New research throws wide open the amount of information that can be simultaneously transmitted by a single light source.
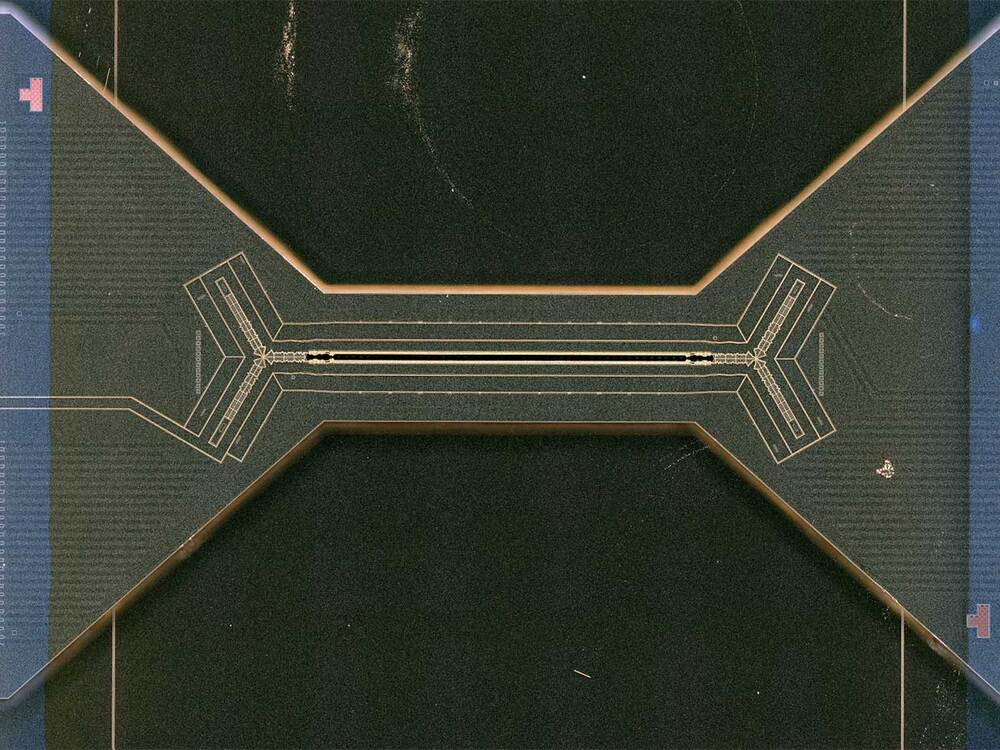
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have found a new way to harness properties of light waves that can radically increase the amount of data they carry. They demonstrated the emission of discrete twisting laser beams from antennas made up of concentric rings roughly equal to the diameter of a human hair, small enough to be placed on computer chips.
The new work, reported in a paper published Thursday, February 252021, in the journal Nature Physics, throws wide open the amount of information that can be multiplexed, or simultaneously transmitted, by a coherent light source. A common example of multiplexing is the transmission of multiple telephone calls over a single wire, but there had been fundamental limits to the number of coherent twisted lightwaves that could be directly multiplexed.