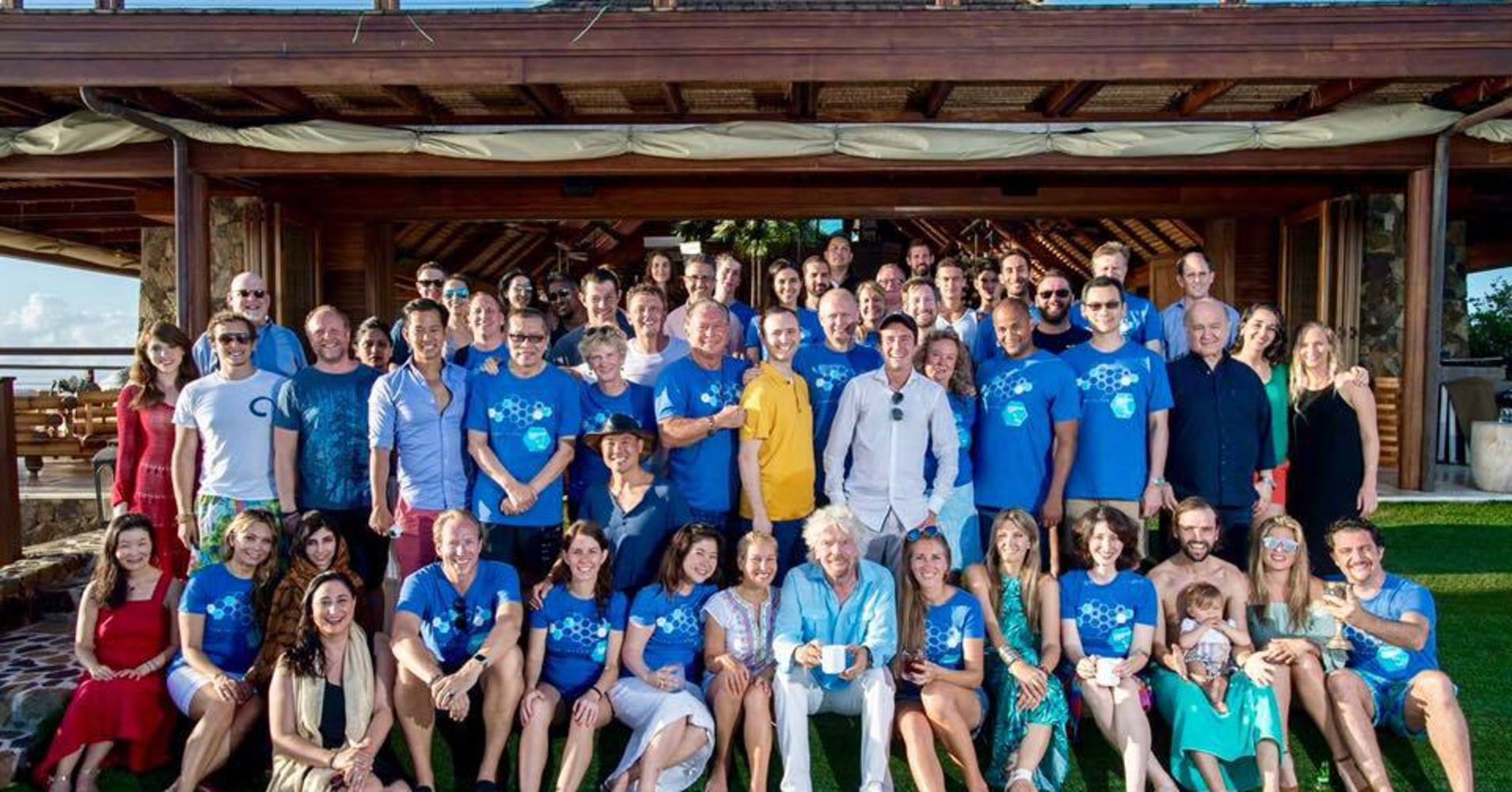
Set on Sir Richard Branson’s Necker Island, the third annual Blockchain Summit, hosted by BitFury, a leading full service Blockchain company, and Bill Tai, a venture investor and technologist, has come to a close. This event was an intimate, if perfectly balanced, gathering of technology, policy, investment and business leaders from around the world and across sectors. Topics ranged from the public policy implications of what is being heralded as a foundational technology, to new emerging business models that can ride on the very rails that enabled the global bonanza of digital currencies like Bitcoin. A key question that underpinned the Summit is if Blockchain could not have existed without the Internet, what could not exist without Blockchain?
Blockchain technology can undoubtedly change industries, especially those that labor under often byzantine, opaque and friction-laden business models. While many of the early pioneers are focusing on finance and insurance, the opportunities for this radical technology may very well reorder society as we know it. The remarkable case of Estonia, for example, shows a country reinventing itself into a future-proof digital state, where citizen services are rendered nearly instantaneously and to people all over the world. Similarly, promising work inspired by the famed Peruvian economist, Hernando de Soto, on improving land registries is being carried out by BitFury in a host of countries. With land and property being the two largest assets people will own — and the principal vehicle of value creation and wealth transfer — an unalterable, secure and transparent registration process should give the world comfort and elected leaders longevity.
What drives this unique technology is the power of distributed singularity, from which Blockchain’s identity pioneers like Dr. Mariana Dahan, who launched the World Identity Network on Necker Island, and Vinny Lingham of Civic, draw their inspiration. Blockchain operates on the basis of a distributed ledger (or database) system, inexorably marching forward recording and time-stamping transactions or records. While some may herald Bitcoin as Blockchain’s “killer app,” it is easy to maintain that the killer app is not the digital currencies that ride on Blockchain’s rails, but rather the rail system altogether. Two trains can ride on rails. But a high-speed maglev train is a decidedly faster mode of transport than a steam engine. Just as the maglev makes little or no contact with the rails enabling low-friction transport, the Blockchain can greatly reduce the friction in how the world transfers and records value.
Read more