CSIRO has made a detailed radio survey of the southern hemisphere, and discovered a million new galaxies.
Although radio astronomy has been around since the 1930s, it is only in recent years that astronomers have been able to make high-resolution maps of the radio sky. Sky maps are difficult for radio telescopes because radio antennas need to be focused on an extremely small patch of sky to capture images in high resolution. But with modern antennas and computer processing, we can now scan the sky quickly enough to map the heavens in a reasonable amount of time.
In the northern hemisphere, the most detailed radio sky maps have been done by the Very Large Array (VLA). In the 1990s the VLA made the first full-sky surveys of the northern sky. After its upgrade in the 2000s, the observatory began the VLA Sky Survey (VLASS), which has mapped nearly 10 million radio sources.
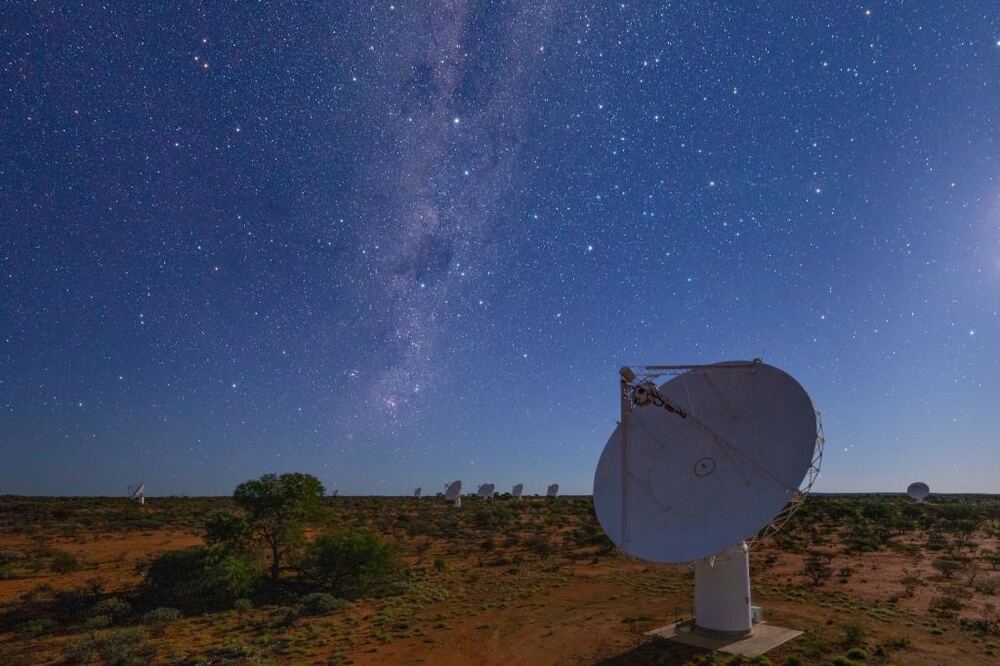
The location of the VLA lets it observe about 80% of the sky, but it cannot see the southern sky very well. For that, you’d need a radio observatory in the southern hemisphere. Fortunately, there is now a powerful radio telescope array in Australia, and it has recently made a detailed radio map.