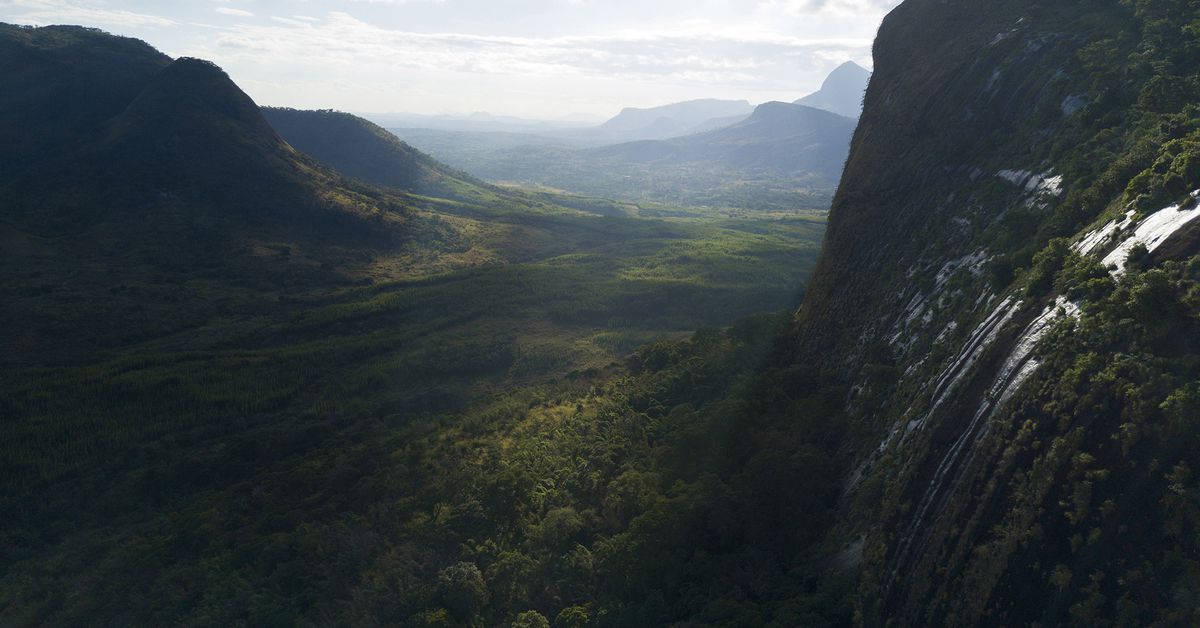
In 2018, what is left to explore in the world? It seems unlikely, say, that humans might find an untouched forest to study, someplace that hasn’t been bulldozed and burnt and exploited within an inch of its life for precious minerals or virgin timber. But that’s exactly what happened this past spring, when a Welsh researcher, Dr. Julian Bayliss, led a 28-person team that included scientists specially selected for their different talents as well as logistics experts, rock climbers, and filmmakers to the top of a mountain in Mozambique.
The story of the Mount Lico expedition began six years ago when Bayliss, a conservation scientist and butterfly expert, happened to spy a small forest atop a mountain using Google Earth. It wasn’t the first time he’d found such a place; Bayliss had been using Google Earth to explore high-altitude rainforests in Africa for around 15 years. In February 2017, the time was finally right: Bayliss brought a drone to the base of the 410-foot sheer rock protuberance (technically known as an inselberg) to confirm that there was a forest on top. This was no small feat. The area surrounding Mount Lico is a patchwork of smallholder farms, tea and eucalyptus plantations, and woodlands. There are no paved roads, no hotels — just rivers to cross, plants to hack away with machetes, and miles of dirt track to navigate.
While locals were aware of Mount Lico and used the natural resources of surrounding forests, its tall, sheer walls meant that it was nearly impossible to access, which made it likely that the land on top was untouched by humans. However, scientists would later find out that someone had been up there at least once.
Read more