The universe of problems that a computer can check has grown. The researchers’ secret ingredient? Quantum entanglement.


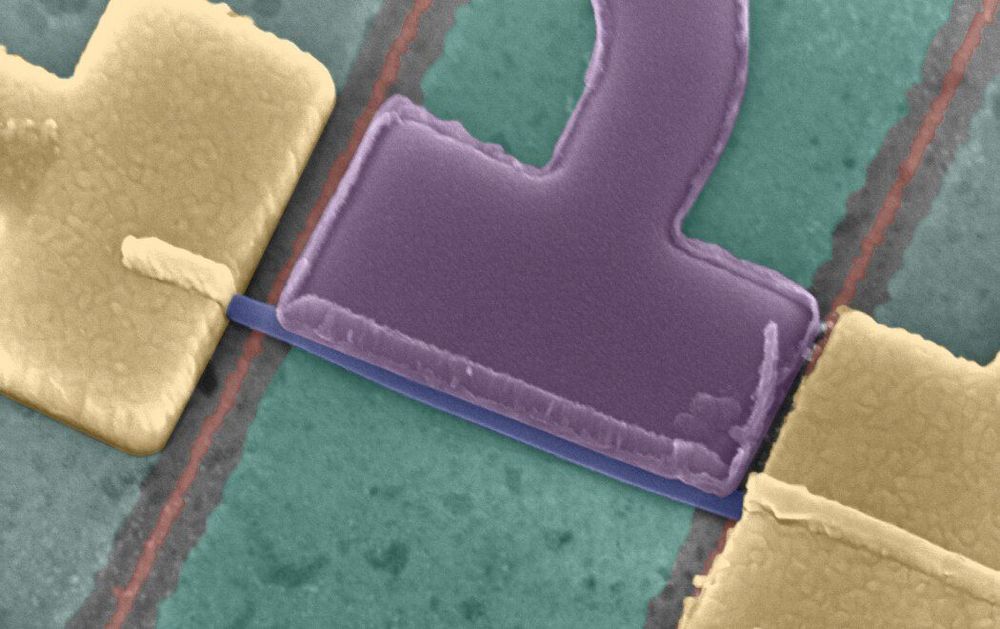
Researchers at Delft University of Technology have recently carried out a study investigating spin-orbit interaction in Majorana nanowires. Their study, published in Physical Review Letters, is the first to clearly show the mechanism that enables the creation of the elusive Majorana particle, which could become the building block of a more stable type of quantum computer.
“Our research is aimed at experimental verification of the theoretically proposed Majorana zero-mode,” Jouri Bommer, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org via email. “This particle, which is its own antiparticle, is of particular interest, because it is predicted to be useful for developing a topological quantum computer.”
Quantum computing is a promising area of computer science that explores the use of quantum-mechanical phenomena and quantum states to store information and solve computational problems. In the future, quantum computers could tackle problems that traditional computing methods are unable to solve, for instance enabling the computational and deterministic design of new drugs and molecules.
A technique to stabilise alkali metal vapour density using gold nanoparticles, so electrons can be accessed for applications including quantum computing, atom cooling and precision measurements, has been patented by scientists at the University of Bath.
Alkali metal vapours, including lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium and caesium, allow scientists to access individual electrons, due to the presence of a single electron in the outer ‘shell’ of alkali metals.
This has great potential for a range of applications, including logic operations, storage and sensing in quantum computing, as well as in ultra-precise time measurements with atomic clocks, or in medical diagnostics including cardiograms and encephalograms.

In the summer of 2018, a team led by MIT researchers reported in the journal Nature that they had successfully embedded electronic devices into fibers that could be used in fabrics or composite products like clothing, airplane wings, or even wound dressings. The advance could allow fabrics or composites to sense their environment, communicate, store and convert energy, and more.
Research breakthroughs typically take years to make it into final products—if they reach that point at all. This particular research, however, is following a dramatically different path.
By the time the unique fiber advance was unveiled last summer, members of Advanced Functional Fabrics of America (AFFOA), a not-for-profit near MIT, had already developed ways to increase the throughput and overall reliability of the process. And, staff at Inman Mills in South Carolina had established a method to weave the advanced fibers using a conventional, industrial manufacturing-scale loom to create fabrics that can use light to both broadcast and receive information.

Physicists at the University of Basel have shown for the first time how a single electron looks in an artificial atom. A newly developed method enables them to show the probability of an electron being present in a space. This allows improved control of electron spins, which could serve as the smallest information unit in a future quantum computer. The experiments were published in Physical Review Letters and the related theory in Physical Review B.
The spin of an electron is a promising candidate for use as the smallest information unit (qubit) of a quantum computer. Controlling and switching this spin or coupling it with other spins is a challenge on which numerous research groups worldwide are working. The stability of a single spin and the entanglement of various spins depends, among other things, on the geometry of the electrons—which previously had been impossible to determine experimentally.
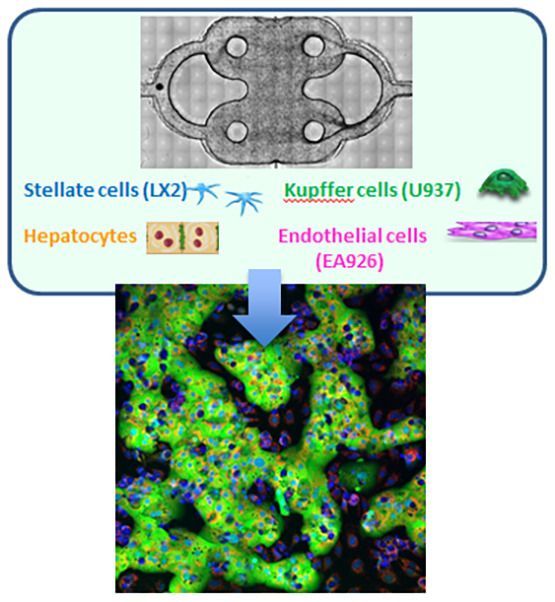
Global Organs-on-chips Market Size, Status and Forecast 2019–2025
The report provides insightful details – how clients enhance their basic leadership capacity within the worldwide Organs-on-chips Market business. Utilizing figures and flowcharts are brief in this report, the specialists represented to the analyzed information in a superior acceptable manner. This report identifies that rapidly changing market trends and competitive landscape with growth significant CAGR during Forecast. Along, with latest marketing factors those are essential to monitor market performance and crucial decisions for progress and profitability.
According to this study, the next Y-o-Y (year over year) Organs-on-chips market will register a XX% CAGR in terms of revenue, the Astonishing Growth market size will reach US$ XX million by 2025, from US$ XX million in 2019. In particular, this report presents the global market share (sales and revenue) of key companies in the Market New Research Study.
The power consumption of data centers around the world is increasing. This creates a high demand for new technologies that could lead to energy-efficient computers. In a new study, physicists at Radboud University have demonstrated that this could also be achieved by using chips whose operation is inspired by that of the human brain. The study was published in the scientific journal Applied Physics Letters on 16 May.
Compared to our current computers, the human brain uses a fraction of the energy to process the same amount of data. This is possible due to the fact that our brains can process data in parallel and store it as well by making connections stronger or weaker.
“We wanted to see if we could implement this property of plasticity in an artificial system and combine it with the rapid and energy-efficient technique to control magnetism using light, which has been applied for some time already,” say Johan Mentink and Theo Rasing, both physicists at Radboud University. “This should eventually lead to energy-efficient and smart computers.”