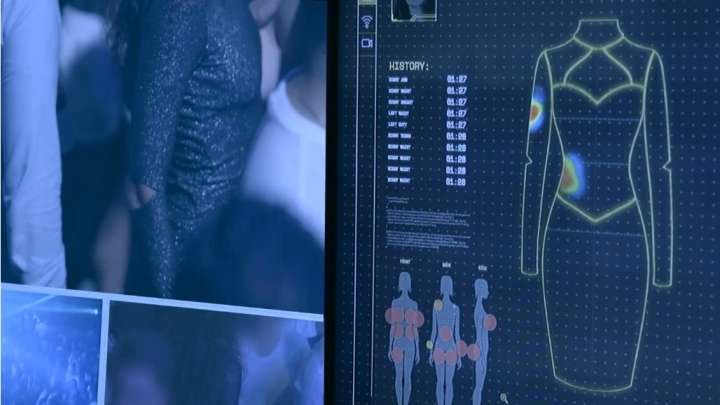
Even after the rise of #MeToo, disbelief is all too commonly the outcome of reporting sexual harassment and assault. Many women describe the experience of having men they trust doubt the severity and frequency of what they have to put up with as painful as the experience itself. Advertising agency Ogilvy wondered if men would be more likely to pay attention to smart clothing than the women in their lives, so they created dresses that keep a record of events.
The dresses have sensors sewn into them that record contact and pressure. Any impact on a sensor is sent via wifi to a computer that not only keeps track of what is happening but translates it into a heat map of location and time of contact with the body.
When three women wore the dresses to a Brazilian party, they were touched non-consensually 157 times in less than four hours – a rate of more than once every five minutes per woman. As the video below shows, this is despite repeatedly telling the men involved to stop.