The things we need to know for the 2016 robotic experience — robot clusters, manufacturing & logistics, food & healthcare, A3 Mexico Coming Soon and robotics integration.
Bold predictions for Collaboration, Connectivity and Convergence rang in 2015. One industry insider even called them prescient. Looking back a year later, we see the five-year forecast materializing faster than expected.
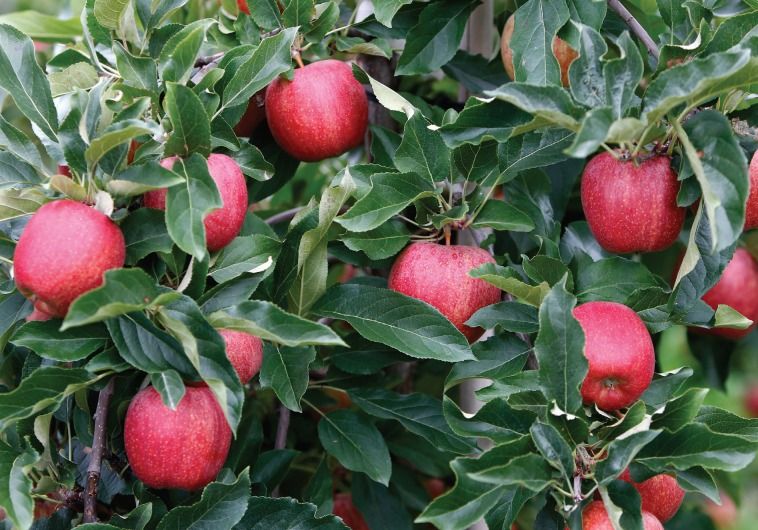
Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT) is more than a buzzword. With drones taking to the skies and autonomous robots navigating our warehouses, local eateries, hotels, hospitals, and stores, and soon our roadways – the differences between industrial, collaborative, and service robots continue to blur. No longer are robots reserved for multinational conglomerates or the rich eccentric with a sweet tooth for high-tech toys. SMEs and your average homeowner can now join the party. Sensors, software, and hardware are getting smarter and cheaper. We’re democratizing robotics for the masses.
It’s taken longer than some had hoped. But we’re approaching the tipping point for many automation technologies. We’re envisioning a world where robots will help the elderly and infirm with everyday tasks, so they can live independently longer. We’re moving closer to Asimov’s robots and to the “mobile, sensate robot” Engelberger anticipated. It’s the paradigm shift foretold by visionaries past and present.