“Wind power has transformed the heart of fossil-fuel country. Can the rest of the United States follow suit?”
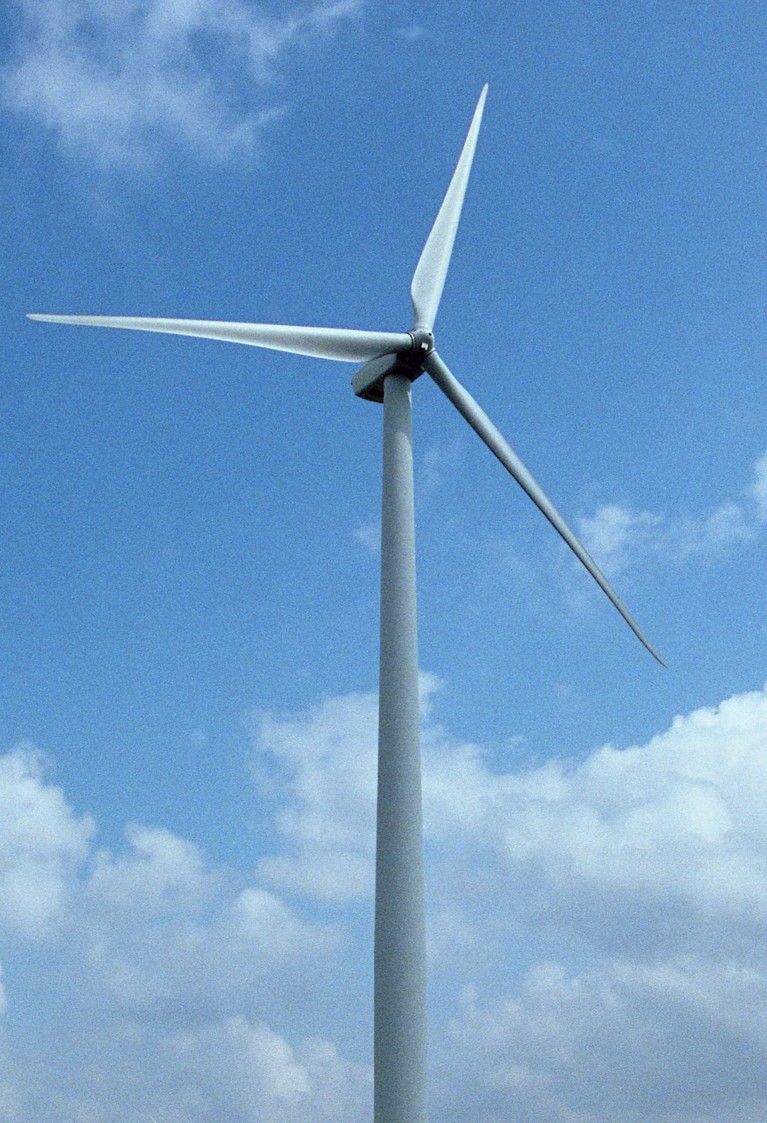


“Wind power has transformed the heart of fossil-fuel country. Can the rest of the United States follow suit?”
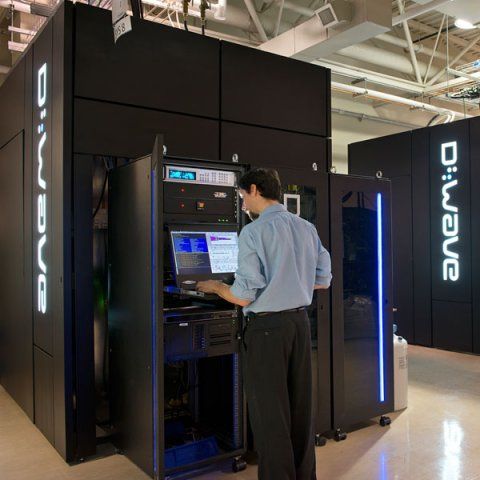

D-Wave Systems announced Tuesday (Sept. 28, 2016) a new 2000-qubit processor, doubling the number of qubits over the previous-generation D-Wave 2X system. The new system will enable larger problems to be solved and performance improvements of up to 1000 times.
D-Wave’s quantum system runs a quantum-annealing algorithm to find the lowest points in a virtual energy landscape representing a computational problem to be solved. The lowest points in the landscape correspond to optimal or near-optimal solutions to the problem. The increase in qubit count enables larger and more difficult problems to be solved, and the ability to tune the rate of annealing of individual qubits will enhance application performance.
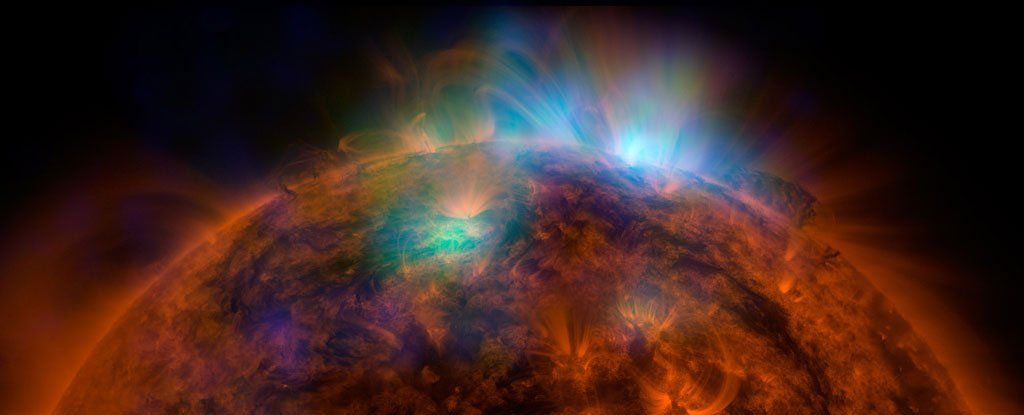

A NASA-funded study has solved a longstanding mystery over the origin of X-rays that permeate space in our Solar System, but in doing so, it’s also discovered an entire group of high-energy X-rays that can’t be explained.
The research comes from a new analysis of data recorded by NASA’s DXL rocket mission, which took flight in 2012 to settle the question of what creates these low-energy X-ray emissions – called the diffuse soft X-ray background – in our corner of the galaxy.
At the time, there were two central hypotheses. X-ray emissions were known to come from solar wind, but scientists also thought they might originate from what’s called the Local Hot Bubble – a theorised region of hot gas that envelops our Solar System. But which was correct?

Realistic hover cars coming to future near you.
The quest to know the mysterious recipe for high-temperature superconductivity, which could enable revolutionary advances in technologies that make or use electricity, just took a big leap forward thanks to new research by an international team of experimental and theoretical physicists.
The research paper appears in the journal Science on Sept. 16, 2016. The research is focused on revealing the mysterious ingredients required for high-temperature superconductivity — the ability of a material’s electrons to pair up and travel without friction at relatively high temperatures, enabling them to lose no energy — to be super efficient — while conducting electricity.
The research team’s achievements are an important step in recent efforts to improve today’s superconducting materials, which have superconducting powers only if they are cooled below a critical temperature, hundreds of degrees below the freezing point of water — temperatures at which helium is a liquid — making them impractical for use in most electronic devices.

According to the Kardashev scale, a Type III civilization is a society that has managed to harness (and control) the energy output of a galaxy. Here’s what that means.
To measure the level of a civilization’s advancement, the Kardashev scale focuses on the amount of energy that a civilization is able to harness. Obviously, the amount of power available to a civilization is linked to how widespread the civilization is (you can’t harness the power of a star if you are confined to your home planet, and you certainly can’t harness the power of a galaxy if you can’t even get out of your solar system).

https://youtube.com/watch?v=jCIbbhL2td8
Nice method for refrig.; now imagine it in autos/ various forms of transportation, buildings, appliances, etc.
NEW YORK, NY – 9/20/2016 (PRESS RELEASE JET) — Haier, a global leader in consumer electronics and appliances has launched a new compressor-free solid-state refrigeration technology. Haier created this new technology through integrating Silicon Valley resources, Haier Group R&D, Haier America R&D, Liquid King, Xi’an Jiaotong University, South China University of Technology and other resources. The new technology breaks the technological bottlenecks of compressor-based refrigeration appliance that have been used in the industry for a century.
How does it work?
The compressor, one of the most important parts of any refrigeration appliance, has been evolving for 40 years and Haier is proud to introduce this new technology, which combines the concept of variable displacement with an oil-free solution. The technology has tremendous potential with regards to superior energy efficiency levels and innovative appliance design. Haier offers a lifetime warranty on the oil-free refrigeration compressor of its high-end refrigerators, a reassurance of their long durability and high performance.

3D printing obviously has many advantages, but energy efficiency is one that is rarely mentioned. In fact, depending on the application and scale, 3D printing produces far few carbon emissions than many other manufacturing options. In an attempt to harness that advantage, the luxurious Dutch Hotel De Slaapfabriek from Teuge is planning to build a unique, 3D printed and zero-footprint conference location that provides a highly inspiring and modern environment. Construction is scheduled to kick off in July 2017, and could be completed in as little as ten days. If successful, it could pave the way for a new environmentally-friendly construction 3D printing paradigm.
This forthcoming structure could not have picked a more inspiring location in the Netherlands. De Slaapfabriek is a luxurious experience hotel in Teuge, The Netherlands (very near to International Airport Teuge in Gelderland). With unique twelve rooms available to clients, it’s a premier location for honeymoons and business trips. Since opening its doors in 2009, De Slaapfabriek has also won award after award, and currently boasts a Booking.com appreciation score of 9.3. The only thing that’s missing is a conference location, and when necessary the luxury breakfast and lounge area is transformed into a conference room. But this is not the best solution, and founders Arvid and Marjo Prigge developed an ambitious plan: to construct a completely new, environmentally-friendly conference location.

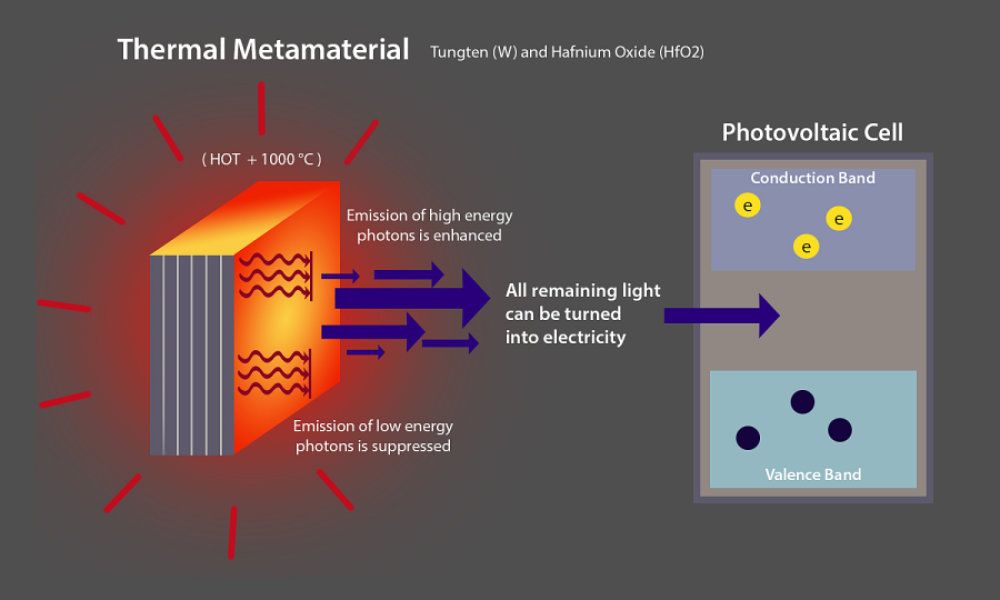
An international research team has used a “thermal metamaterial” to control the emission of radiation at high temperatures, an advance that could bring devices able to efficiently harvest waste heat from power plants and factories.
Roughly 50 to 60 percent of the energy generated in coal and oil-based power plants is wasted as heat. However, thermophotovoltaic devices that generate electricity from thermal radiation might be adapted to industrial pipes in factories and power plants, as well as on car engines and automotive exhaust systems, to recapture much of the wasted energy.
In new findings, researchers demonstrated howto restrict emission of thermal radiation to a portion of the spectrum most needed for thermophotovoltaic technology.

28’ Singularity — The only boat in the world like it — no more will be built!! Nothing comes close to the boats’ style, design and sea handling capabilities!
RANDALL BURG
[email protected]
http://www.rbyachts.com
TWITTER: lovethatyacht
Unique aluminum Mono-hull, twin Volvo 300 hp diesel engines, full electronics, generator and full air conditioning, full marine head with sink, interior and exterior seating for 10 plus seating for three at the helm, removable Bimini canvas cockpit cover and power arch for easy instill, retractable stainless aft cocklpit railing, custom aluminum three axle trailer.
www.rbyachts.com
One of the most unusual One-Of-A-Kind custom boats ever built!
A startup called Proterra has been working on electric buses for years, and its latest model has a pretty impressive range. Its Catalyst E2 Series buses can drive up to 350 miles on a single charge, which means it can go a quite a bit further than Tesla’s top-tier Model S that already boasts a 300-plus-mile range. The vehicle can also outlast its predecessor that can only go for 258 miles. As Wired notes, electric buses might even be better than cars, since they don’t need a huge network of charging stations. They drive a set route, so cities can simply install some where they’re bound to pass — the E2 might not even need to recharge until the end of the day. Further, not everyone can afford an electric vehicle, but most people can afford to ride a bus.
The Catalyst E2 Series buses are powered by two gargantuan batteries the size of mattresses that can store up to 660 kWh. Its lightweight frame, along with its regenerative braking system, also helps it achieve that impressive range. The only thing that might hold cities and companies back from purchasing E2 is that one will set them back $799,000, over twice the amount of a typical diesel bus. Proterra is probably hoping that government subsidies, coupled with the fuel and maintenance savings they’ll get, can convince them to buy the vehicle. If you’re in Los Angeles, you might be able to ride one of the first E2 buses scheduled to hit the road in 2017.