than gravity. When the centrifuge finally releases the rocket at launch speed, it should, practically speaking, fly through the stratosphere until it fires its engines at the periphery of our atmosphere.
And the revolution has already begun.
Today’s genetic moment is not the stuff of science fiction. It’s not Jules Verne’s fanciful 1865 prediction of a moon landing a century before it occurred. It’s more equivalent to President Kennedy’s 1962 announcement that America would send men to the moon within a decade. All of the science was in place when Kennedy gave his Houston speech. The realization was inevitable; only the timing was at issue. Neil Armstrong climbed down the Apollo 11 ladder seven years later.
We have all the tools we need to alter the genetic makeup of our species. The science is here. The realization is inevitable. Timing is the only variable.

HONG KONG, Feb. 11, 2020 /PRNewswire/ — Infectious diseases represent an important portion of global public health concerns¸ in particular with regard to the current global outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). The challenge of frontline diagnosis in hospitals, clinics and ports is that infectious diseases could exhibit similar symptoms or can be asymptomatic. The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) today announced the development of the world’s most comprehensive automated multiplex diagnostic system (the System) which includes a fully automated machine and a multiplex full-screening panel for the point-of-care genetic testing (POCT) of respiratory infectious disease including the 2019-nCoV.

In October 2019, Liu and his colleagues published a paper in Nature, describing an even newer technology, called prime editing. Prime editing can not only make all twelve of the possible base substitutions, it can also make multiple-base insertions or deletions, without requiring a double-strand break. It achieves this with a multi-step operation that first cuts one strand, then performs the appropriate substitution, insertion, or deletion, and then nicks the second strand to allow the bases on the second strand to be replaced by bases that complement the ones substituted, inserted into or deleted from the first strand. The result is a modified stretch of DNA that had never been completely separated. This has the effect of massively reducing the number of off-target modifications.
This new prime editing variant of CRISPR technology, can make the same corrections to the defects that cause sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia that standard CRISPR/Cas9 has now made in human subjects, but with less opportunity for unwanted off-target changes. Furthermore, its possible applicability is much wider. The ClinVar database lists over 75,000 pathogenic mutations in the human genome. Of these, over 89% are potentially correctable by prime editing.
From zinc fingers to TALE, to CRISPR/Cas9 to base editing and now to prime editing, progress in gene editing has been accelerating. The next advances are currently being aggressively pursued in laboratories all over the world. It will probably be several years before the therapies that are currently being researched are applied routinely in a clinical setting. However, for people who up until recently have had no hope for a cure to a disease suffered by their child, or even themselves, these are exciting times. The prospect of effective treatments, or even cures, is now a valid cause for hope.