https://youtube.com/watch?v=Pi7iCUSXctY
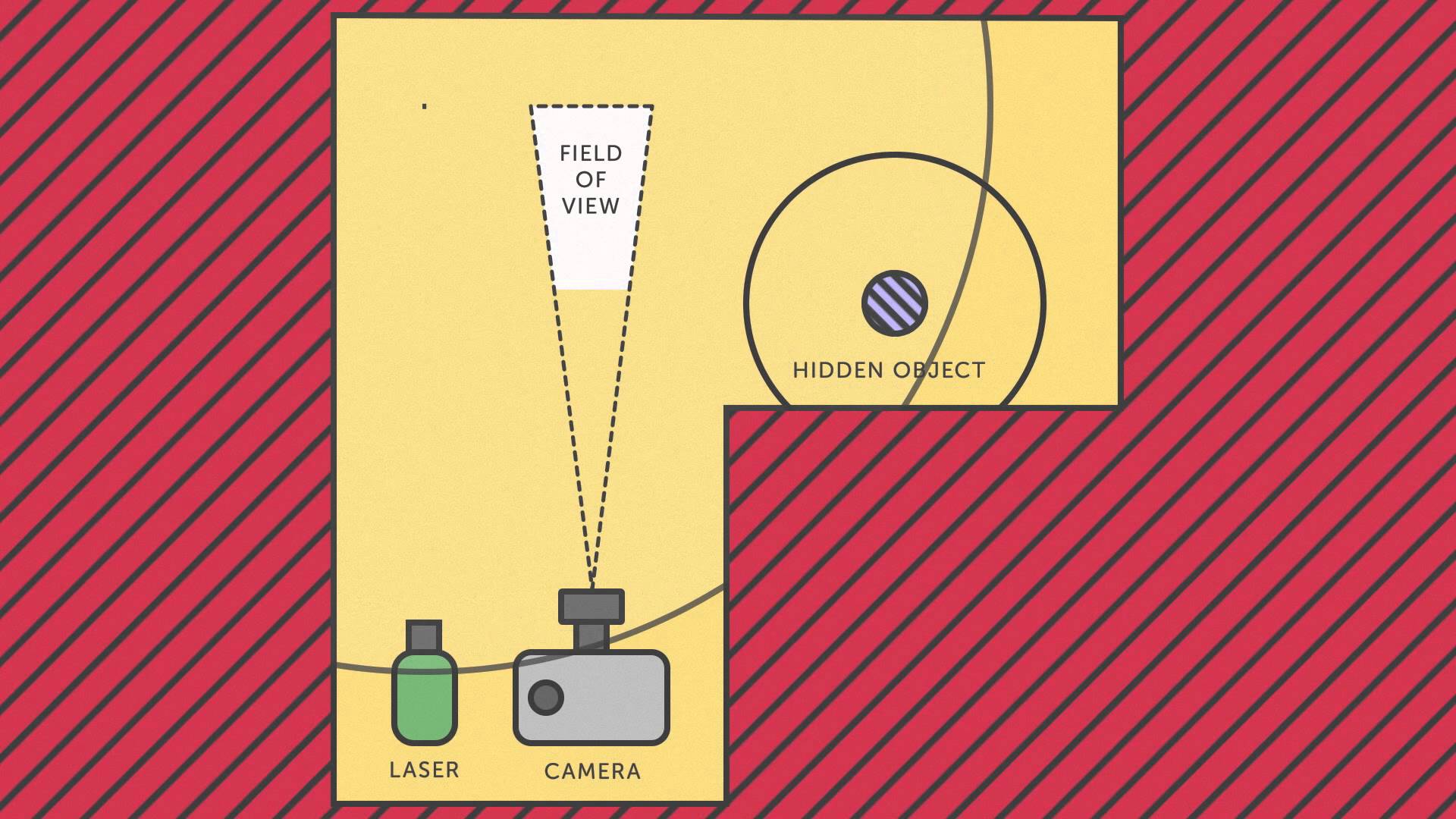
How can a person see around a blind corner? One answer is to develop X-ray vision. A more mundane approach is to use a mirror. But if neither are an option, a group of scientists led by Genevieve Gariepy have developed a state-of-the-art detector which, with some clever data processing techniques, can turn walls and floors into a “virtual mirror”, giving the power to locate and track moving objects out of direct line of sight.
The shiny surface of a mirror works by reflecting scattered light from an object at a well-defined angle towards your eye. Because light scattered from different points on the object is reflected at the same angle, your eye sees a clear image of the object. In contrast, a non-reflective surface scatters light randomly in all directions, and creates no clear image.
However, as the researchers at Heriot-Watt University and the University of Edinburgh recognised, there is a way to tease out information on the object even from apparently random scattered light. Their method, published in Nature Photonics, relies on laser range-finding technology, which measures the distance to an object based on the time it takes a pulse of light to travel to the object, scatter, and travel back to a detector.
Read more