There won’t be a single “winner” in the field.


Get ready for the next generation of wifi technology: Wi-fi 6 (for so it is named) is going to be appearing on devices from next year. But will you have to throw out your old router and get a new one? And is this going to make your Netflix run faster? Here’s everything you need to know about the new standard.
A brief history of wifi
Those of you of a certain age will remember when home internet access was very much wired—only one computer could get online, a single MP3 took half an hour to download, and you couldn’t use the landline phone at the same time.

In this video, we’ll be discussing the evolution of computing – more specifically, the evolution of the technologies that have brought upon the modern computing era.
[0:30–5:33] — Starting off we’ll look at, the origins of computing from as far back as 3000 BC with the abacus and progressing to discuss some of the first mechanical computers. After this, we’ll get to see the first signs of modern computing emerge, through the use of electromechanical relays in computers along with punched cards for data I/O.
[5:33–8:36] — Following that we’ll discuss, the 1st generation of modern computing, the vacuum tube era. The first technology that was fully digital and resembled how modern computers operate.
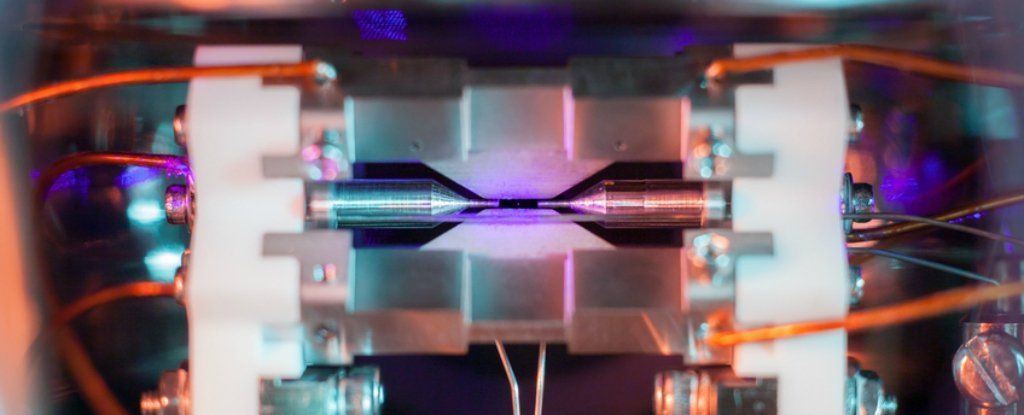
Humanity is producing so much data every single minute that we either need to slow down, or scientists need to crack the problem of finding better ways of storing that data ASAP. Now, new research has taken us one step closer to the ultimate in compact data storage: putting data on a single atom.
As the basic building blocks of all matter, atoms are the smallest object we could possibly store a bit (a 1 or a 0) on, potentially shrinking down the size of existing hard drives by about a thousand times or so, if we can figure out how to get it to work.
Scientists have already made progress in storing bits on atoms, but only on a small scale and in tightly controlled lab conditions, which usually means extremely cold setups.
The display screens of modern televisions, cell phones and computer monitors rely on liquid crystals—materials that flow like liquids but have molecules oriented in crystal-like structures. However, liquid crystals may have played a far more ancient role: helping to assemble Earth’s first biomolecules. Researchers reporting in ACS Nano have found that short RNA molecules can form liquid crystals that encourage growth into longer chains.
Scientists have speculated that life on Earth originated in an “RNA world,” where RNA fulfilled the dual role of carrying genetic information and conducting metabolism before the dawn of DNA or proteins. Indeed, researchers have discovered catalytic RNA strands, or “ribozymes,” in modern genomes. Known ribozymes are about 16–150 nucleotides in length, so how did these sequences assemble in a primordial world without existing ribozymes or proteins? Tommaso Bellini and colleagues wondered if liquid crystals could help guide short RNA precursors to form longer strands.
To find out, the researchers explored different scenarios under which short RNAs could self-assemble. They found that at high concentrations, short RNA sequences (either 6 or 12 nucleotides long) spontaneously ordered into liquid crystal phases. Liquid crystals formed even more readily when the researchers added magnesium ions, which stabilized the crystals, or polyethylene glycol, which sequestered RNA into highly concentrated microdomains. Once the RNAs were held together in liquid crystals, a chemical activator could efficiently join their ends into much longer strands. This arrangement also helped avoid the formation of circular RNAs that could not be lengthened further. The researchers point out that polyethylene glycol and the chemical activator would not be found under primordial conditions, but they say that other molecular species could have played similar, if less efficient, roles.

LOS ANGELES (PRWEB) September 27, 2018
The Arch Mission Foundation today announced the creation of an archive of knowledge encoded into synthetic DNA by Microsoft, Twist Bioscience Corporation, and the University of Washington to be included in the Lunar Library™. The DNA Archive will feature 10,000 crowdsourced images and the full text of 20 important books, among other items. The data is encoded into billions of synthetic DNA molecules and encapsulated for long-term preservation. Collectively this data will represent the first Special Collection of the Lunar Library, which the Arch Mission Foundation announced last spring.
The Arch Mission Foundation sought partners that could help curate these materials and assist in achieving a remarkable collection that reflects both the best of human knowledge, as well as the most ambitious technical abilities in the emerging new field of molecular data storage. Molecular data storage is a new technology for storing and retrieving data from molecules of synthetic, non-living DNA.

During last September’s Ignite conference, Microsoft heavily emphasized its quantum computing efforts and launched both its Q# programming language and development kits.
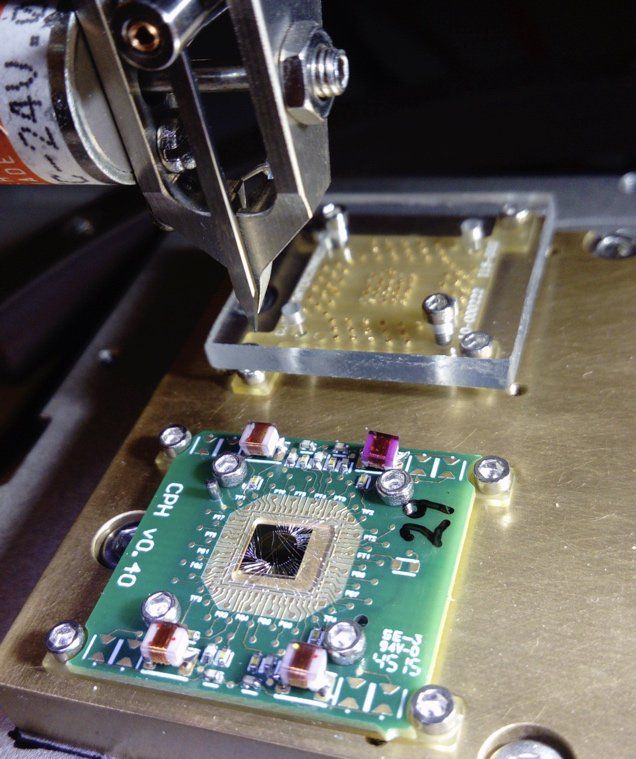
This year, the focus is on other things, and the announcements about quantum are few and far between (and our understanding is that Microsoft, unlike some of its competitors, doesn’t have a working quantum computing prototype yet). It did, however, announce an addition to its Quantum Development Kit that brings a new chemical simulation library to tools for getting started with quantum computing.
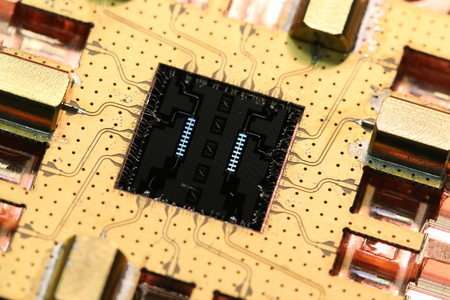
Conventional computers store information in a bit, a fundamental unit of logic that can take a value of 0 or 1. Quantum computers rely on quantum bits, also known as a “qubits,” as their fundamental building blocks. Bits in traditional computers encode a single value, either a 0 or a 1. The state of a qubit, by contrast, can simultaneously have a value of both 0 and 1. This peculiar property, a consequence of the fundamental laws of quantum physics, results in the dramatic complexity in quantum systems.
Quantum computing is a nascent and rapidly developing field that promises to use this complexity to solve problems that are difficult to tackle with conventional computers. A key challenge for quantum computing, however, is that it requires making large numbers of qubits work together—which is difficult to accomplish while avoiding interactions with the outside environment that would rob the qubits of their quantum properties.
New research from the lab of Oskar Painter, John G Braun Professor of Applied Physics and Physics in the Division of Engineering and Applied Science, explores the use of superconducting metamaterials to overcome this challenge.

Physicists face the same hard problem as neuroscientists do: the problem of bridging objective description and subjective experience. Physics has encountered consciousness. Quantum theory says an object remains in a superposition of possibilities until observed. We can consider a quantum state as being about our knowledge rather than a direct description of physical reality. The physics of information just may be that bridging of quantum-to-digital reality of subjective experience. We are now at the historic juncture when quantum computing could reveal quantum information processing underpinnings of subjectivity. Quantum mechanics is a spectacularly successful theory of fundamental physics that allows us to make probabilistic predictions derived from its mathematical formalism, but the theory doesn’t tell us precisely how these probabilities should be interpreted in regards to phenomenology, i.e. our experiential reality. There are basically three main interpretive camps within quantum mechanics from which stem at least a dozen further interpretations.
By Alex Vikoulov.
“A quantum possibility is more real than a classical possibility, but less real than a classical reality.” –Boris Tsirelson.