Is free will a phantom of brain chemistry, or are we truly in control of our lives? A question debated by great minds for millenia.




Roche and its Genentech subsidiary have committed up to $12 billion to Recursion in return for using its Recursion Operating System (OS) to advance therapies in 40 programs that include “key areas” of neuroscience and an undisclosed oncology indication.
Recursion OS applies machine learning and high-content screening methods in what the companies said would be a “transformational” model for tech-enabled target and drug discovery.
The integrated, multi-faceted OS is designed to generate, analyze and glean insights from large-scale proprietary biological and chemical datasets—in this case, extensive single-cell perturbation screening data from Roche and Genentech—by integrating wet-lab and dry-lab biology at scale to phenomically capture chemical and genetic alterations in neuroscience-related cell types and select cancer cell lines.
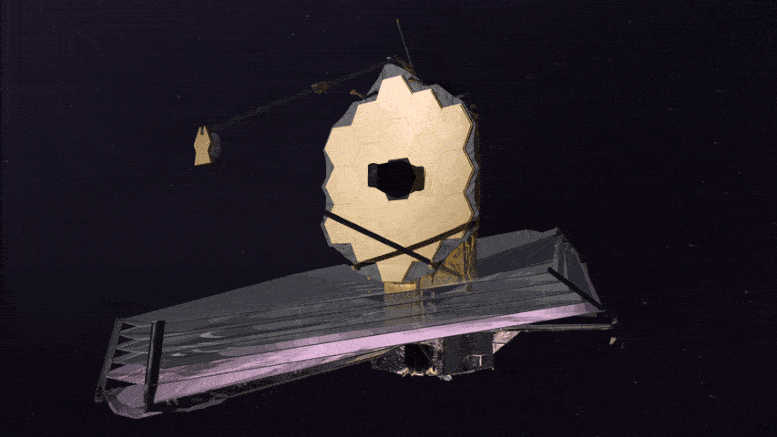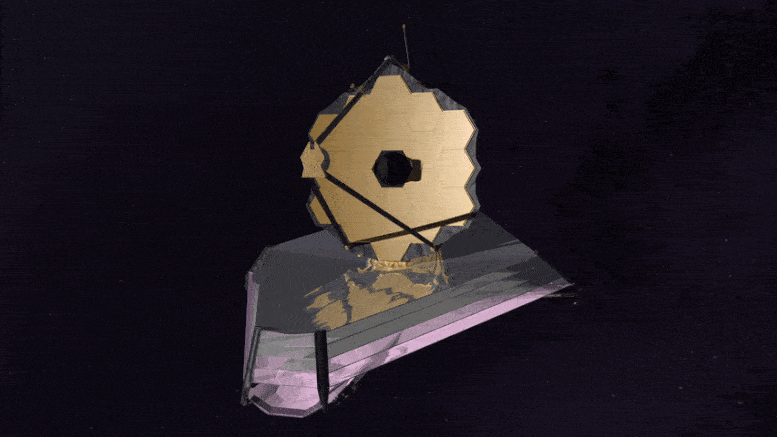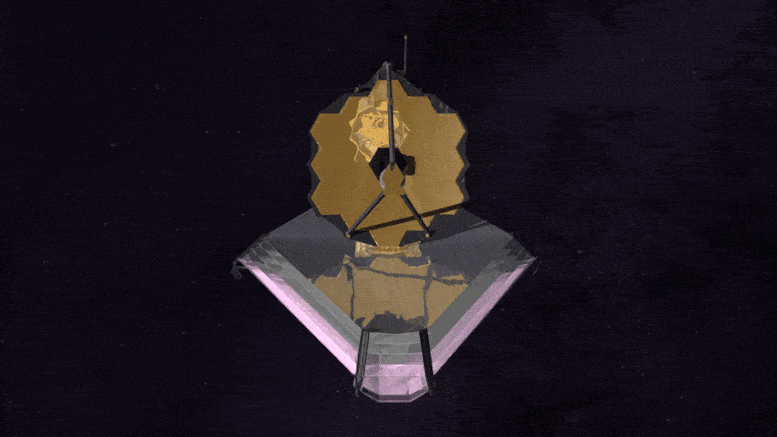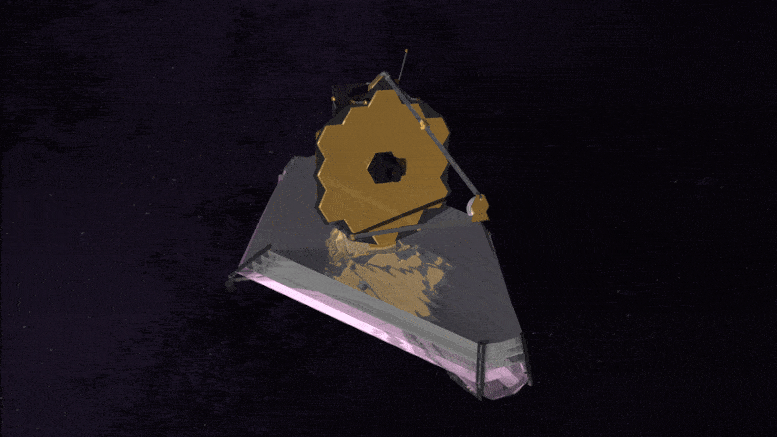
The James Webb Space Telescope is the largest, most powerful, and most technologically challenging space telescope ever built.
The Webb Telescope is so large; it must be folded like origami to fit inside its rocket fairing for the ride into space. Once in space, unfolding and readying Webb for science is a complex process that will take about six months.
Webb is designed to see the most distant galaxies in the Universe and study how galaxies evolved over cosmic time. Webb will study planets orbiting other stars looking for the chemical signatures of the building blocks of life. Webb will also study planets within our own solar system.
Sorry if re-post…
A team of researchers affiliated with a large number of institutions in Japan has developed a vaccine that tricks the immune system into removing senescent cells. In their paper published in the journal Nature Aging, the group describes their vaccine, how it works and how effective it was when given to test mice.
Prior research has shown that part of the aging process is the development of senescent cells —cells that outlive their usefulness but fail to die naturally. Instead, they produce chemicals that can lead to inflammation, aging and a host of other ailments. Prior research has shown that senescence occurs when cells stop dividing. Prior research has also shown that senescent cells can lead to tumor growth in some instances and tumor suppression in others. Senescence also plays a role in tissue repair, and its impacts on the body vary depending on factors such as overall health and age. It is suspected that senescence is related to telomere erosion, and in some cases, environmental factors that lead to cell damage. In this new effort, the researchers have developed a vaccine that creates antibodies that attach to senescent cells, marking them for removal by white blood cells.
The team was able to create the vaccine after identifying a protein made in senescent cells but not in healthy active cells. That allowed them to develop a type of vaccine based on the amino acids in the protein. When injected, the vaccine incites the body to produce antibodies that bind only to senescent cells, and that sets off an immune response that involves sending white blood cells to destroy the senescent cells.
This research can also offer a glimpse at how other forms of thinking might be organized. “It lets us get at this issue of what are the options for a nervous system or behavior,” Weissbourd says. It’s hard to put yourself into the mind of a jellyfish—their life cycle of polyps and spores is utterly alien, their weird array of sensory organs have no analogues to our own. Clytia have specialized balance organs called statocysts; other species of jellyfish have sensors called rhopalia that detect light or chemical changes in the surrounding water.
Researchers have observed some things that could be thought of as akin to our emotional states; for example, Clytia display a unique set of behaviors when spawning, and they perform their feeding action more quickly when they’re hungry. “But they might have a totally different set of nervous system states,” Weissbourd says.
These gene-tweaked jellies are an exciting new platform for research, says Sprecher. Future experiments will improve our understanding of modular nervous systems, not only in jellyfish but in more complex species too. These are ancient creatures, but we know so little about how they see the world, or if it even makes sense to think of them as “seeing” in the way that mammals do. Literally peering inside them could help provide the answers.

Senescent cells refer to those that have stopped dividing but do not die. They damage nearby healthy cells by releasing chemicals that cause inflammation.
The team identified a protein found in senescent cells in humans and mice and created a peptide vaccine based on an amino acid that constitutes the protein.
The vaccine enables the body to create antibodies that attach themselves to senescent cells, which are removed by white blood cells that adhere to the antibodies.

The DeepMind team has made probably the most ambitious attempt yet to deploy AI to calculate electron density, the end result of DFT calculations. “It’s sort of the ideal problem for machine learning: you know the answer, but not the formula you want to apply,” says Aron Cohen, a theoretical chemist who has long worked on DFT and who is now at DeepMind.
A team led by scientists at the London-based artificial-intelligence company DeepMind has developed a machine-learning model that suggests a molecule’s characteristics by predicting the distribution of electrons within it. The approach, described in the 10 December issue of Science1, can calculate the properties of some molecules more accurately than existing techniques.
“To make it as accurate as they have done is a feat,” says Anatole von Lilienfeld, a materials scientist at the University of Vienna.
The paper is “a solid piece of work”, says Katarzyna Pernal, a computational chemist at Lodz University of Technology in Poland. But she adds that the machine-learning model has a long way to go before it can be useful for computational chemists.

Atom ’s electrons are arranged in energy shells. Like concertgoers in an arena, each electron occupies a single chair and cannot drop to a lower tier if all its chairs are occupied. This fundamental property of atomic physics is known as the Pauli exclusion principle, and it explains the shell structure of atoms, the diversity of the periodic table of elements, and the stability of the material universe.
Now, MIT
MIT is an acronym for the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It is a prestigious private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts that was founded in 1861. It is organized into five Schools: architecture and planning; engineering; humanities, arts, and social sciences; management; and science. MIT’s impact includes many scientific breakthroughs and technological advances.
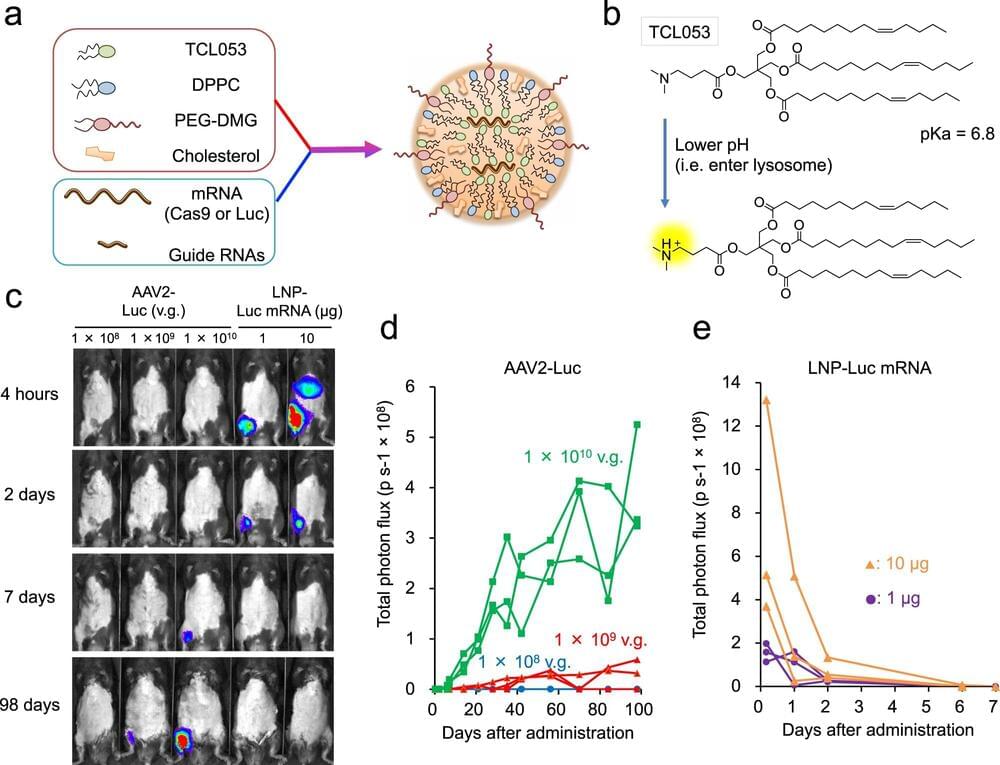
Many intractable diseases are the result of a genetic mutation. Genome editing technology promises to correct the mutation and thus new treatments for patients. However, getting the technology to the cells that need the correction remains a major challenge. A new study led by CiRA Junior Associate Professor Akitsu Hotta and in collaboration with Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited as part of the T-CiRA Joint Research Program reports how lipid nanoparticles provide an effective means for the delivery to treat Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in mice.
Last year’s Nobel Prize for Chemistry to the discoverers of CRISPR-Cas9 cemented the impact of genome editing technology. While CRISPR-Cas9 can be applied to agriculture and livestock for more nutritious food and robust crops, most media attention is on its medical potential. DMD is just one of the many diseases that researchers foresee a treatment using CRISPR-Cas9.
“Oligonucleotide drugs are now available for DMD, but their effects are transient, so the patient has to undergo weekly treatments. On the other hand, CRISPR-Cas9 effects are long lasting,” said Hotta.