https://youtube.com/watch?v=96vtlLnSHG0
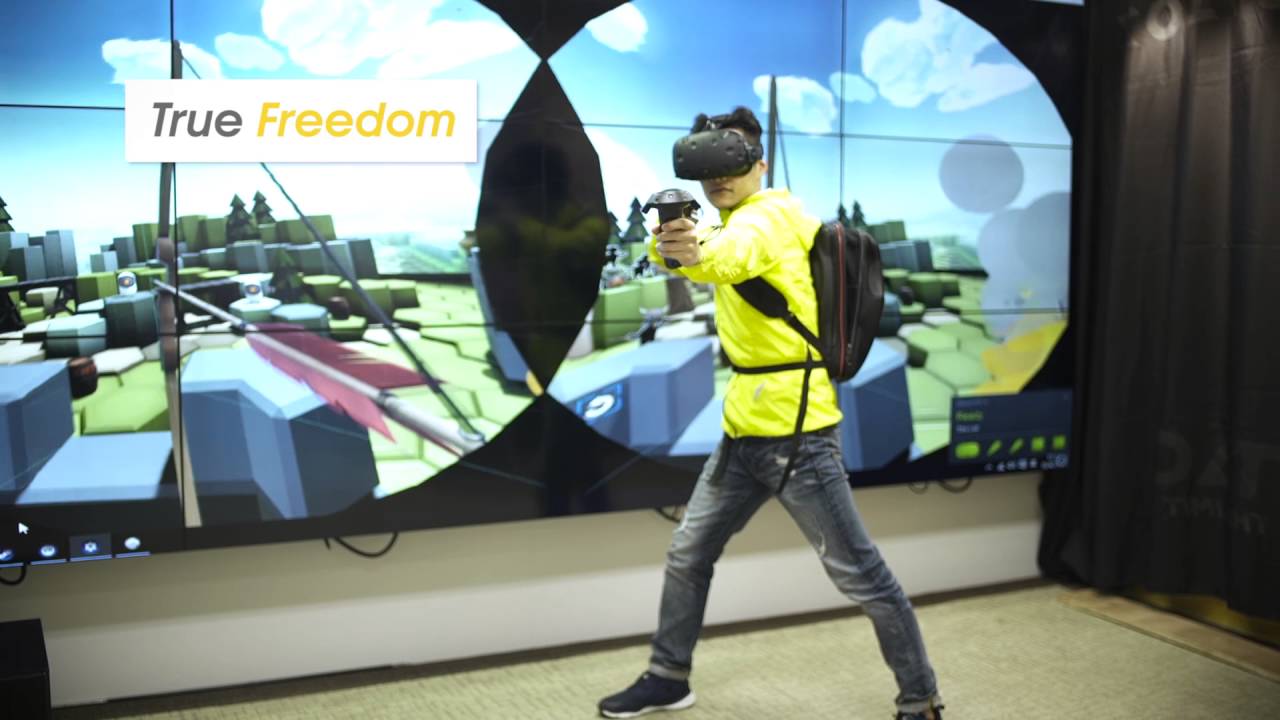
Zotac specializes in making small computers, like their Magnus EN980, which packs a lot of powerful hardware into a tiny space. The company has used their proficiency with making compact hardware and applied it to this virtual reality backpack; it’s wireless and battery-powered, so you can explore an open space without having to worry about tripping on any wires.
The promotional video cites the possibility of tripping on wires as the main reason why you’d want one of these, but that justification might not be enough to sell you on it. Wireless VR headsets don’t exist yet, but they will soon. Optoma has been working on a cloud-based wireless VR headset; the reason that other companies haven’t done that yet is because of concerns about lag or reduction in picture quality. Optoma claims their headset doesn’t have these issues, and if that’s true, they could end up competing handily with Sony and Oculus, both of which require the user to remain plugged in at all times. Optoma’s headset won’t launch for another year, so until then, hardware developers have had to come up with some other ways to go wireless with VR.
Zotac’s backpack seems like one possible solution, and it certainly increases the user’s ability to take VR with them on the go. You could take this thing out to an electricity-free cabin in the middle of nowhere, so long as the battery’s charged up. (Also, most people probably go to remote cabins for reasons other than trying out a cool VR headset, but … shhh.)