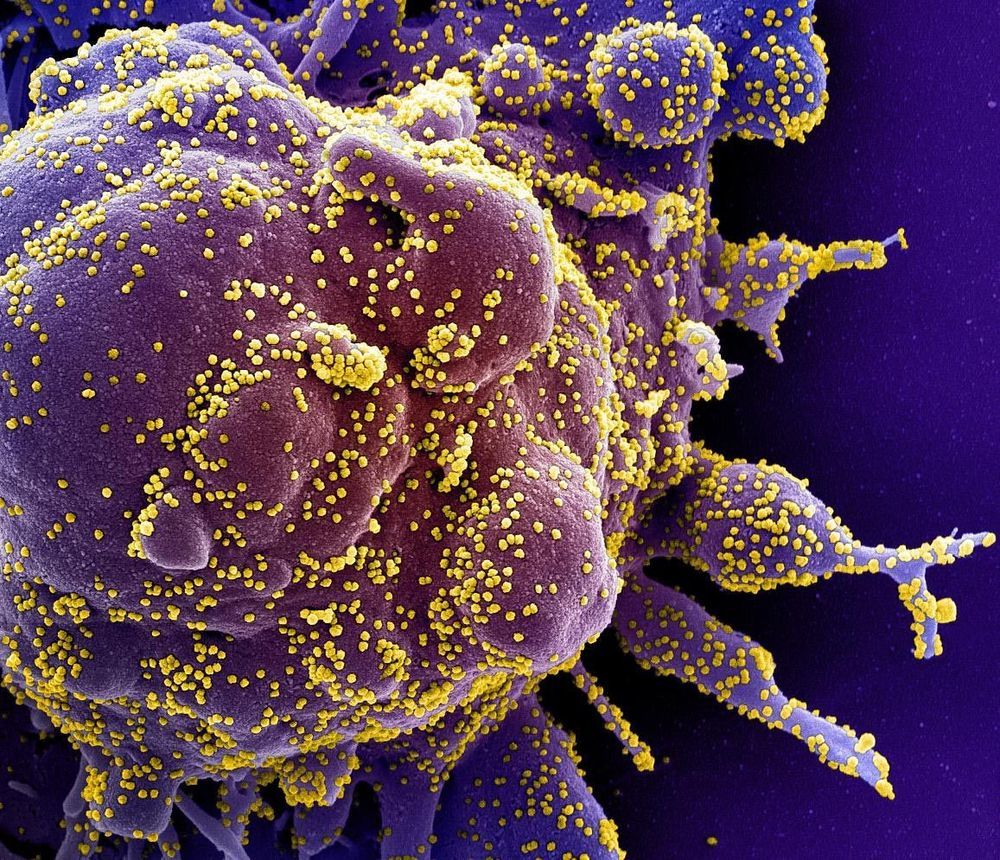
Pfizer has already made “several hundred thousand doses” of a potential coronavirus vaccine as it prepares to seek emergency use in the US by November.
The drugmaker told the Mail on Sunday that scientists in its main British lab have also unearthed drugs that could provide a potential complete cure for COVID-19, as opposed to merely a preventative vaccine.
The firm’s UK boss, Ben Osborn, said the company is manufacturing the huge stockpile of its current vaccine candidate in Belgium “at risk and at scale,” calling it “tremendously exciting.”