
Category: energy


How Nikola Tesla Used ‘Spirituality’ & Philosophy To Learn About Reality, ‘Limitless’ Energy & Science
I will say that many great innovators and inventors had some sort of spiritualism that they drew from to provide another angle on how to see/ perfect an idea or innovation. Jobs, Tesla, Edison, Bell, da Vinci, Carver, etc.
The Properties of Space.
Science works best when in harmony with nature. If we put these two together, we can discover great technologies that can only come about when the consciousness of the planet is ready to embrace them. One example is “free energy,” also known as “zero-point energy,” which utilizes the substance that exists all around us and converts it into usable energy. This would give us a limitless source of energy, and would practically wipe out all poverty on the planet. (more on this later in the article)
The properties of space have been postulated by many, from ancient Vedic philosophy, Eastern Mystics, various ancient civilizations throughout human history all the way to Descartes, Einstein, Newton and more. Humans are curious beings, and our quest to discover “what is” will never end.
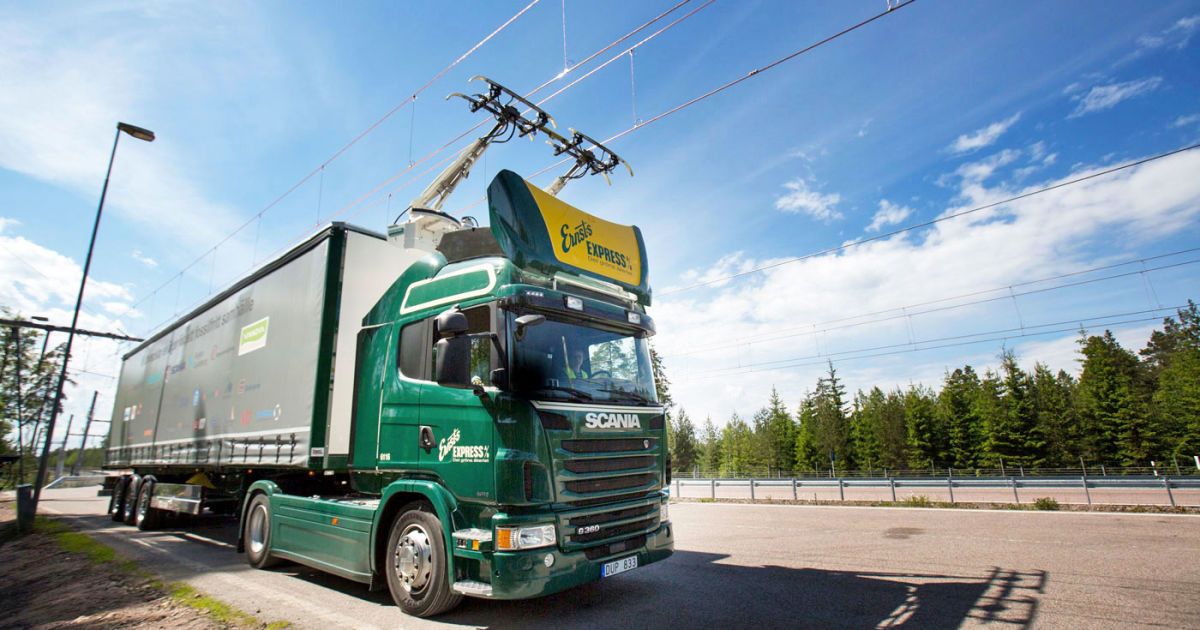


Sweden debuts the world’s first ‘electric highway’
Underground wireless charging will be a better idea!
Fossil fuels are bad for the planet, and freight haulage is one of the more carbon-intensive activities that operate today. That’s why Siemens and Scania have teamed up to trial what’s being called the world’s first “electric highway.” Much like an electrified railroad, the 1.2 mile stretch has a series of wires hanging overhead that a pantograph-equipped truck can connect to. Then, the vehicle can deactivate its fuel-burning engine and coast along on that delicious, dirt-cheap electricity, switching back when the wires stop.
Scania official Claes Erixon has said that the project is “one important milestone on the journey towards fossil-free transport.” Cleantech Canada quotes an unnamed Siemens representative, who says the move could cut energy consumption in half. As it stands, this is the culmination of a two-year project to develop this test track, with more work to be done to determine if it could be rolled out across the country. That is, unless, an alternative freight-transport network that’s even more energy-efficient and speedy, can make its case to governments across the world.

Terrifying Laser Bazooka Is Like a Handheld Death Star
Ah, science. wink
In the right hands, broken electronics can be turned into something useful again. But useful isn’t the best way to describe Drake Anthony’s 200-watt laser bazooka made from a bunch of old DLP projectors he bought off eBay. Words like incredibly dangerous, do-not-try-this-at-home, or “are you crazy?” seem more appropriate.
For comparison, the handheld laser pointers used during PowerPoint presentations measure in at a measly 0.005-watts, while the FDA limits the lasers that most consumers can buy to a maximum power rating of 0.5-watts. That means that Drake’s creation, which focuses four 50-watt lasers through a massive lens—is 400 times more powerful than what the FDA will let you play with. And those rules are there for a good reason. Lasers can be deadly!


Fully-autonomous drone launcher never needs a pilot
Having UAVs conduct routine aerial surveillance is already having a transformative effect on farming and and energy production but they can only operate when there’s a human at the controls. That’s about to change thanks to an autonomous drone system that not only flies but also maintains itself. Tel Aviv-based UAV Airobotics has debuted a completely automated patrol drone system of the same name that is capable of operating with virtually no human intervention.
The system is composed of three parts: the drone itself, the “Airbase” robotic base station and the command software. It uses an “Optimus” UAV that can carry a 1-kilogram payload for up to 30 minutes. When the UAV finishes its patrol, it will land atop the base station whereupon a robotic arm will automatically swap out its battery and payload. All of this is controlled by the integrated software which enables users to pre-program flight paths as well as view real-time video and data feeds. The Airobotic system will likely find use in the mining and oil and gas industries as an aerial mapping platform, though it could easily be applied to any repetitive delivery or flyover task.
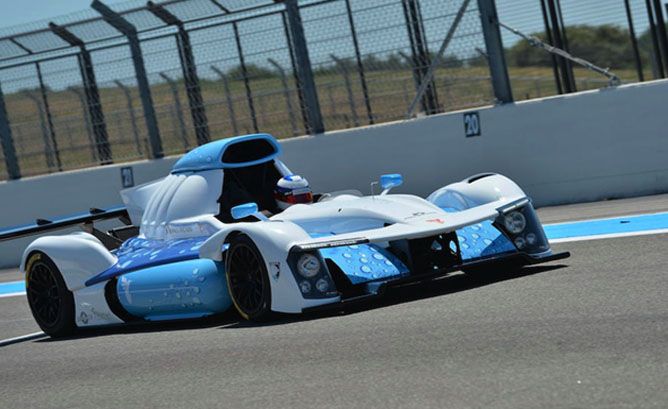

Hydrogen-Powered Race Car Runs Laps at Le Mans
Ford’s GT claimed first place in its class at the 24 Hours of Le Mans on the 50th anniversary of the first of its four outright victories in the 1960s, and Porsche’s 919 Hybrid snatched a second consecutive Le Mans victory.
The unheralded news of this year’s Le Mans race, however, is a hydrogen fuel cell race car completed laps on the Le Mans circuit for the first time in history.
The pioneering car was a Green GT H2, driven around the French track by former Formula 1 driver Olivier Panis during a break in qualifying, and again before the race started.
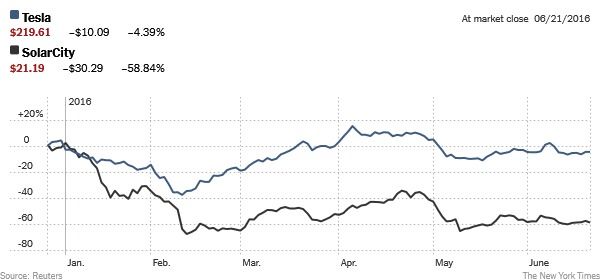
Elon Musk Aims to Shore Up SolarCity by Having Tesla Buy It — By Michael J. de la Merced and Peter Eavis | The New York Times
” … Tesla Motors said on Tuesday that it had offered to buy SolarCity in an all-stock deal, one that could value the latter at as much as $2.8 billion. The aim, Mr. Musk argues, is to create a renewable-energy giant, collecting clean electricity and putting it to work propelling cars.”
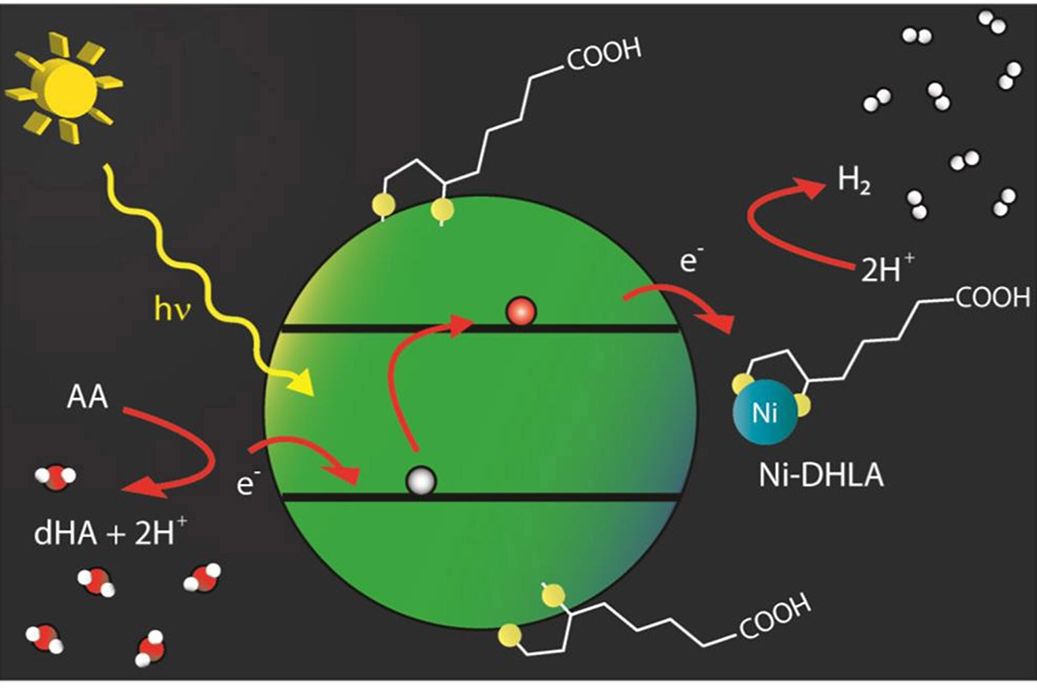
Ultrafast dynamics of semiconductor nanocrystals
Spectroscopy studies of charge transfer from cadmium selenide quantum dots to molecular nickel catalysts reveal unexpectedly fast electron transfer, enabling exceptional photocatalytic hydrogen production.
![]()
A key challenge facing the US is the harvesting, production, storage, and distribution of energy to support economic prosperity with responsible environmental management. Currently, fossil fuels provide more than 80% of the energy consumed in the US (even when significant increases in the use of alternative sources of energy in recent years are accounted for).1 For the US Department of Defense in particular, volatility in the price and availability of fossil fuels leads to significant short- and long-term financial, operational, and strategic risks.2 There is, therefore, clearly a need for new alternative sources of energy.