Is Bitcoin money? To its users the answer is probably yes, but to many people the answer is less clear. Alan Greenspan, for example, said in December 2013: “I do not understand where the backing of Bitcoin is coming from. There is no fundamental issue of capabilities of repaying it in anything which is universally acceptable, which is either intrinsic value of the currency or the credit or trust of the individual who is issuing the money, whether it’s a government or an individual.” Indeed, one of the things holding back the adoption of cybercurrencies such as Bitcoin is that they do not fit well with traditional ideas about money.
Answers to the question “what is money” have typically fallen into one of three camps. The first, known as metallism or bullionism, holds that money needs to be backed by precious metal. The second camp is chartalism (from the Latin charta for a record) which holds that coins and other money objects are just tokens, that the state agrees to accept as payment of things like taxes. Finally, there is the dominant, hands-off school of thought, which most mainstream economists would agree with, which says that money has no unique or special qualities, but instead is defined by its roles, e.g. a medium of exchange.
Bullionists and chartalists therefore emphasise a different aspect of money – the inherent value or the authorising stamp – while most economists treat it as an inert chip. But none of them seem to apply well to emerging cybercurrencies, which are not backed by precious metal or the state, and (at least at first) are not much use as a medium of exchange. So how do they become money? The answer to this question is that money has quantum properties which allow it to be booted up from the ether.
Quantum money
To see why money has quantum properties, consider for example a U.S. dollar bill. On the one hand, it is a physical object which can be owned, traded, and valued. On the other hand, it represents “1”, which is why it is emblazoned (in fifteen places) with that number. And numbers and things are as different as waves and particles. Numbers live in the abstract, virtual world of mathematics, while things live in the real world – and it is the tension between its two sides which give money its powerful but often paradoxical nature. Numbers are exact, while qualities such as perceived value depend on the person and the context. Numbers can grow without limits, while natural processes tend to be bounded. Numbers are universal, while objects can be owned, or become scarce. Numbers are hard and fixed, like the particle aspect of matter. Concepts or judgments such as worth or value are fuzzy, like the wave aspect of matter.
The trade of money objects for goods or labor in a market means that those things attain a numerical value as well, namely the price, by contagion, just as the atoms in iron spontaneously align in a magnetic field. Market prices are therefore an emergent property of the system, in the sense that they emerge from the use of money objects.
Money objects are unique in that their value is designed to be objectively fixed and stable. For other goods, their values are indeterminate until the moment they are exchanged for money (just as, according to quantum mechanics, the position or momentum of a particle is fundamentally undetermined until it is measured, at which point it “chooses” a value). This special status makes money objects desirable in themselves. It is often said that money is just a medium of exchange so need have no value itself; but by attaching numbers to money objects, in a kind of alchemy, we make them valuable.
The word “quantum” has been applied to all kinds of thing outside physics and is often misused to evoke a vague sense of spooky, non-mechanistic behavior. However the use of the term, and more generally the comparison with non-Newtonian physics, is constructive here for the following reasons:
- Money is seen as a fundamental quantity (from the Latin quantum).
- Money objects contain a fixed amount of monetary value, in the same way that an electron contains a fixed amount of charge.
- Money objects bind the virtual to the real, and abstract number to the fuzzy idea of value, in a way similar to the particle/wave duality in quantum physics.
- Just as the properties of a substance such as water emerge from the quantum interactions of molecules, so prices emerge from the use of money objects.
- Money serves as a means to quantify value, in the sense of reducing it to a mathematical quantity – but as in quantum measurement, the process is approximate.
(Finally, economics is often accused of physics envy – so why not go all the way!) By attaching numbers to our idea of value, in order to quantify it, the money system binds together two very different things, and it this fusion which gives rise to its complex behavior.
Emerging markets
Implicit to traditional theories is the idea that money has to be backed by some pre-existing quantity, be it real (e.g. metal) or virtual (e.g. the law of the state). It therefore inherits its value from outside. But from a quantum perspective, rather than money being backed by something of monetary value, it is the other way round – market value comes from the use of money. This has implications for the way we interpret phenomena such as cybercurrencies, and in particular helps to explain their ability to boot themselves up from nothing more than a set of rules and an internet connection.
As mentioned above, money objects are desirable in themselves – so the more something looks like money, the more valuable its numbers become, in a self-reinforcing dynamic. And just as market prices emerge from the use of money objects, so the money system expands with its markets. A cybercurrency is supported not by metal or the state, but by something much more distributed and amorphous – its network of users. A property of networks is that their power expands rapidly with size. The value of a cybercurrency therefore grows in the same way with the size of the network of users, so can initially be near-zero. It is therefore not necessary to begin with an external debt or a source of value, because the two can expand together. Numbers which were just numbers, can suddenly become worth a great deal.
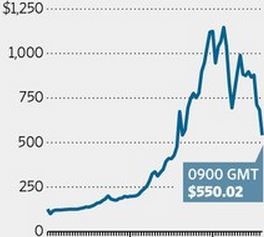
When Satoshi Nakomoto mined the first bitcoins in January 2009, he (if it is a he) had to give them away to get people interested. They had numbers, but no value. In October of that year, users set up a web site quoting a price which corresponded to the cost of electricity required to mint a coin (about 0.0008 dollars per bitcoin). Once a price was available, people began to trade, but it remained a game – until May 2010 when a software engineer managed to buy two pizzas for 10,000 BTC, by posting a request on the Bitcoin forum. Someone accepted the bitcoins and ordered the pizzas using a credit card. Bitcoin was becoming money, and it never looked back.
One reason cybercurrencies have met with resistance, from economists such as Alan Greenspan but also the general public, is because they do not conform to our traditional ideas about money and value. When the first bitcoins were mined, they had neither inherent value, nor the power of an authority. Instead the two aspects – the real and the virtual – grew together, reinforcing each other as the number of users expanded. The problem is therefore not with cybercurrencies, but with theories of money which were shaped by previous monetary eras of gold standard or state fiat currencies.
Adapted from the full paper available at SSRN.

 Over the long term, national currency is likely to be debased by debt, social welfare, war, political ambition, and a desire to redistribute fruits of labor, typically to assuage political ambitions. A built in mechanism of inflation forces a hidden tax and enables legislators to spend beyond the consent of their constituents.
Over the long term, national currency is likely to be debased by debt, social welfare, war, political ambition, and a desire to redistribute fruits of labor, typically to assuage political ambitions. A built in mechanism of inflation forces a hidden tax and enables legislators to spend beyond the consent of their constituents.