Nature waded through the literature on the coronavirus — and summarized key papers as they appeared.

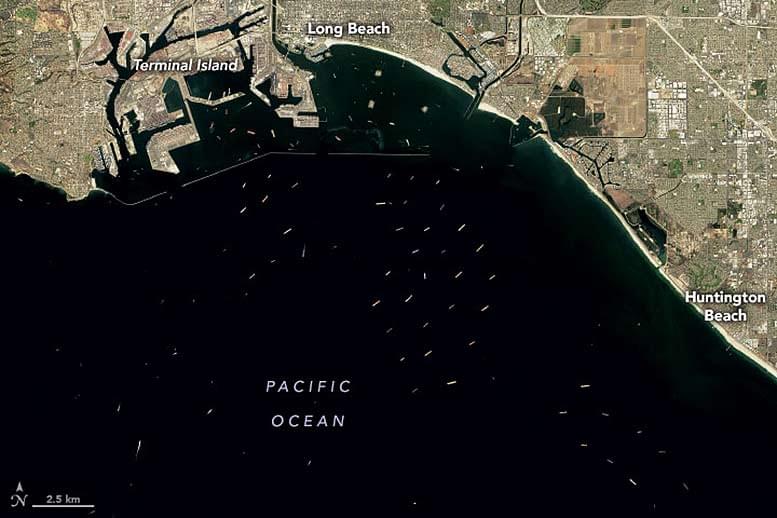
The pandemic has disrupted global supply chains and markets in ways that have led to backlogs of cargo ships at key ports.
Booming demand for consumer and goods, labor shortages, bad weather, and an array of COVID-related supply chain snarls are contributing to backlogs of cargo ships at ports around the world.
Among those seaports are the Port of Los Angeles and Port of Long Beach in Southern California, the two busiest container ports in the United States. On October 10 2021, the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 captured this natural-color image of dozens of cargo ships waiting offshore for their turn to unload goods. On the same day, the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA.
By contrast, Lewis’s studies suggest it is extremely difficult for B. burgdorferi to evolve resistance to hygromycin. The chemical resembles essential nutrients that spirochaetes cannot make themselves and take up using a specific transporter, so mutations that block the take-up of hygromycin would also deprive spirochaetes of these nutrients.
Lewis says his team isn’t the first to discover the value of hygromycin. It was studied as a potential treatment for a pig disease in the 1980s but abandoned.
Vaccines against Lyme disease are also being developed, but eradicating the disease would be an even better option.

“If we had a delta type of Nipah virus, we would suddenly have a highly transmissible virus with a 50 per cent mortality rate,” Dame Sarah Gilbert said during an event at the Cheltenham Festival of Literature in the United Kingdom on Thursday.
So, what is the Nipah virus and should we be worried?
The Nipah virus is not new and has been lurking for years. In 1,999 the virus arrived in central Malaysia after it found a host in bats, who then stopped over to eat from fruit trees that hung over pig farms.
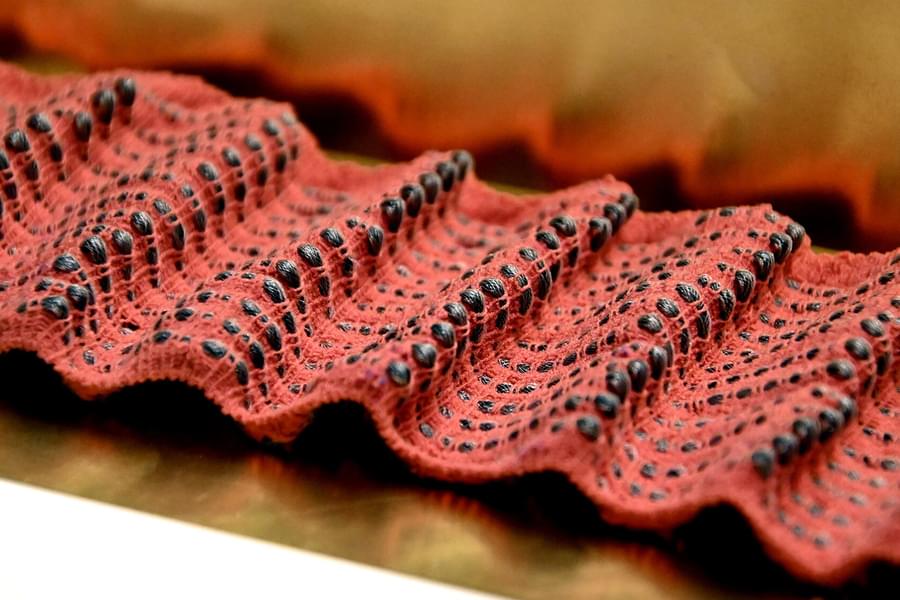
“Robotic” textiles could help performers and athletes train their breathing, and potentially help patients recovering from post-surgery breathing changes.
A new kind of fiber developed by researchers at MIT and in Sweden can be made into clothing that senses how much it is being stretched or compressed, and then provides immediate tactile feedback in the form of pressure, lateral stretch, or vibration. Such fabrics, the team suggests, could be used in garments that help train singers or athletes to better control their breathing, or those help patients recovering from disease or surgery to recover their breathing patterns.
Full Story:
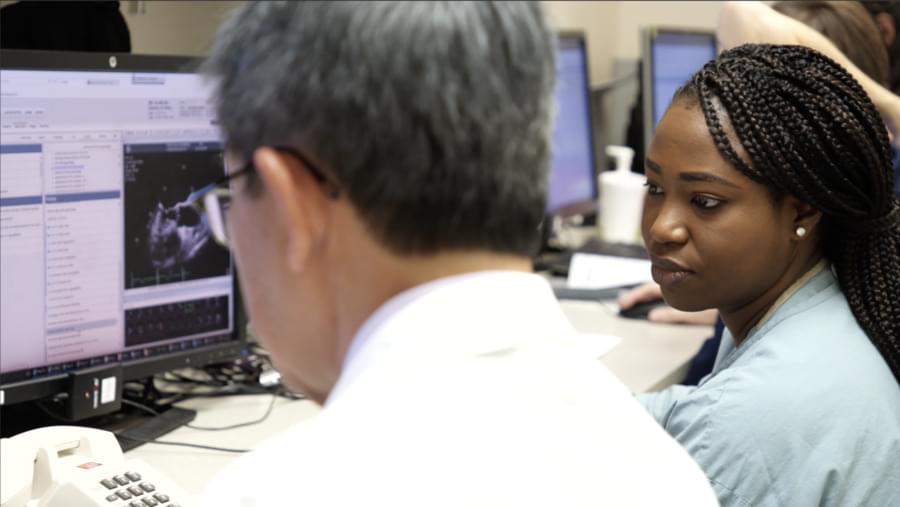

Artificial intelligence is transforming industries around the world — and health care is no exception. A recent Mayo Clinic study found that AI-enhanced electrocardiograms (ECGs) have the potential to save lives by speeding diagnosis and treatment in patients with heart failure who are seen in the emergency room.
A dedicated practitioner, Adedinsewo is a Mayo Clinic Florida Women’s Health Scholar and director of research for the Cardiovascular Disease Fellowship program. Her clinical research interests include cardiovascular disease prevention, women’s heart health, cardiovascular health disparities, and the use of digital tools in cardiovascular disease management.
Full Story:

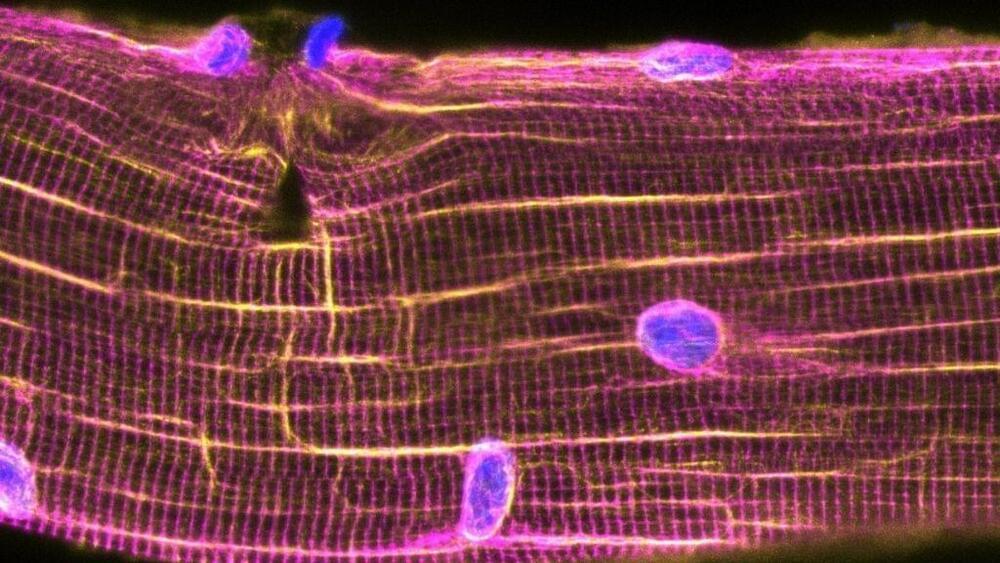
Exercise leaves muscles riddled with microscopic tears, so after a rigorous workout, the control centers of muscle cells — called nuclei — scoot toward these tiny injuries to help patch them up, scientists recently discovered.
In the new study, published Oct. 14 in the journal Science, researchers uncovered a previously unknown repair mechanism that kicks in after a run on the treadmill. Striking images show how, shortly after the exercise concludes, nuclei scuttle toward tears in the muscle fibers and issue commands for new proteins to be built, in order to seal the wounds. That same process likely unfolds in your own cells in the hours after you return home from the gym.

Photosynthesizing algae injected into the blood vessels of tadpoles supply oxygen to their brains.
Leading a double life in water and on land, frogs have many breathing techniques – through the gills, lungs, and skin – over the course of their lifetime. Now German scientists have developed another method that allows tadpoles to “breathe” by introducing algae into their bloodstream to supply oxygen. The method developed, presented October 13 in the journal iScience, provided enough oxygen to effectively rescue neurons in the brains of oxygen-deprived tadpoles.
“The algae actually produced so much oxygen that they could bring the nerve cells back to life, if you will,” says senior author Hans Straka of Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich. “For many people, it sounds like science fiction, but after all, it’s just the right combination of biological schemes and biological principles.”
In this post I outline my journey creating a dynamic NFT on the Ethereum blockchain with IPFS and discuss the possible use cases for scientific data. I do not cover algorithmic generation of static images (you should read Albert Sanchez Lafuente’s neat step-by-step for that) but instead demonstrate how I used Cytoscape.js, Anime.js and genomic feature data to dynamically generate visualizations/art at run time when NFTs are viewed from a browser. I will also not be providing an overview of Blockchain but I highly recommend reading Yifei Huang’s recent post: Why every data scientist should pay attention to crypto.
W h ile stuck home during the pandemic, I’m one of the 10 million that tried my hand at gardening on our little apartment balcony in Brooklyn. The Japanese cucumbers were a hit with our neighbors and the tomatoes were a hit with the squirrels but it was the peppers I enjoyed watching grow the most. This is what set the objective for my first NFT: create a depiction of a pepper that ripens over time.
How much of the depiction is visualization and how much is art? Well that’s in the eye of the beholder. When you spend your days scrutinizing data points, worshiping best practices and optimizing everything from memory usage to lunch orders it’s nice to take some artistic license and make something just because you like it, which is exactly what I’ve done here. The depiction is authentically generated from genomic data features but obviously this should not be viewed as any kind of serious biological analysis.