MIT researchers have developed a new material inspired by camel fur made from two layers that can keep perishable goods cool without needing any power. The two-layer passive cooling system is made of hydrogel and aerogel. Researchers say that it can be used to keep foods or pharmaceutical cool for days without needing electricity.
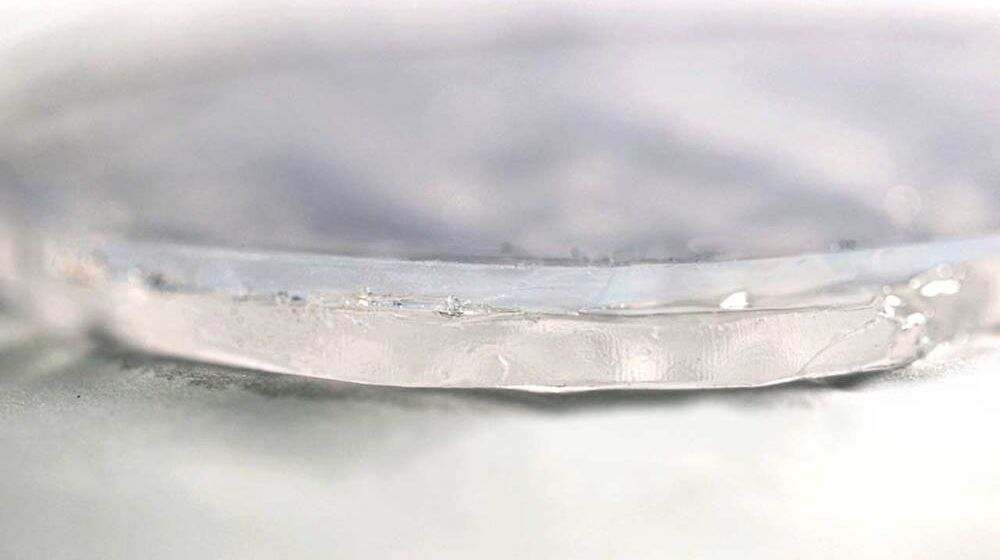
The material can be seen in the photo above, its top layer is aerogel, and the bottom layer is a hydrogel. Material is inspired by camel fur, which helps keep the animals cool and helps them to conserve water in the scorching desert environment. It seems counterintuitive that a thick coat of fur would help camels to stay cool, but tests have shown that a shaved camel loses 50 percent more moisture than an unshaved one under ideal conditions.
The bottom layer of MIT’s material is a substitute for sweat glands made of hydrogel. This gelatin-like substance is mostly water contained in a sponge-like matrix that allows the water to evaporate easily. The upper aerogel layer plays the part of the fur, keeping out external heat while allowing the vapor to pass through. Hydrogels have been used for cooling applications in the past. Field tests have found that MIT’s material can provide cooling of more than seven degrees Celsius for five times longer than hydrogel alone despite being less than half an inch thick.