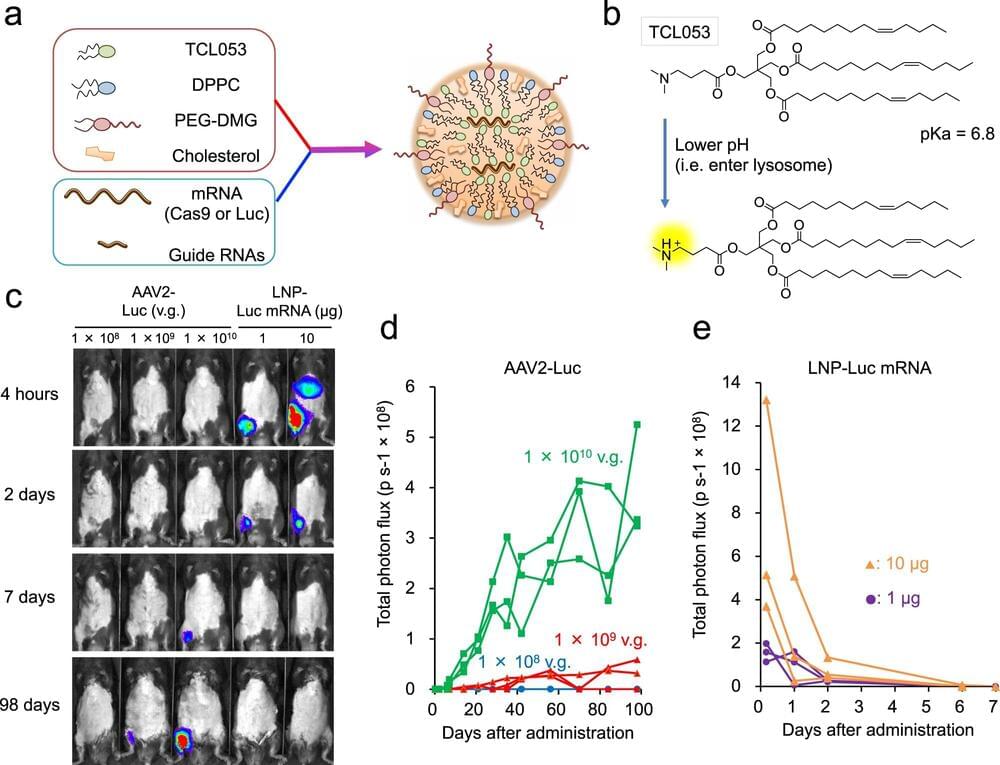
Many intractable diseases are the result of a genetic mutation. Genome editing technology promises to correct the mutation and thus new treatments for patients. However, getting the technology to the cells that need the correction remains a major challenge. A new study led by CiRA Junior Associate Professor Akitsu Hotta and in collaboration with Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited as part of the T-CiRA Joint Research Program reports how lipid nanoparticles provide an effective means for the delivery to treat Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in mice.
Last year’s Nobel Prize for Chemistry to the discoverers of CRISPR-Cas9 cemented the impact of genome editing technology. While CRISPR-Cas9 can be applied to agriculture and livestock for more nutritious food and robust crops, most media attention is on its medical potential. DMD is just one of the many diseases that researchers foresee a treatment using CRISPR-Cas9.
“Oligonucleotide drugs are now available for DMD, but their effects are transient, so the patient has to undergo weekly treatments. On the other hand, CRISPR-Cas9 effects are long lasting,” said Hotta.