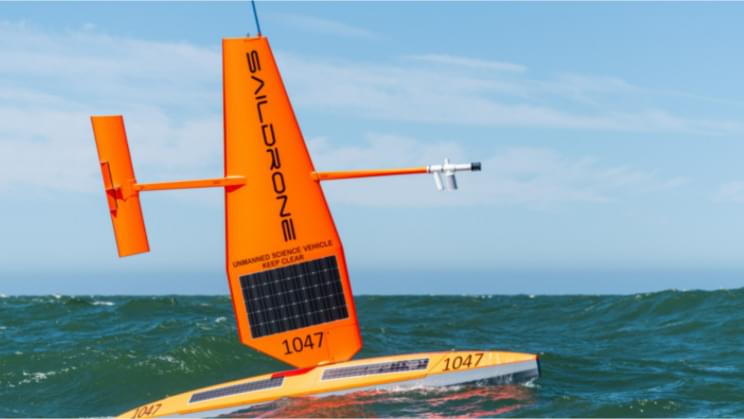
The same Saildrones captured the first-ever video from inside a major hurricane from sea level in September.
Six autonomous Saildrones are taking off on a six-month journey to tackle some of Earth’s most challenging ocean conditions, in order to improve climate change and weather forecast computer models, reported CNN.
They will travel to the Gulf Stream throughout the winter months where they will collect data about the process by which oceans absorb carbon (carbon uptake). So far, the numbers on this type of activity have only been estimates produced by statistical methods that cannot, therefore, be relied upon.
“This Saildrone mission will collect more carbon dioxide measurements in the Gulf Stream region in winter than has ever been collected in this location and time of year,” said Jaime Palter, a scientist at the University of Rhode Island who is co-leading the research.
“With this data, we will sharpen our quantification of ocean carbon uptake and the processes that enable that uptake in this dynamic region.”
This work will be crucial to properly estimate the Global Carbon Budget.
Full Story: