Interesting.
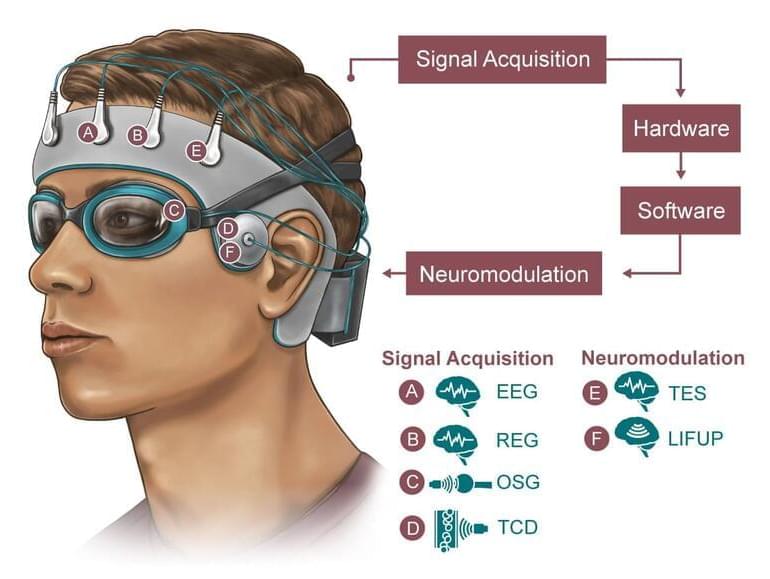
Everybody knows sleep is important, but there’s still a lot we don’t understand about what it actually does to the brain – and how its benefits could be boosted. To investigate, the US Army has awarded researchers at Rice University and other institutions a grant to develop a portable skullcap that can monitor and adjust the flow of fluid through the brain during sleep.
Most of us are familiar with the brain fog that comes with not getting enough sleep, but the exact processes going on in there remain mysterious. In 2012 scientists made a huge breakthrough in the field by discovering the glymphatic system, which cleans out toxic waste products from the brain during deep sleep by flushing it with cerebrospinal fluid. Disruptions to sleep – and therefore the glymphatic system – have been increasingly associated with neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s.
Studying the glymphatic system could provide new insights into sleep disorders and how to treat them, but currently it requires big bulky MRI machines. So the US Army is funding researchers at Rice University, Houston Methodist and Baylor College of Medicine to develop a wearable skullcap.


 .
.