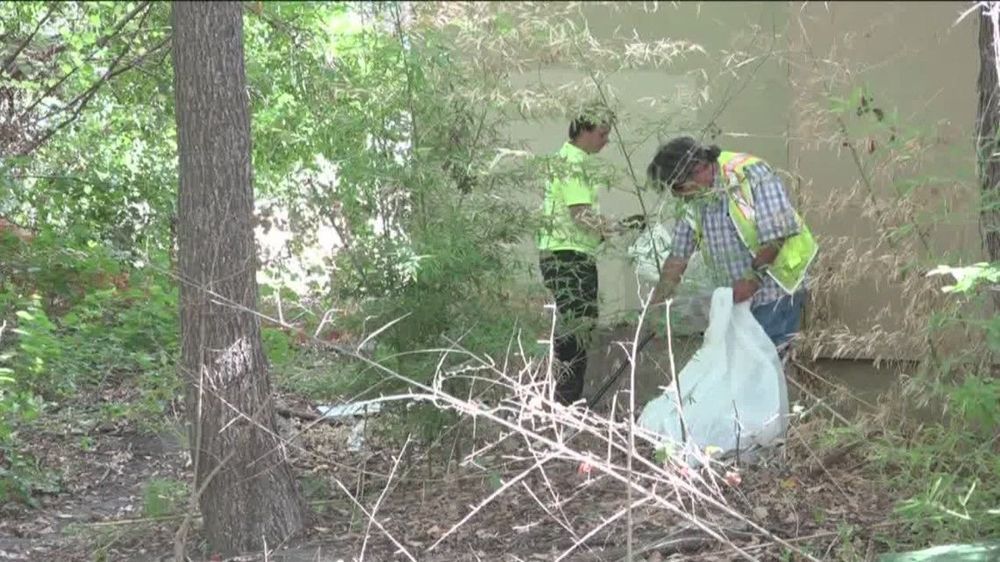
The employees get paid $15 an hour cleaning the green space in Austin.
AUSTIN, Texas — The homeless often face barriers when trying to find employment. This week, after reaching the one-year anniversary of their new program, a nonprofit said they are making a difference for those trying to get on their feet and find a job.
In October 2018, The Other Ones Foundation (Too Found) created its Workforce First program to provide the homeless with jobs cleaning the green space in Austin and reduce panhandling.
Since its inception, the organization has provided more than 130 jobs and paid out more than $100,000 in earned income to the homeless or at-risk, according to Chris Baker, the executive director of the nonprofit.