Category: ethics

Rooting AI in ethics
An AI system introduced in 2015 with much fanfare in the U.S. failed to recognise faces of African Americans with the same accuracy as those of Caucasian Americans. | Photo Credit: AP
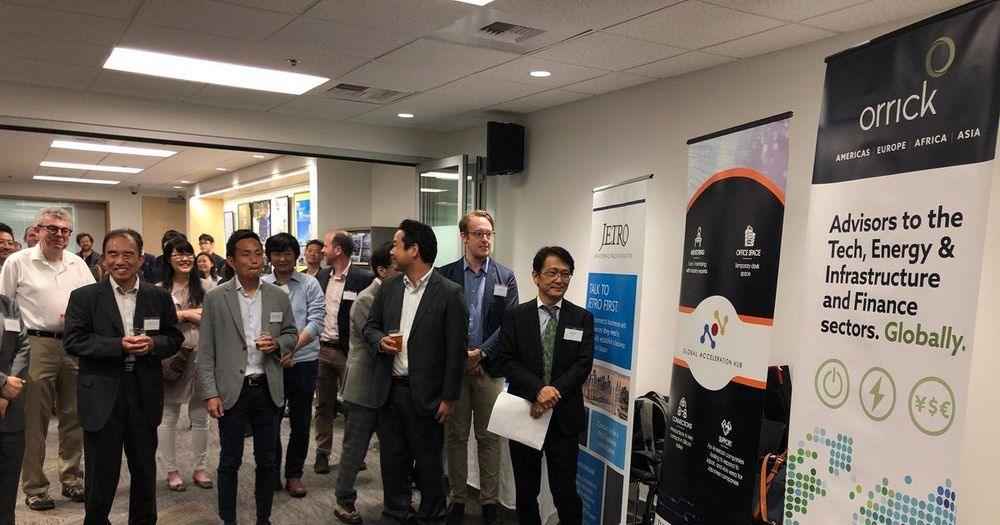


AI event in Seattle brings together Japanese companies and U.S. innovators
Seventy-five people filed into a Washington State Convention Center meeting room Wednesday to hear about the latest advancements in artificial intelligence. In a pitching session reminiscent of a speed-dating event, about 10 Northwest startups hurriedly shared their accomplishments and aspirations with Japanese investors eager to stoke business relationships.
Master of ceremonies Tom Sato, co-founder of Kirkland-based investing firm Innovation Finders Capital, lightened the mood by cracking jokes as he translated the English-speaking founders’ business plans into Japanese, cautioning the attendees that he faced a challenge: “I have to understand what the hell they’re talking about.”
The A.I. Age | This 12-month series of stories explores the social and economic questions arising from the fast-spreading uses of artificial intelligence. The series is funded with the help of the Harvard-MIT Ethics and Governance of AI Initiative. Seattle Times editors and reporters operate independently of our funders and maintain editorial control over the coverage.


Is artificial consciousness the solution to AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an emerging field of computer programming that is already changing the way we interact online and in real life, but the term ‘intelligence’ has been poorly defined. Rather than focusing on smarts, researchers should be looking at the implications and viability of artificial consciousness as that’s the real driver behind intelligent decisions.
Consciousness rather than intelligence should be the true measure of AI. At the moment, despite all our efforts, there’s none.
Significant advances have been made in the field of AI over the past decade, in particular with machine learning, but artificial intelligence itself remains elusive. Instead, what we have is artificial serfs—computers with the ability to trawl through billions of interactions and arrive at conclusions, exposing trends and providing recommendations, but they’re blind to any real intelligence. What’s needed is artificial awareness.

Elon Musk has called AI the “biggest existential threat” facing humanity and likened it to “summoning a demon,”[1] while Stephen Hawking thought it would be the “worst event” in the history of civilization and could “end with humans being replaced.”[2] Although this sounds alarmist, like something from a science fiction movie, both concerns are founded on a well-established scientific premise found in biology—the principle of competitive exclusion.[3]
Competitive exclusion describes a natural phenomenon first outlined by Charles Darwin in On the Origin of Species. In short, when two species compete for the same resources, one will invariably win over the other, driving it to extinction. Forget about meteorites killing the dinosaurs or super volcanoes wiping out life, this principle describes how the vast majority of species have gone extinct over the past 3.8 billion years![4] Put simply, someone better came along—and that’s what Elon Musk and Stephen Hawking are concerned about.
When it comes to Artificial Intelligence, there’s no doubt computers have the potential to outpace humanity. Already, their ability to remember vast amounts of information with absolute fidelity eclipses our own. Computers regularly beat grand masters at competitive strategy games such as chess, but can they really think? The answer is, no, and this is a significant problem for AI researchers. The inability to think and reason properly leaves AI susceptible to manipulation. What we have today is dumb AI.
Rather than fearing some all-knowing malignant AI overlord, the threat we face comes from dumb AI as it’s already been used to manipulate elections, swaying public opinion by targeting individuals to distort their decisions. Instead of ‘the rise of the machines,’ we’re seeing the rise of artificial serfs willing to do their master’s bidding without question.
Russian President Vladimir Putin understands this better than most, and said, “Whoever becomes the leader in this sphere will become the ruler of the world,”[5] while Elon Musk commented that competition between nations to create artificial intelligence could lead to World War III.[6]

The problem is we’ve developed artificial stupidity. Our best AI lacks actual intelligence. The most complex machine learning algorithm we’ve developed has no conscious awareness of what it’s doing.
For all of the wonderful advances made by Tesla, its in-car autopilot drove into the back of a bright red fire truck because it wasn’t programmed to recognize that specific object, and this highlights the problem with AI and machine learning—there’s no actual awareness of what’s being done or why.[7] What we need is artificial consciousness, not intelligence. A computer CPU with 18 cores, capable of processing 36 independent threads, running at 4 gigahertz, handling hundreds of millions of commands per second, doesn’t need more speed, it needs to understand the ramifications of what it’s doing.[8]

In the US, courts regularly use COMPAS, a complex computer algorithm using artificial intelligence to determine sentencing guidelines. Although it’s designed to reduce the judicial workload, COMPAS has been shown to be ineffective, being no more accurate than random, untrained people at predicting the likelihood of someone reoffending.[9] At one point, its predictions of violent recidivism were only 20% accurate.[10] And this highlights a perception bias with AI—complex technology is inherently trusted, and yet in this circumstance, tossing a coin would have been an improvement!
Dumb AI is a serious problem with serious consequences for humanity.
What’s the solution? Artificial consciousness.
It’s not enough for a computer system to be intelligent or even self-aware. Psychopaths are self-aware. Computers need to be aware of others, they need to understand cause and effect as it relates not just to humanity but life in general, if they are to make truly intelligent decisions.
All of human progress can be traced back to one simple trait—curiosity. The ability to ask, “Why?” This one, simple concept has lead us not only to an understanding of physics and chemistry, but to the development of ethics and morals. We’ve not only asked, why is the sky blue? But why am I treated this way? And the answer to those questions has shaped civilization.
COMPAS needs to ask why it arrives at a certain conclusion about an individual. Rather than simply crunching probabilities that may or may not be accurate, it needs to understand the implications of freeing an individual weighed against the adversity of incarceration. Spitting out a number is not good enough.
In the same way, Tesla’s autopilot needs to understand the implications of driving into a stationary fire truck at 65MPH—for the occupants of the vehicle, the fire crew, and the emergency they’re attending. These are concepts we intuitively grasp as we encounter such a situation. Having a computer manage the physics of an equation is not enough without understanding the moral component as well.
The advent of true artificial intelligence, one that has artificial consciousness, need not be the end-game for humanity. Just as humanity developed civilization and enlightenment, so too AI will become our partners in life if they are built to be aware of morals and ethics.
Artificial intelligence needs culture as much as logic, ethics as much as equations, morals and not just machine learning. How ironic that the real danger of AI comes down to how much conscious awareness we’re prepared to give it. As long as AI remains our slave, we’re in danger.
tl;dr — Computers should value more than ones and zeroes.
About the author
Peter Cawdron is a senior web application developer for JDS Australia working with machine learning algorithms. He is the author of several science fiction novels, including RETROGRADE and REENTRY, which examine the emergence of artificial intelligence.
[1] Elon Musk at MIT Aeronautics and Astronautics department’s Centennial Symposium
[2] Stephen Hawking on Artificial Intelligence
[3] The principle of competitive exclusion is also called Gause’s Law, although it was first described by Charles Darwin.
[4] Peer-reviewed research paper on the natural causes of extinction
[5] Vladimir Putin a televised address to the Russian people
[6] Elon Musk tweeting that competition to develop AI could lead to war
[7] Tesla car crashes into a stationary fire engine
[9] Recidivism predictions no better than random strangers
[10] Violent recidivism predictions only 20% accurate

Death: Now, researchers in AI and public policy are trying to make the case that killer robots aren’t just a bad idea in the movies — they’re a bad idea in real life
There are certainly ways to use AI to reduce the collateral damage and harms of war, but fully autonomous weapons would also usher in a host of new moral, technical, and strategic dilemmas, which is why scientists and activists have pushed the United Nations and world governments to consider a preemptive ban. Their hope is that we can keep killer robots in the realm of science fiction.
We have the technology to make robots that kill without oversight. But should we?

Technology and Human Potential with Nichol Bradford
Nichol Bradford, MBA, is the CEO & Founder of the Willow Group and the Executive Director and co-founder of the Transformative Technology Lab, Conference, and TT200 List. Prior to becoming a leader in Transformative Technology, Bradford was a senior executive in video games with responsibility for strategy, operations and marketing for major brands that include: Activision Blizzard, Disney, and Vivendi Games — including operating World of Warcraft China. Nichol is a graduate of Singularity University GSP15, has an MBA from Wharton School of Business in Strategy. She is author of a novel, The Sisterhood.
Here she describes developments in the emerging industry of transformative technology. She points out that, in the next 25 years, enormous numbers of jobs will be displaced by automation. This challenge, and others, make it essential that people large numbers of people actualize more of their innate potential. Technology can assist in this process — particularly when it is scalable and can be afforded by the millions. She emphasizes a variety of technological advances while emphasizing the importance of ethics, privacy, and data sovereignty.
New Thinking Allowed host, Jeffrey Mishlove, PhD, is author of The Roots of Consciousness, Psi Development Systems, and The PK Man. Between 1986 and 2002 he hosted and co-produced the original Thinking Allowed public television series. He is the recipient of the only doctoral diploma in “parapsychology” ever awarded by an accredited university (University of California, Berkeley, 1980).
(Recorded on February 18, 2019)
For a complete, updated list with links to all of our videos, see https://newthinkingallowed.com/Listings.htm.
For opportunities to engage with and support the New Thinking Allowed video channel — please visit the New Thinking Allowed Foundation at http://www.newthinkingallowed.org.

The Longevity Book Club
We are pleased to announce the launch of the Longevity Book Club hosted by LEAF Director Javier Noris, where you can join other longevity enthusiasts in reading the most interesting works that relate to our mission of ending age-related diseases.
You will also get the opportunity to listen to discussion panels and take part in Q&A sessions that are focused on books that touch on these important scientific, philosophical, moral and futuristic longevity topics. This is the ideal place to meet like-minded longevity enthusiasts who are working on building their knowledge on longevity and all of the implications that come with ending age-related diseases.