Elon Musk was challenged to fix South Australia’s energy problem in 2017, and just two years on he’s saved Australians millions.
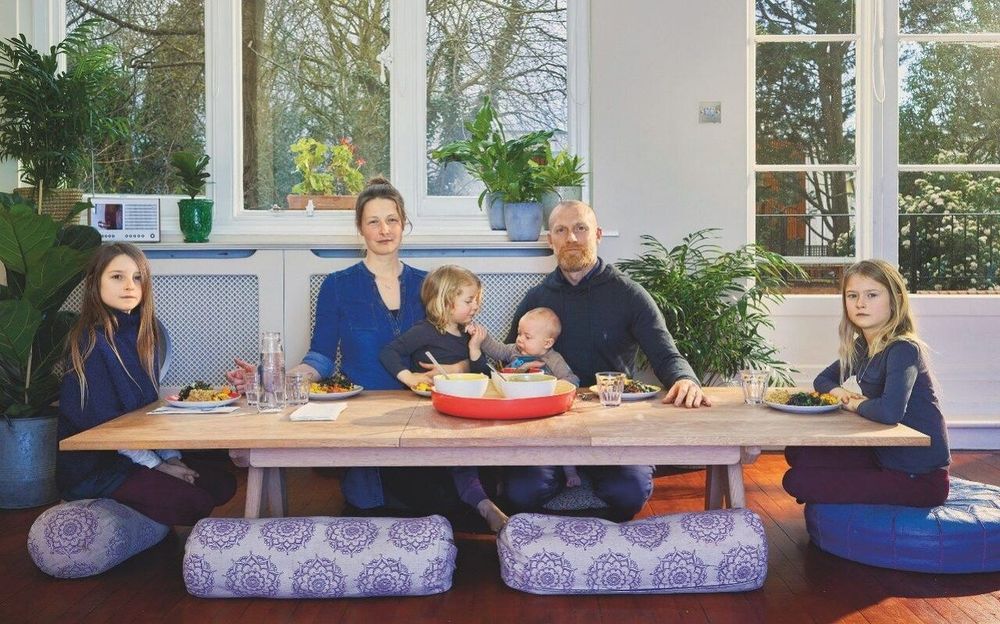



It’s 5pm in the Farrant household and Jack, six, and Thomas, four, are currently manifesting their desires in the form of Lego. To an outsider this looks like two small children playing with toys, but their mother Catherine proudly points out that Jack has built a yacht – something he is helping his family to acquire via visualisation exercises.
‘Dinner’s ready,’ calls out the nanny. In line with the family’s Paleo diet – of anti-inflammatory, natural foods – they have octopus cooked with lemongrass, and fish-bone broth. ‘Yes, my favourite,’ cries Jack happily, while his mum explains exactly what the broth is: ‘It’s an age-old elixir that’s made from boiling wild bones. It’s very high in iodine, which most of us are deficient in.’
After dinner, the children can continue to express their creativity, or watch some television – though if they’re going to do the latter after 6pm they need to put on their ‘blue-light blockers’, glasses with amber lenses to block the blue light of technology from affecting their sleep. ‘We also do red-light therapy,’ explains Catherine, pointing to a red dinosaur lamp in the boys’ bedroom. ‘It’s to help the body’s natural rhythms of sunset with exposure to red colours at night, and blue and white light in the morning.’

Powerful antibiotics and widespread sanitation practices have expanded lifespans across the industrialized world. But they have also come at a cost. Our microbiomes, or the trillions of microbes collectively working in our bodies to help regulate our immune system and food digestion, have lost much of its health-promoting bacteria because of our modern lifestyles and sanitation practices.
Scientists across the world are now looking to the planet’s few remaining pre-industrialized societies to see what industrialized guts have lost–and in doing so, could fundamentally change the way scientists think about germs. Thomas Morton heads to the Central African Republic to see this emerging field of microbiome science.
Check out VICE News for more: http://vicenews.com
Follow VICE News here:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/vicenews
Twitter: https://twitter.com/vicenews
Tumblr: http://vicenews.tumblr.com/
Instagram: http://instagram.com/vicenews
More videos from the VICE network: https://www.fb.com/vicevideo
#VICEonHBO

The coronavirus outbreak in China has had a foreseeable but unintended consequence. Truck drivers have refused to make deliveries into areas either identified as or suspected of harboring the disease.
This has interrupted not only the flow of minerals out of the affected areas but also the refining and manufacturing of metals, food, and fuel. Among the under-reported deficiencies thereby caused the most important ones for the global rare earths production and utilization industries is the interruption in the flow of chemical reagents necessary for refining rare earths and for producing metals, alloys, and magnets.
Critical materials-based supply chains may be hanging by a thread, the thread of the size of existing Chinese inventories. The coronavirus outbreak in China has had a foreseeable but unintended consequence.

If there was a public vote about human gene enhancement, would you vote YES or NO?
Our species is on the cusp of a revolution that will change every aspect of our lives but we’re hardly talking about it.
After three and a half billion years of evolution, two hundred and fifty thousand years of them as the ass-kicking bipedal hominins we call homo sapiens, we are on the verge of taking control of our evolutionary process unlike never before. This revolution will take hundreds of years to play out but it has already begun.
Sure, we influenced natural selection when we invented farming and modern medicine, but take a human baby from eleven thousand years ago and place him in a modern family and he’ll grow up just like any other kid. Then take a kid from a thousand years from now and place him in the same family. My belief is that the future child brought back to the present will not fit in nearly as well. He will be stronger and smarter with enhanced sensory and other capabilities. And we will have engineered him. We will have engineered us all.
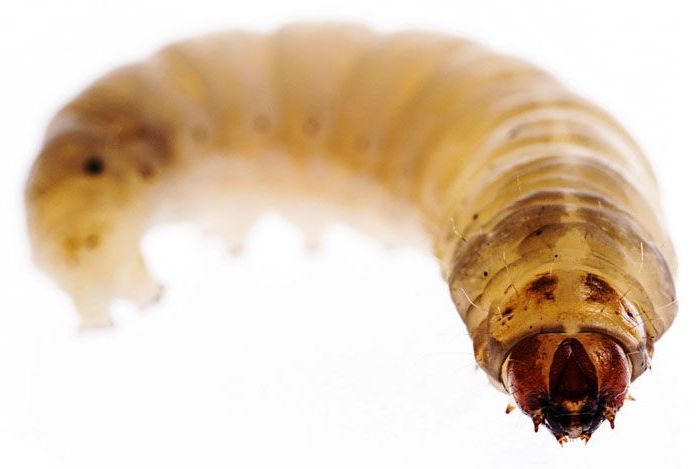

“The problem of plastic pollution is too large to simply throw worms and there is still a lot to do before we can parlay this work into making a meaningful contribution,” Cassone said. “Also, the larvae tend to eat less plastic with longer times on that type of diet. By understanding the process – why the breakdown of plastic occurs so rapidly in the waxworm—we can then begin to develop ways to really make a meaningful impact to plastic pollution.”
He continued: “Now that we know the microbiome plays a role, if we can better understand how the bacteria works together with the worm and what kind of conditions cause it to flourish, perhaps this information can be used to design better tools to eliminate plastics from our environment.”
Not all are convinced, however. Till Opatz, from the Department of Chemistry at the Johannes Gutenberg University, Germany, was critical of the initial findings that caterpillars digest plastic. At the time he and his colleagues said they disagreed with the methodology and conclusions reported, adding the study “does not provide sufficient proof” that G. mellonella can chemically destroy polyethylene.

The fact that self-driving trucks did not initially capture the public imagination is perhaps not entirely shocking. After all, most people have never been inside a truck, let alone a self-driving one, and don’t give them more than a passing thought. But just because trucks aren’t foremost in most people’s thoughts, doesn’t mean trucks don’t impact everyone’s lives day in and day out. Trucking is an $800 billion industry in the US. Virtually everything we buy — from our food to our phones to our furniture — reaches us via truck. Automating the movement of goods could, therefore, have at least as profound an impact on our lives as automating how we move ourselves. And people are starting to take notice.
As self-driving industry pioneers, we’re not surprised: we have been saying this for years. We founded Kodiak Robotics in 2018 with the vision of launching a freight carrier that would drive autonomously on highways, while continuing to use traditional human drivers for first- and last-mile pickup and delivery. We developed this model because our experience in the industry convinced us that today’s self-driving technology is best-suited for highway driving. While training self-driving vehicles to drive on interstate highways is complicated, hard work, it’s a much simpler, more constrained problem than driving on city streets, which have pedestrians, public transportation, bikes, pets, and other things that make cities great to live in but difficult for autonomous technology to understand and navigate.
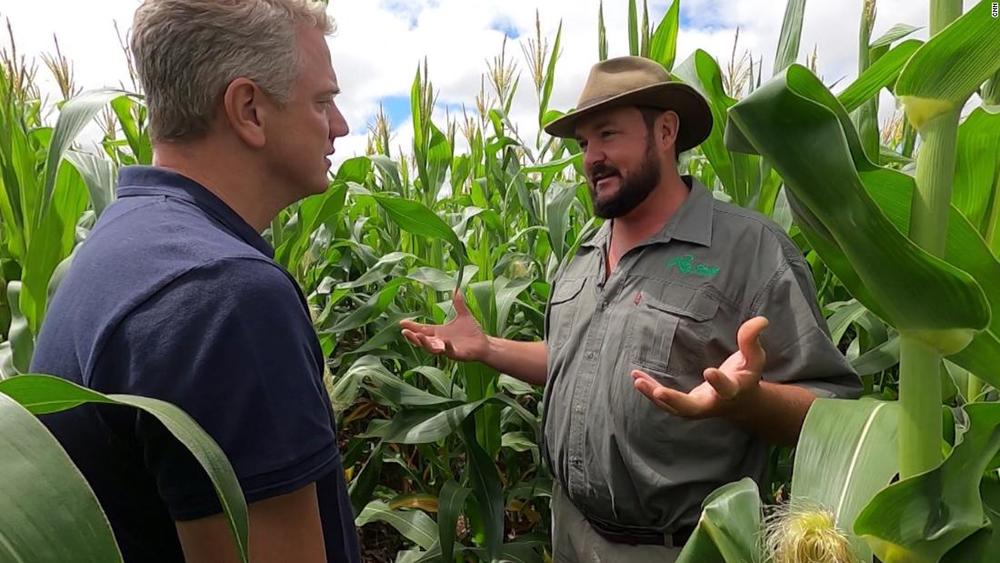

A quiet revolution is reshaping the agricultural world, with farmers like Danie Slabbert saying that if we want to save the planet, it’s not so much about what we eat, but how we farm. CNN’s David McKenzie reports.

CropBox is a shipping container farm system featuring the latest technology in precision farming.