Chronic increases of the cytokine IL-17a circulating in the blood of mice reduced microglia activity in one region of the hippocampus, an area of the brain critical for memory and learning.




This is the FIRST part of the interview with Rodolfo Goya.
In this video Professor Goya talks about his role in the original experiment and the progress in his current study to reproduce the results with young blood plasma.
Professor Rodolfo Goya is Senior Scientist at The National Scientific and Technical Research Council in Argentina where he is a biochemist and researcher.
Dr. Goya has led a number of studies on cellular reprogramming and restoration of function in important organs, such as the thymus and the brain. He is also studying different aspects of cryopreservation.
He was one of the authors of the paper “Reversing age: dual species measurement of epigenetic age with a single clock” and is now working in his lab to reproduce and extend the results.
If you would like to support our channel, we’d love a coffee…thank you!
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/mhealthspan
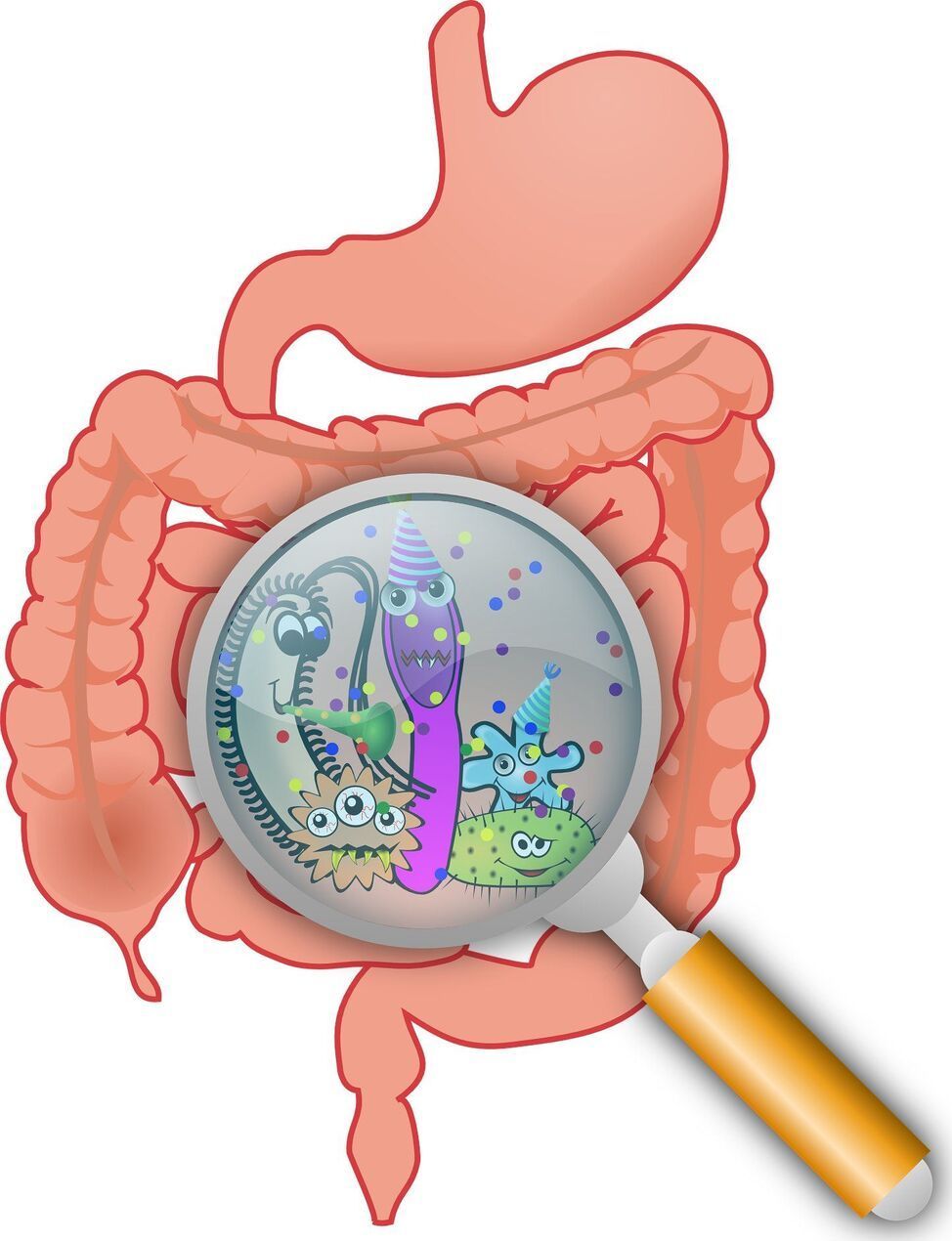
The gut microbiome is an integral component of the body, but its importance in the human aging process is unclear. ISB researchers and their collaborators have identified distinct signatures in the gut microbiome that are associated with either healthy or unhealthy aging trajectories, which in turn predict survival in a population of older individuals. The work is set to be published in the journal Nature Metabolism.



TOKYO — SoftBank Group has urged some of its high-profile portfolio companies to accelerate plans for stock market listings, telling them they should capitalize on strong investor appetite for the booming tech sector.
The Japanese tech investment group led by Chairman and CEO Masayoshi Son hopes many of the businesses in its nearly $100 billion Vision Fund will tap the bullish sentiment for tech companies after the coronavirus pandemic, sources familiar with SoftBank’s strategy say.
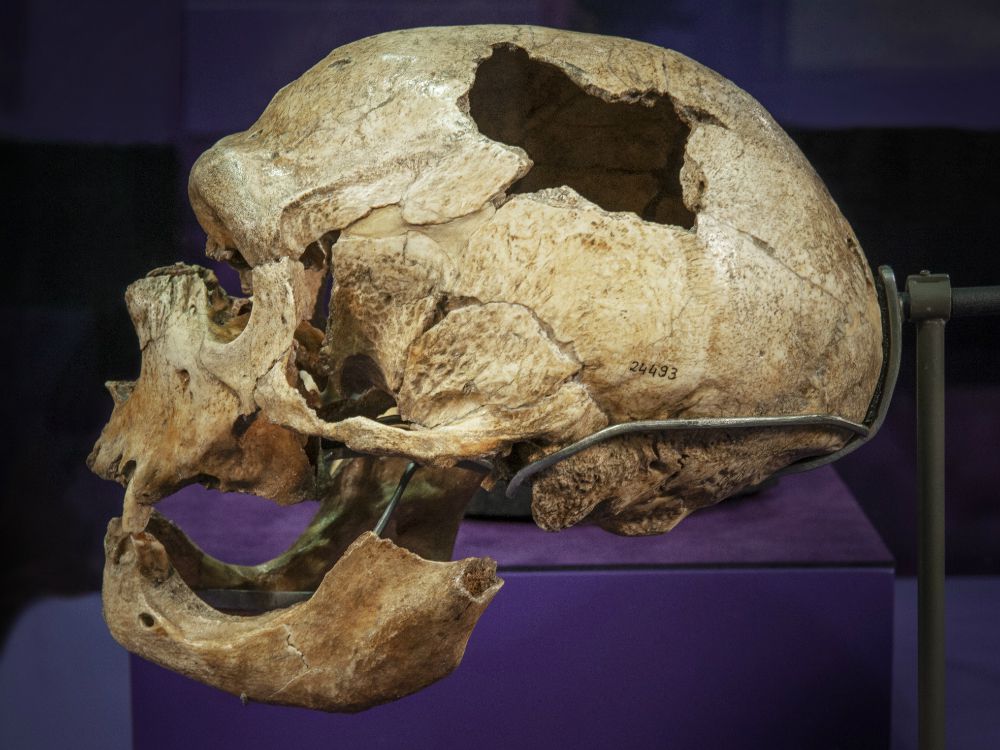

While the brain tissue of modern humans are typically smooth and spherical, the study, which was published in Science on Feb 11, found that the tissue created with the ancient genes were smaller and had rough, complex surfaces.
“The question here is what makes us human,” Muotri told CNN. “Why are our brains so different from other species including our own extinct relatives?”

