CRISPR is revolutionizing experimental therapies, but where should society draw the line?
Category: biotech/medical
Researchers at Microsoft have developed a faster way to write data into DNA — a biological alternative to the bits on a hard drive.
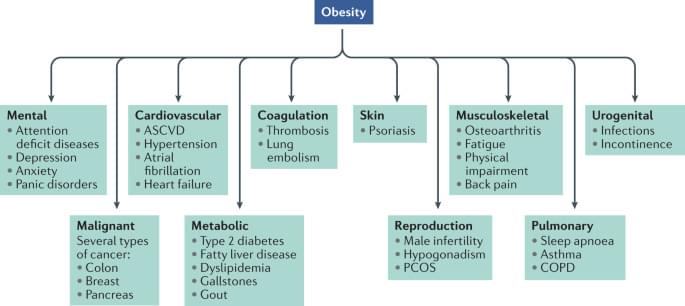
The development of therapies that are capable of safely achieving sizeable and sustained body weight loss has proved tremendously challenging. Here, Müller et al. provide an overview of the history of anti-obesity drug development, focusing on lessons learned, ongoing challenges and recent advances in the field.
In this episode, I talk to world-renowned biologist David Sinclair about aging and longevity. David rejects the notion that the deterioration of health is a natural part of growing old and asserts that aging is a disease itself that we need to reverse. But how will a reset of our biological clocks affect our interactions, responses to adversity, morality, and how we live our lives? We discuss the ethical implications of limitless lifespans and also touch on the topics of death, evolution, genetics, medicine, and data tracking.
Bio.
Dr. David Sinclair is a professor in the department of genetics and co-director of the Paul F. Glenn Center for Biology of Aging Research at Harvard Medical School and co-founder of the scientific journal Aging. He is best known for his work on understanding why we age and how to slow its effects. In addition to being a co-founder of several biotechnology companies, he’s the author of the book Lifespan: Why We Age – and Why We Don’t Have To. Dr. Sinclair was listed by TIME magazine as one of the “100 most influential people in the world”.
Website: sinclair.hms.harvard.edu.
Twitter: @davidasinclair.
Topics.
00:02:26 David’s “sticky beak” personality.
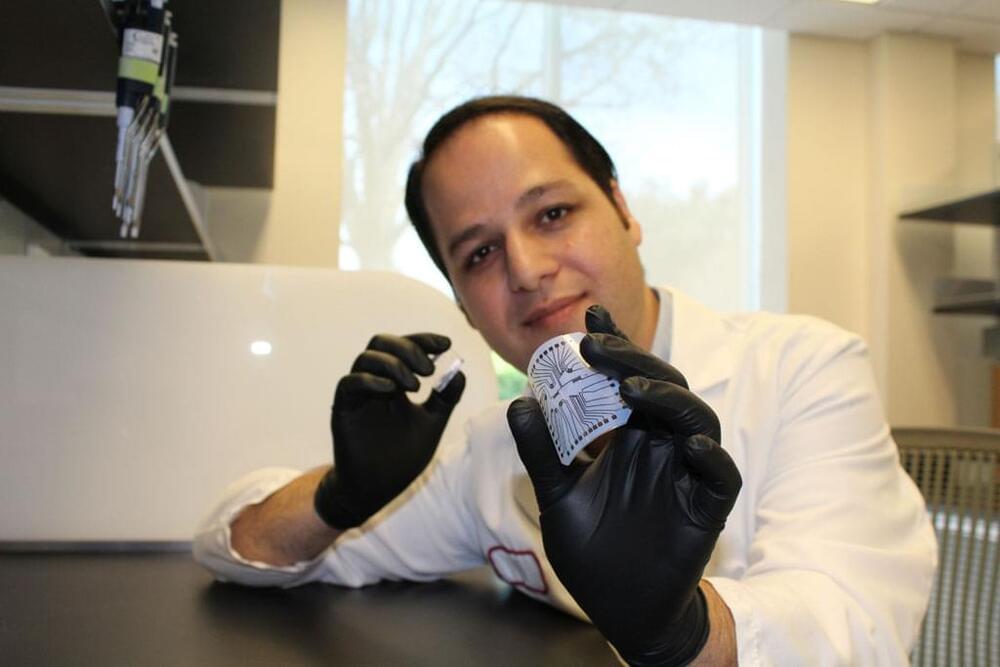
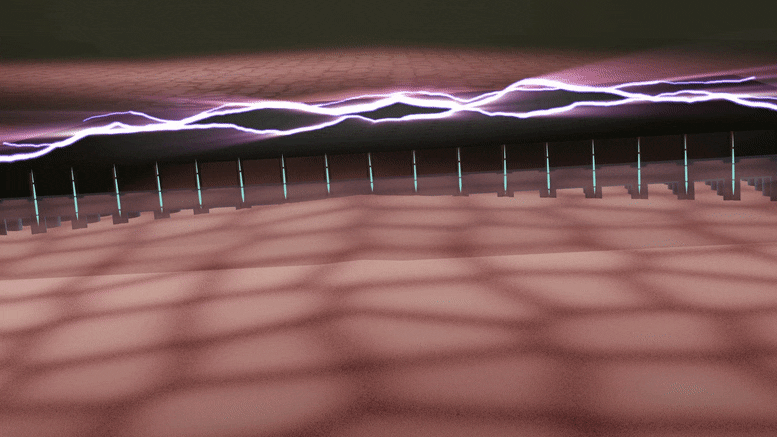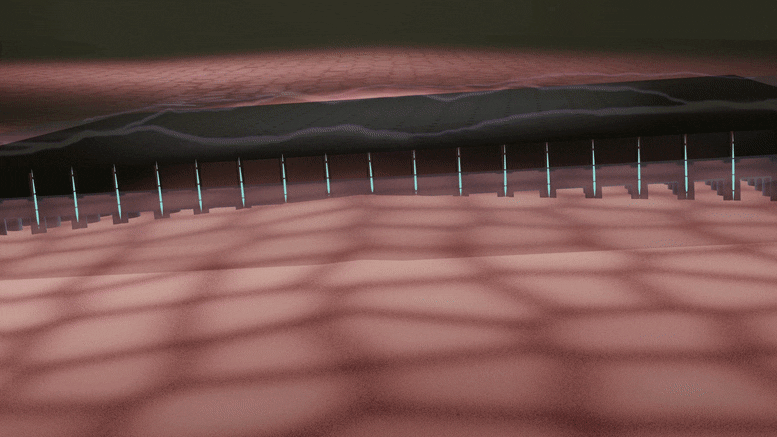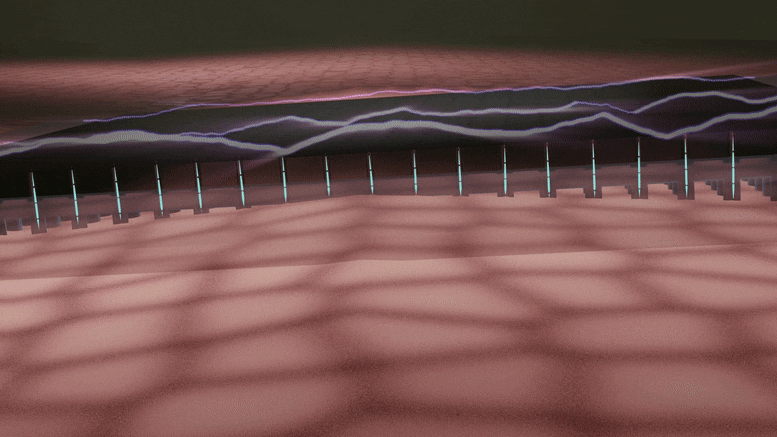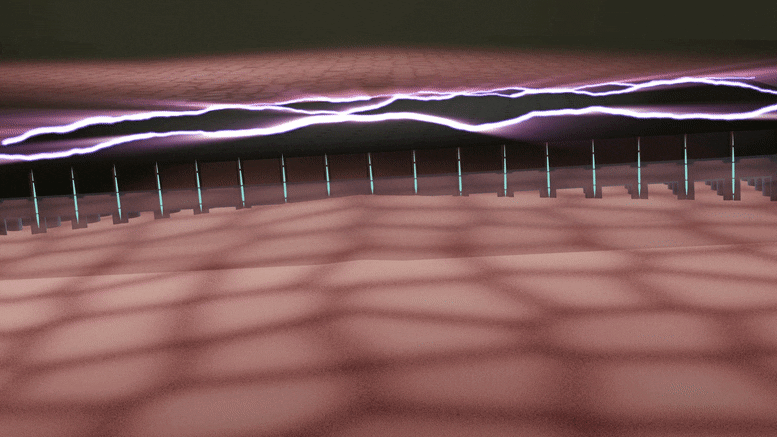
A silicon device that can change skin tissue into blood vessels and nerve cells has advanced from prototype to standardized fabrication, meaning it can now be made in a consistent, reproducible way. As reported in Nature Protocols, this work, developed by researchers at the Indiana University School of Medicine, takes the device one step closer to potential use as a treatment for people with a variety of health concerns.
The technology, called tissue nanotransfection, is a non-invasive nanochip device that can reprogram tissue function by applying a harmless electric spark to deliver specific genes in a fraction of a second. In laboratory studies, the device successfully converted skin tissue into blood vessels to repair a badly injured leg. The technology is currently being used to reprogram tissue for different kinds of therapies, such as repairing brain damage caused by stroke or preventing and reversing nerve damage caused by diabetes.
Bongard said they found that the xenobots, which were initially sphere-shaped and made from around 3,000 cells, could replicate. But it happened rarely and only in specific circumstances. The xenobots used “kinetic replication” — a process that is known to occur at the molecular level but has never been observed before at the scale of whole cells or organisms, Bongard said.
The US scientists who created the first living robots say the life forms, known as xenobots, can now reproduce — and in a way not seen in plants and animals.
Formed from the stem cells of the African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) from which it takes its name, xenobots are less than a millimeter (0.04 inches) wide. The tiny blobs were first unveiled in 2020 after experiments showed that they could move, work together in groups and self-heal.
Now the scientists that developed them at the University of Vermont, Tufts University and Harvard University’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering said they have discovered an entirely new form of biological reproduction different from any animal or plant known to science.
Circa 2017
“Enabling early detection of diseases is one of the greatest opportunities we have for developing effective treatments,” Esfandyarpour said. “Maybe $1 in the U.S. doesn’t count that much, but somewhere in the developing world, it’s a lot of money.”
A two-part system
A combination of microfluidics, electronics and inkjet printing technology, the lab-on-a-chip is a two-part system: A clear silicone microfluidic chamber for housing cells sits on top of a reusable electronic strip.
Circa 2018 #artificialintelligence #doctor
Abstract: Online symptom checkers have significant potential to improve patient care, however their reliability and accuracy remain variable. We hypothesised that an artificial intelligence (AI) powered triage and diagnostic system would compare favourably with human doctors with respect to triage and diagnostic accuracy. We performed a prospective validation study of the accuracy and safety of an AI powered triage and diagnostic system. Identical cases were evaluated by both an AI system and human doctors. Differential diagnoses and triage outcomes were evaluated by an independent judge, who was blinded from knowing the source (AI system or human doctor) of the outcomes. Independently of these cases, vignettes from publicly available resources were also assessed to provide a benchmark to previous studies and the diagnostic component of the MRCGP exam. Overall we found that the Babylon AI powered Triage and Diagnostic System was able to identify the condition modelled by a clinical vignette with accuracy comparable to human doctors (in terms of precision and recall). In addition, we found that the triage advice recommended by the AI System was, on average, safer than that of human doctors, when compared to the ranges of acceptable triage provided by independent expert judges, with only a minimal reduction in appropriateness.
From: Yura Perov N [view email]
[v1] Wed, 27 Jun 2018 21:18:37 UTC (54 KB)
Biodiversity conservation, public health and improved livelihoods — dr gladys kalema-zikusoka, founder and CEO, conservation through public health.
Dr. Gladys Kalema-Zikusoka, is the Founder and CEO of Conservation Through Public Health (CTPH — https://ctph.org/), a 16-year old non-profit organization, based in Uganda, that promotes conservation by improving the quality of life of people and wildlife to enable them to coexist in and around protected areas in Africa, and she has become one of the leading conservationists and scientists working to save the critically endangered mountain gorillas of East Africa.
Dr. Kalema-Zikusoka is also on the Scientific Advisory Group for the Origins of Novel Pathogens (SAGO) of the World Health Organization (https://www.who.int/groups/scientific-advisory-group-on-the-origins-of-novel-pathogens-(sago)/about)
Dr. Kalema-Zikusoka trained as a veterinarian at the University of London’s Royal Veterinary College. Between 1996 and 2000, she set up the first Veterinary Unit at the Uganda Wildlife Authority. From 2000 to 2003, she completed a zoological medicine residency and masters in specialized veterinary medicine at North Carolina State University and North Carolina Zoological Park.
Dr. Kalema-Zikusoka became an Ashoka Fellow in 2007 for merging Uganda’s wildlife management and rural public health programs to create common resources for both people and animals.
Prior to setting up CTPH, Dr. Kalema-Zikusoka also did a certificate in Non-profit management from Duke University. Most recently in 2016, she completed an MBA in Global Business and Sustainability – Social Entrepreneurship Track.
Dr. Kalema-Zikusoka’s most recent awards include the 2017 World Wildlife Day Award from the Ministry of Tourism, Wildlife and Antiquities (MTWA) for outstanding contribution to conservation in Uganda and 2017 Golden Jubilee Award from the President of Uganda for distinguished service to the nation as a veterinarian and conservationist on International Women’s Day.
Other awards include San Diego Zoo’s 2008 “Conservation in Action Award,” the 2009 Whitley Gold Award for outstanding leadership in grassroots nature conservation; 2011 Wings World Quest Women of Discovery Humanitarian Award, and 2014 CEO Communications Africa’s Most Influential Women in Business and Government Award in Medicine and Veterinary category.
Bridging Technology And Medicine For The Modern Healthcare Ecosystem — Dr. Mona G. Flores, MD, Global Head of Medical AI, NVIDIA.
Dr. Mona Flores M.D., is the Global Head of Medical AI, at NVIDIA (https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/author/monaflores/), the American multinational technology company, where she oversees the company’s AI initiatives in medicine and healthcare to bridge the chasm between technology and medicine.
Dr. Flores first joined NVIDIA in 2018 with a focus on developing their healthcare ecosystem. Before joining NVIDIA, she served as the chief medical officer of digital health company Human-Resolution Technologies after a 25+ year career in medicine and cardiothoracic surgery.
Dr. Flores received her medical degree from Oregon Health and Science University, followed by a general surgery residency at the University of California at San Diego, a Postdoctoral Fellowship at Stanford, and a cardiothoracic surgery residency and fellowship at Columbia University in New York.
Dr. Flores also has a Masters of Biology from San Jose State and an MBA from the University at Albany School of Business. She initially worked in investment banking for a few years before pursuing her passion for medicine and technology.