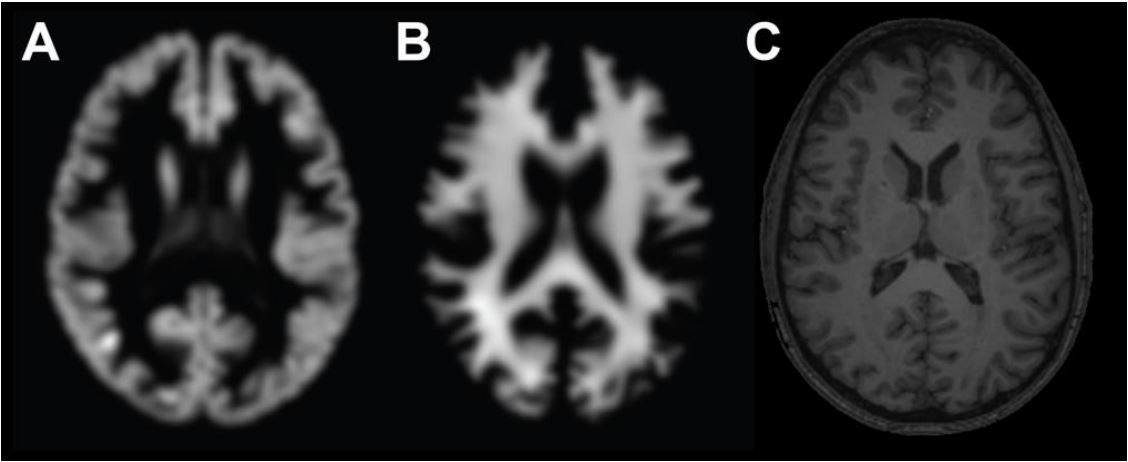
Determining brain age from an MRI scan has always been a time-consuming business. Now an AI machine gives the answer in seconds.
Category: biotech/medical
Researchers at University of California, Santa Barbara, have designed a functional nanoscale computing element that could be packed into a space no bigger than 50 nanometres on any side.
In 1959, renowned physicist Richard Feynman, in his talk “Plenty of Room at the Bottom” spoke of a future in which tiny machines could perform huge feats. Like many forward-looking concepts, his molecule and atom-sized world remained for years in the realm of science fiction. And then, scientists and other creative thinkers began to realise Feynman’s nanotechnological visions.
You have the power to change the future of medicine and how we treat age-related diseases. Here is an example of how grassroots fundraising is changing science.
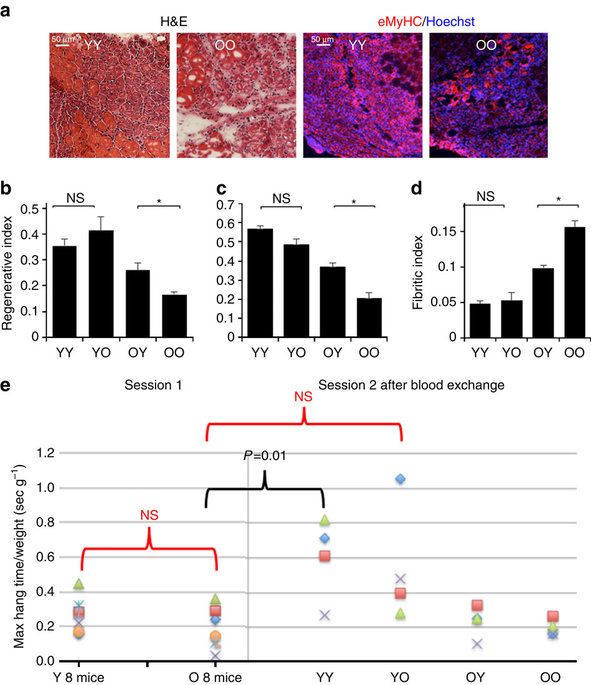
Joining the circulatory system of an old with a young animal has been shown to rejuvenate old tissues. Here the authors describe a comparatively simple blood infusion system that allows for the controlled exchange of blood between two animals, and study the effects of a single exchange on various tissues.
The CellAge AMA is open for questions, come along and ask about biotechnology, senolytics and so on.
Welcome to the CellAge AMA with Mantas Matjusaitis, PhD student in synthetic biology and founder of CellAge. I am here to talk about our work to improve the targeting of dysfunctional “senescent” cells in the body, and thereby aid in their eventual removal. This is important because removal of these cells has been shown to be a critical component in the effort to improve healthy human lifespan.
In short, CellAge is going to develop synthetic DNA promoters which are specific to senescent cells, as the promoters that are currently used for this purpose, such as the p16 gene promoter, suffer from various issues and limitations (not comprehensively targeting all senescent cells, collateral damage in targeting some cells that are not senescent, etc.). You can find more details in our technology video here, and on our Lifespan.io information page.
Seeing as our primary mission is to expand the interface between synthetic biology and aging research, as well as drive translational research forward, we will offer the senescence reporter assay we develop to academics for free. We predict that in the very near future this assay will be also used as a quality control step in the cell therapy manufacturing process to make cell therapies safer.
In Brief
- Facebook billionaire Mark Zuckerberg recently opened his wallet in order to create BioHub, a $600 million center that will focus on working to create a human cell directory.
- By mapping the trillions of cells in the human body, experts would be able to develop new drugs and vaccines to combat — and potentially end — disease.
Last month, we reported on the Human Cell Atlas, a project that plans to provide a detailed reference map of the human body’s trillions of cells. Yes, trillions. Once completed, the project could revolutionize healthcare by giving doctors and researchers a better way to predict, diagnose, and treat diseases.
Initiatives like this need funding – so Facebook billionaire Mark Zuckerberg opened his wallet and founded BioHub, a $600 million center that will focus on helping create a human cell directory. Zuckerberg and his wife, Priscilla Chan, plan to give away $3 billion over 10 years to fight disease, and BioHub is the couple’s first initiative.
Excellent overview on BMI technology.
Less than a century ago, Hans Berger, a German psychiatrist, was placing silver foil electrodes on his patients’ heads and observing small ripples of continuous electrical voltage emerging from these. These were the first human brain waves to ever be recorded. Since Hans Berger’s first recordings, our knowledge on the brain structure and function has developed considerably. We now have a much clearer understanding of the neuronal sources that generate these electrical signals and the technology that is now available allows us to get a much denser and accurate picture of how these electrical signals change in time and across the human scalp.
The recording and analysis of brain signals has advanced to a level where people are now able to control and interact with devices around them with the use of their brain signals. The field of brain-computer interfaces has in fact garnered huge interest during the past two decades, and the development of low-cost hardware solutions together with the continuously evolving signal analysis techniques, have brought this technology closer to market than ever before.
Research in the field of brain-computer interfaces was primarily propelled by the need of finding novel communication channels for individuals suffering from severe mobility disorders as in the case of patients with locked-in syndrome. People suffering from the condition have a perfectly functioning brain but are trapped inside their body, which no longer responds to the signals being transmitted from their brain.
Check out the The Longevity Reporter interview with CellAge as they talk about rejuvenation biotechnology.
Innovative new startup Cell Age is using synthetic biology to develop new ways of targeting and removing senescent cells. We caught up with CEO Mantas Matjusaitis for an interview as their first fundraiser goes live on Lifespan.io (find it here)
Could you tell us a little bit about your approach and what makes you different?
We are a synthetic biology company which will use proven proprietary methods to develop tools and therapies to specifically target senescent cells. Early on, we will be focusing on developing novel approaches to identify senescent cells and this will help to screen for new drugs as well as move the field forward in general. Importantly, we will offer our first products for free to researchers from academia, because, in the end, our mission is to help the society and scientific community and we think this is the right way forward. Later on, our tools will be used to make cell-based therapies safer by removing senescent cells before the transplantations. And eventually, we are aiming to help create safe and accurate gene therapies to help fight age-related diseases like osteoarthritis, atherosclerosis and more.
Excercise is the best low cost activity you can do as part of your personal longevity strategy. Here we see data showing it can improve resistance to oxidative stress.
Researchers digging deeper into the mechanisms by which exercise produces benefits have found that it improves the resistance of blood vessels to oxidative stress. With age the presence of oxidizing molecules and oxidative modification of proteins, preventing correct function, increases for reasons that include damage to mitochondria, the power plants of the cell. Oxidative damage to molecular machinery is somewhere in the middle of the chain of cause and effect that starts with fundamental forms of damage to cells and tissues and spirals down into age-related diseases. Near all of this oxidation is repaired very quickly, the damaged molecules dismantled and recycled, but in most contexts more of it over the long term is worse than less of it.
Quote: