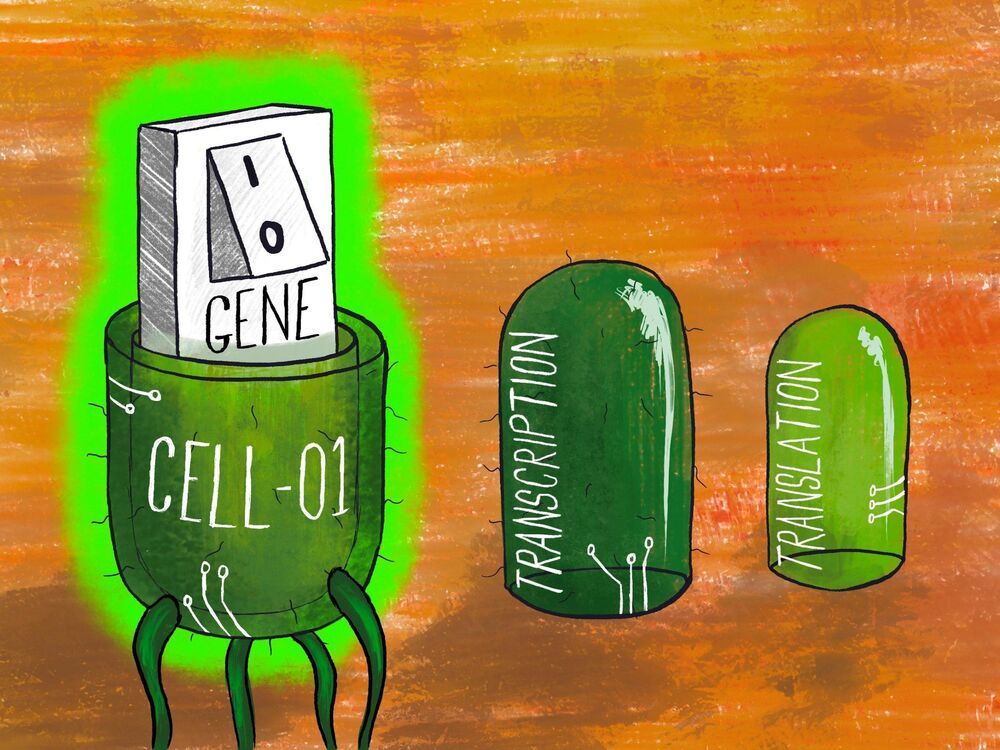
In a recent study led by the University of Bristol, scientists have shown how to simultaneously harness multiple forms of regulation in living cells to strictly control gene expression and open new avenues for improved biotechnologies.
Engineered microbes are increasingly being used to enable the sustainable and clean production of chemicals, medicines and much more. To make this possible, bioengineers must control when specific sets of genes are turned on and off to allow for careful regulation of the biochemical processes involved.
Their findings are reported in the journal Nature Communications.