https://youtube.com/watch?v=a_mYvSVG3QY
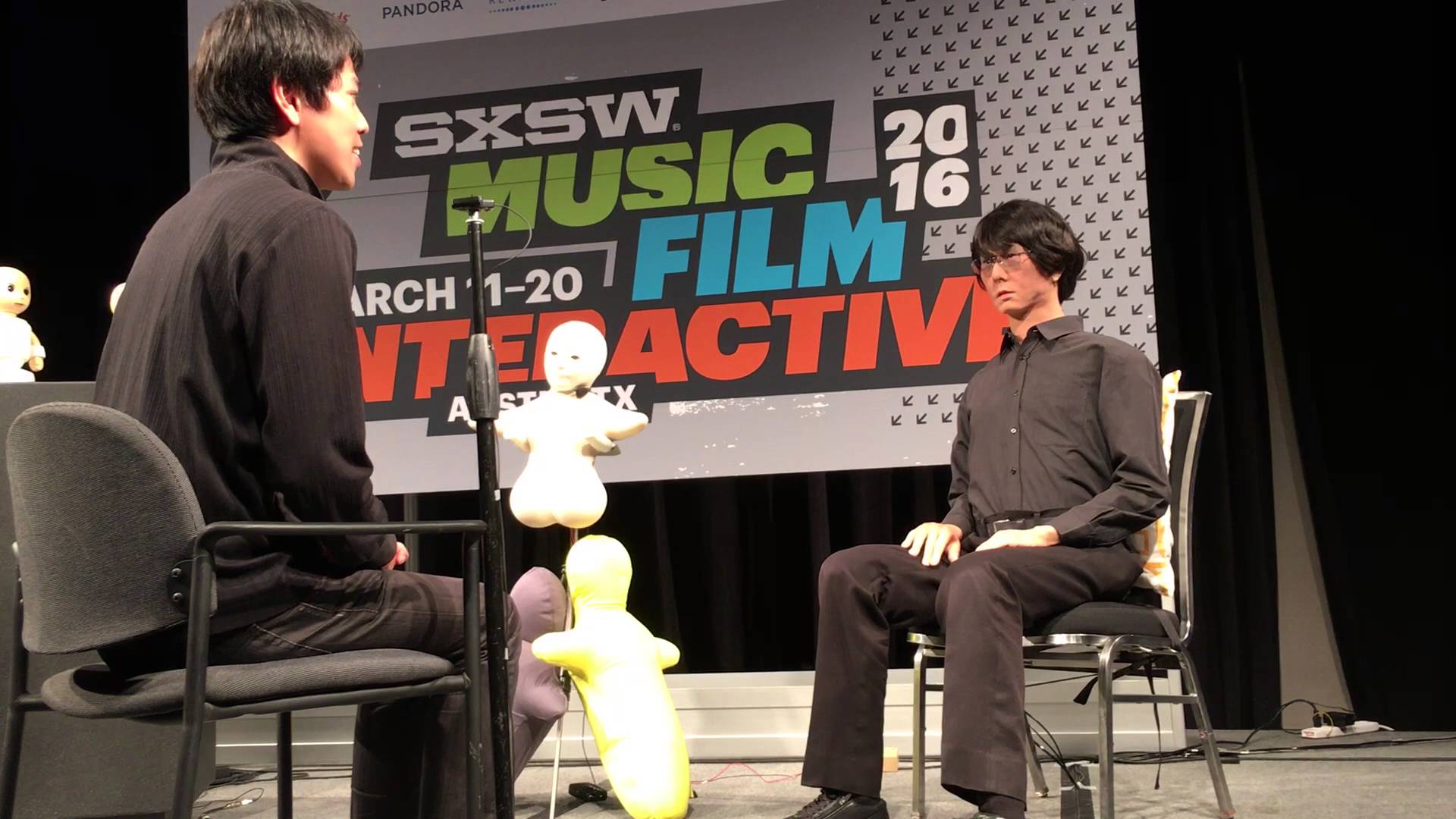
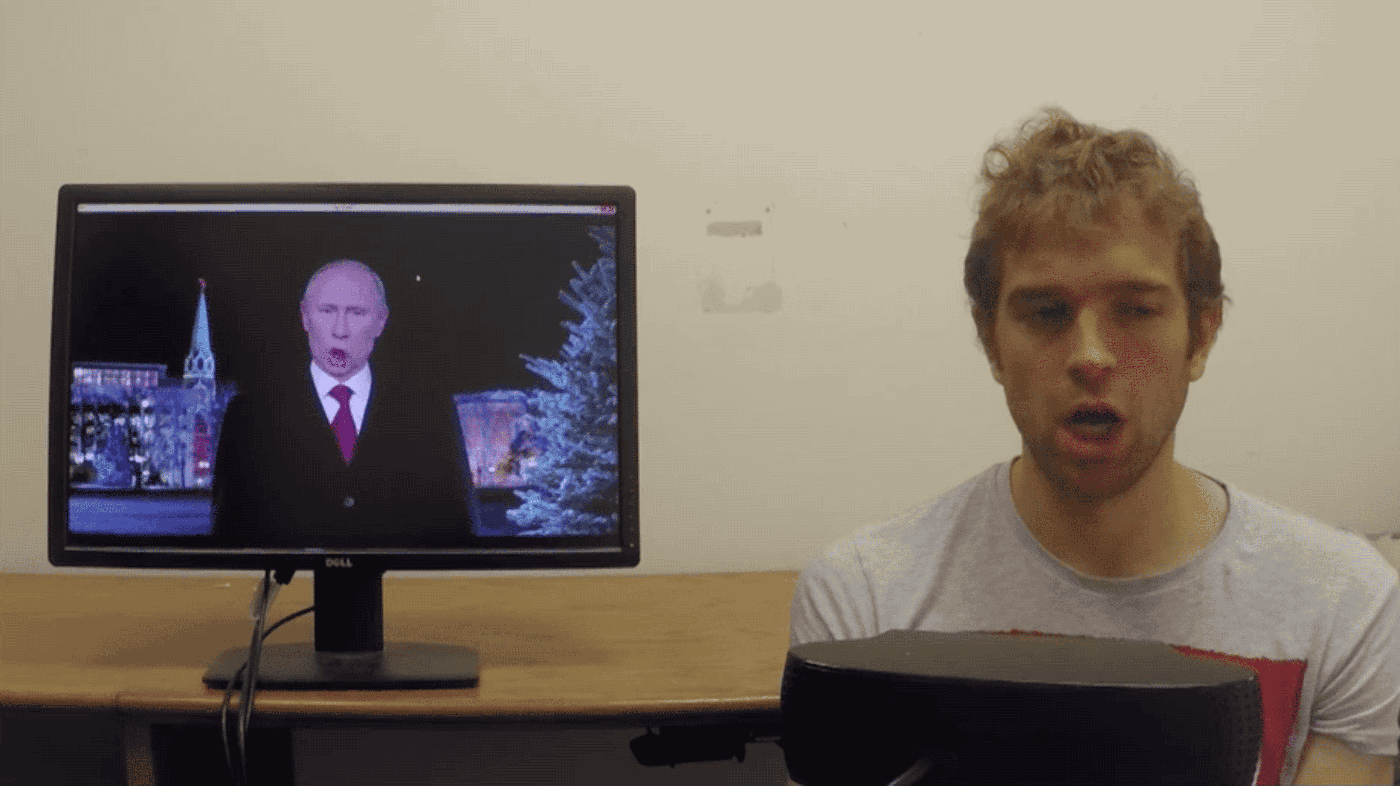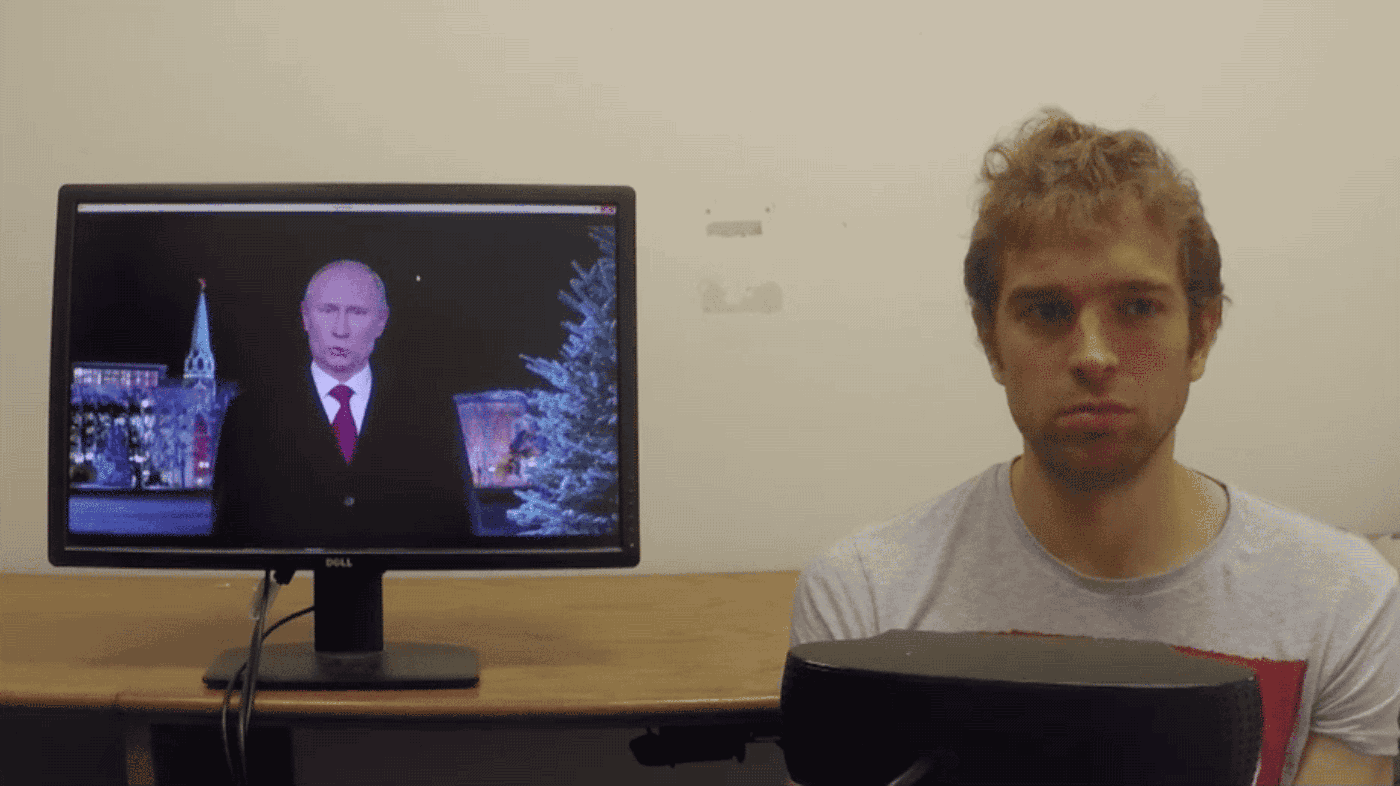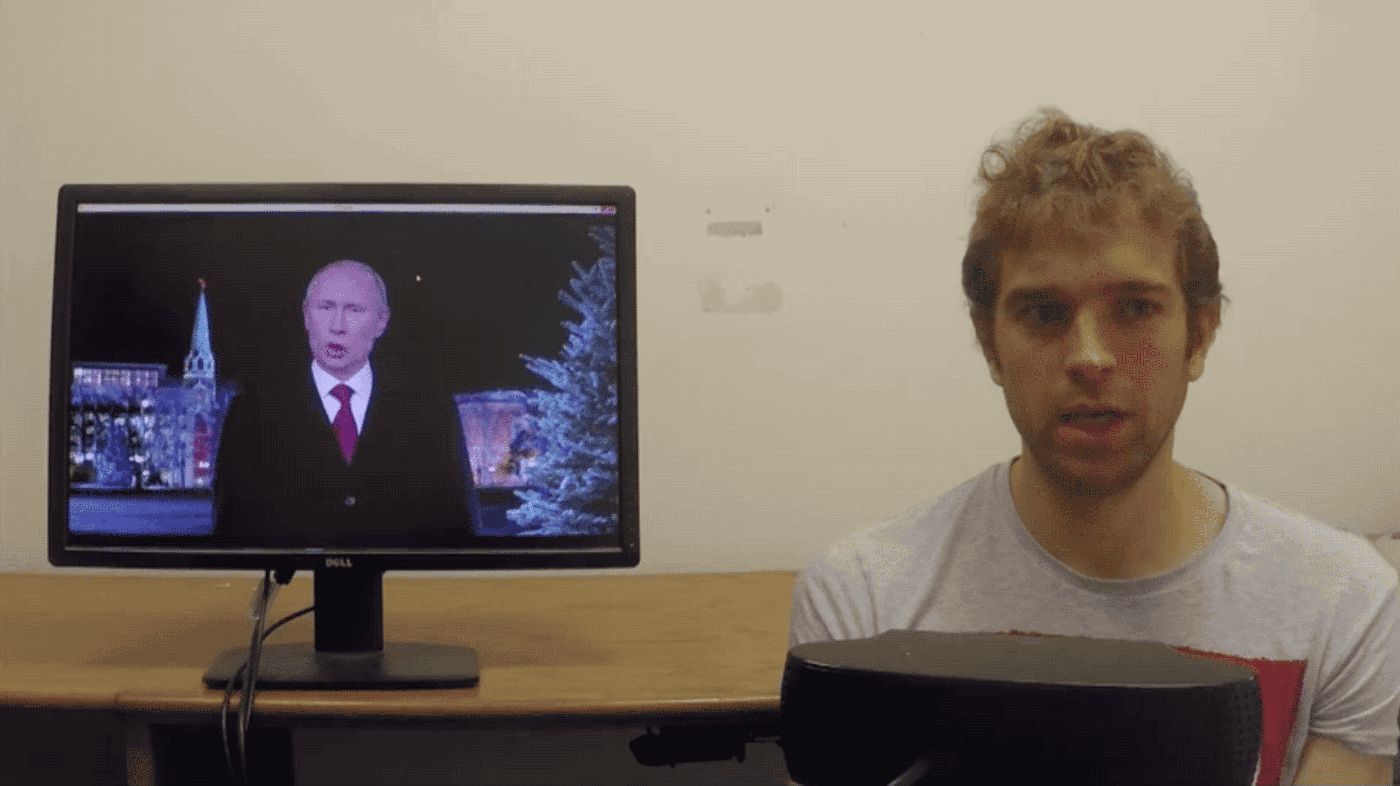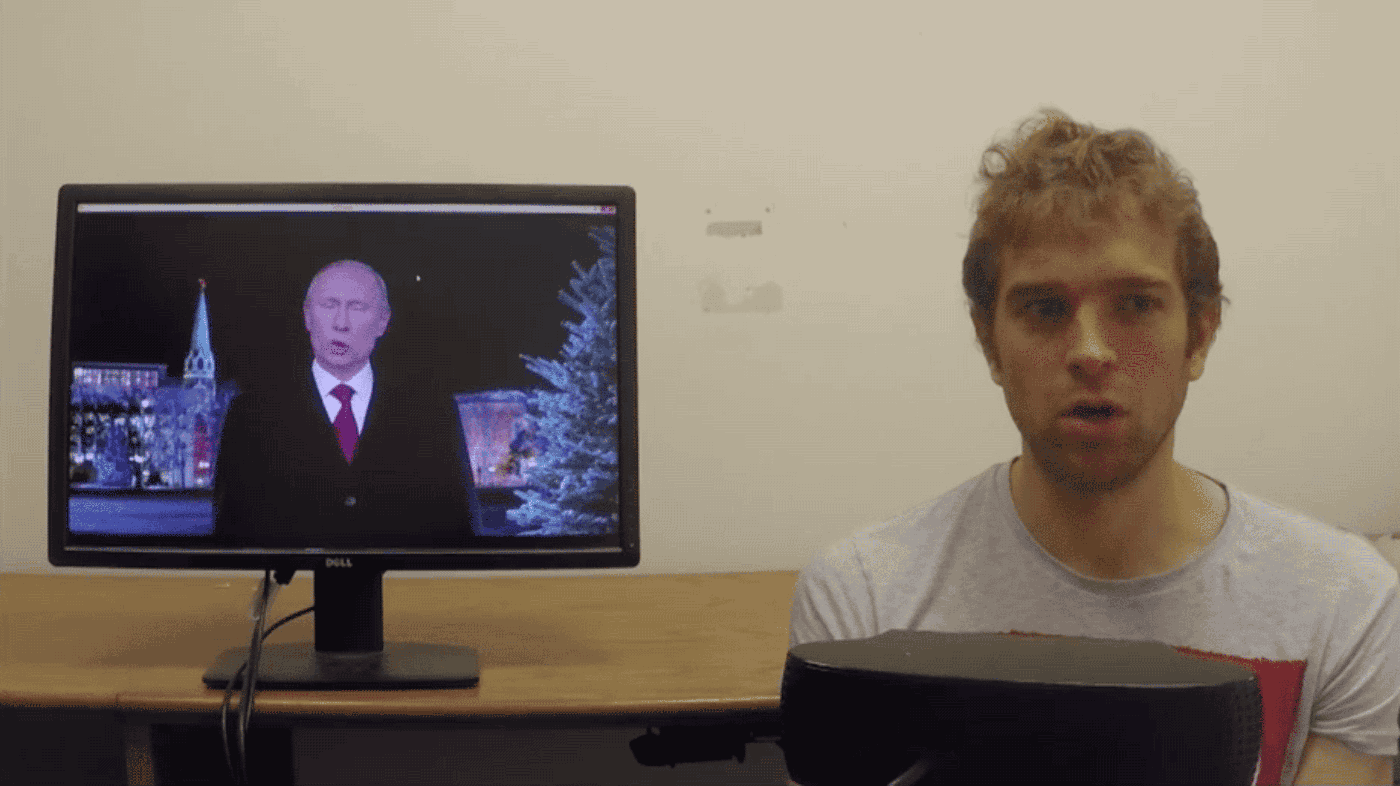
For those unfamiliar, SXSW is a week-long, trendy, if not seriously geeky festival of film and culture, panels and discussions. This year, one of the strangest – and either most disturbing or most compelling, depending on where you stand – talks was delivered by Hiroshi Ishiguro, a Japanese inventor and roboticist. The Osaka University professor was speaking about human-like androids and what roles they might fill within society in the near future. Ishiguro discussed his greatest and most marvellous creation to date: a “Geminoid” (robot in his own likeness) whose human appearance has been deftly created through with a plastic skull, a metal skeleton and silicon skin – and is controlled by an external computer. It would be hard, at a glance, to tell the two apart. In fact, the Geminoid held an autonomous conversation in Japanese, on stage, in front of an audience of hundreds.
Geminoid is not Ishiguro’s first uncannily human robot. In 2005, he developed a female android named Repliee Q1Expo, telling the BBC, “I have developed many robots before, but I soon realised the importance of its appearance. A human-like appearance gives a robot a strong feeling of presence. Repliee Q1Expo can interact with people. It can respond to people touching it. It’s very satisfying.”
At SXSW on Sunday, Ishiguro discussed how he imagined these human-looking robots might become a part of the everyday sooner than we think; as receptionists, language tutors and museum-guides. In fact, he discussed how he and his team have tried and tested the robots in everyday situations. “Japanese males hate to talk to the shopkeeper because it signals they want to buy something,” he explained. “But they don’t hesitate to talk to the android.” He then jokingly added that it helps that “[a] robot never tells a lie, and that is why the android can sell lots of clothes.” Which begs a couple of questions including why do Japanese males have problems interacting with shopkeepers, and what happens to the shopkeeper in this scenario?