One-band effective mass model is used to simulation of electron gas properties in quantum well. We calculate of dispersion curves for first three subbands. Calculation results of Fermi energy, effective mass at Fermi level as function of electron concentration are presented. The obtained results are good agreement with the experimental dates.
Category: energy

Vencore Labs To Assist DARPA In Protecting The Nation’s Electrical Grid
CHANTILLY, Va., Sept. 13, 2016 /PRNewswire/ — Vencore Labs Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Vencore Inc., announced today that it has been awarded two prime contracts for the Rapid Attack Detection, Isolation and Characterization Systems (RADICS) program led by the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). The contracts have a total value of $17M and work is slated to begin in August of this year.
The objective of the RADICS program is to develop technologies for detecting and responding to cyberattacks on critical U.S. infrastructure, with an ultimate goal of enabling cyber and power engineers to restore electrical service within seven days in the event of a major attack. Vencore Labs, a leader in smart grid security and monitoring, will conduct research and deliver technologies in three of five technical areas (TA).
Metal to insulator transition understood
Physicists have for the first time succeeded in directly visualising on small scales how a material abruptly changes its state from conducting to insulating at low temperatures. Researchers Erik van Heumen of the University of Amsterdam and Alex McLeod from the University of California thereby provide evidence for a 60-year-old theory that explains this phenomenon and pave the way for more energy efficient technologies. The team’s experiments are described in the latest edition of Nature Physics.
Materials that conduct electricity at high temperature but are insulating at lower temperatures have been known for decades. However, until recently it was not possible to directly measure how such phase transitions proceed on small length scales. Using a new technique, Van Heumen and McLeod are now able to visualise the changes taking place in the material during such a phase transition on the nanometer scale.
In their experiments, the team observed a so-called percolation transition taking place among the electrons in the material. Above a certain critical temperature, the electrons can move relatively easily through the material enabling the flow of electrical current. When the temperature drops below a threshold temperature, small imperfections in the material trigger a kind of traffic jam for the electrons. Starting from small nanometer length scales, this traffic jam slowly grows outwards across the entire material. The previously freely moving electrons come to an abrupt halt and the material loses its conducting properties.

Turing’s new phone: Too good to be true in reality
Turing Robot Industries (TRI) has huge plans regarding its new phone. The third in the series phone, has such high-tech plans lined up for it that these plans itself make you cringe on the grounds of practicality and reality. The plans of the company for this phone include an 18 GB RAM, three Snapdragon 830’s, 6.4-inch 4K display, 1.2 TB storage 60MP iMAX 6K Quad Rear Camera Triplet Lens at f/1.2, and a 20MP front camera.
It will have 4G VoLTE enabled 4 Nano SIMs, support Parallel Tracking and Mapping API. This entire package will be powered by a 120wh battery which will also use a triple power source. This would be in the form of a supercooled 3,600mAh graphene battery and a pair of 2,600mAh Li-Ion Hydrogen Fuel cells powering your device (and maybe also your home).

Tech groups urging Congress to sue Obama admin to block giving control of Internet to authoritarian regimes
An alliance of technology organizations and conservatives are urging Congress to file suit against the Obama administration to block the transference of control over Internet domain names to an international board. The alliance claims that doing so will give authoritarian regimes power to decide who can and cannot have a presence on the web, Fox News reported Saturday.
Since 1998, a division of the U.S. Commerce Department called the National Telecommunications Information Administration, or NTIA, has issued domain names. But in September the Obama administration is set to allow the U.S. government’s contract to lapse so that the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) will then be operated by a global board of directors, and the responsibility will fall to it instead.
Critics of the administration’s decision fear that it will allow Russia, China and Iran to then have a stake in governing the Internet, giving them “de facto” power to tax domain names and quash free speech.
US Air Force advances rocket technology
The United States is one step closer to eliminating its reliance on Russian technology to launch its military satellites.
The Hydrocarbon Boost Technology Demonstrator, a U.S. Air Force technology effort focused on development of Oxygen Rich Staged Combustion rocket engine technology, has recently completed its first full-scale component test at 100-percent power.
The development of Oxygen Rich Staged Combustion technology has been deemed a critical technology for the nation to help eliminate the United States’ reliance on foreign rocket propulsion technology.
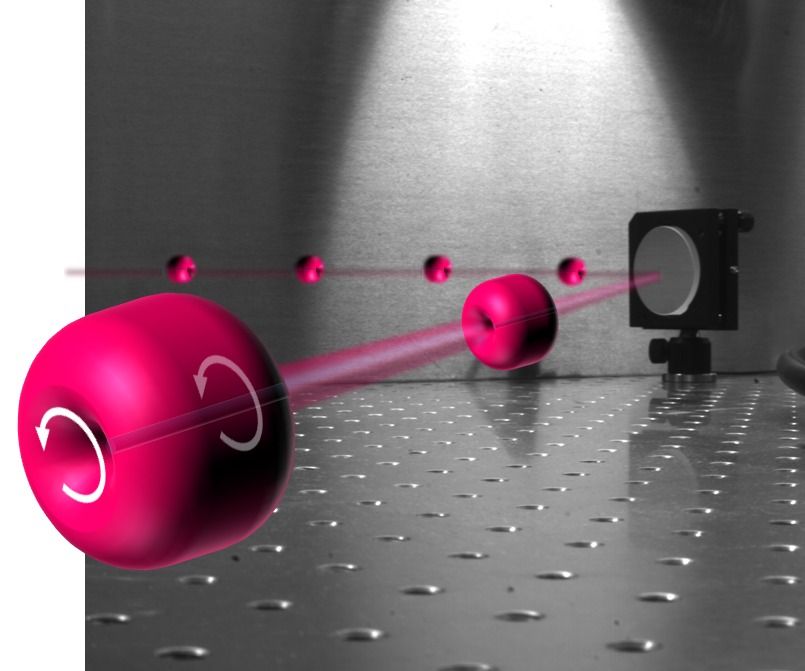
Physicists discover ‘smoke rings’ made of laser light
Most basic physics textbooks describe laser light in fairly simple terms: a beam travels directly from one point to another and, unless it strikes a mirror or other reflective surface, will continue traveling along an arrow-straight path, gradually expanding in size due to the wave nature of light. But these basic rules go out the window with high-intensity laser light.
Powerful laser beams, given the right conditions, will act as their own lenses and “self-focus” into a tighter, even more intense beam. University of Maryland physicists have discovered that these self-focused laser pulses also generate violent swirls of optical energy that strongly resemble smoke rings. In these donut-shaped light structures, known as “spatiotemporal optical vortices,” the light energy flows through the inside of the ring and then loops back around the outside.
The vortices travel along with the laser pulse at the speed of light and control the energy flow around it. The newly discovered optical structures are described in the September 9, 2016 issue of the journal Physical Review X.

Drones armed with anti-laser lasers that trick controls of enemy lasers into missing the drone
To defend against military lasers, Adsys Controls of Irvine, California, has created Helios, which can be carried on drones. To do much damage, an offensive laser needs to remain focused on its target for several seconds. Helios stops a laser from doing this by disrupting the systems controlling the beam – the Achilles’ heel for all such weapons. “Beam control is a critical function of high-energy lasers,” says Adsys CEO Brian Goldberg.
Helios can detect an incoming laser beam and identify its key characteristics, such as power, wavelength, pulse frequency and its source. Helios then interferes with the beam control – possibly by firing back a low-power laser of its own – so the attacking laser cannot fix on the target. “It provides permanent protection,” says Goldberg. “It’s not just buying time.”
He will not say exactly how the interference is done, but it may involve fooling the control system into thinking it is hitting its target despite the laser actually pointing a few metres to the side. A direct hit would have produced a big burst of reflected light, so a pulse sent back by an anti-laser laser could make it look like the original laser was on target.

Time crystals might exist after all
(Phys.org)—Are time crystals just a mathematical curiosity, or could they actually physically exist? Physicists have been debating this question since 2012, when Nobel laureate Frank Wilczek first proposed the idea of time crystals. He argued that these hypothetical objects can exhibit periodic motion, such as moving in a circular orbit, in their state of lowest energy, or their “ground state.” Theoretically, objects in their ground states don’t have enough energy to move at all.
In the years since, other physicists have proposed various arguments for why the physical existence of time crystals is impossible—and most physicists do seem to think that time crystals are physically impossible because of their odd properties. Even though time crystals couldn’t be used to generate useful energy (since disturbing them makes them stop moving), and don’t violate the second law of thermodynamics, they do violate a fundamental symmetry of the laws of physics.
However, now in a new paper published in Physical Review Letters, physicists from the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB) and Microsoft Station Q (a Microsoft research lab located on the UCSB campus) have demonstrated that it may be possible for time crystals to physically exist.