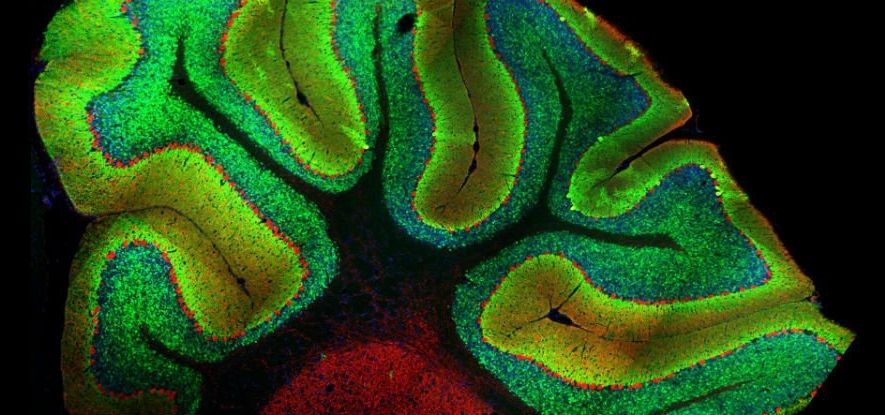
One of the best-known regions of the brain, the cerebellum accounts for just 10 percent of the organ’s total volume, but contains more than 50 percent of its neurons.
Despite all that processing power, it’s been assumed that the cerebellum functions largely outside the realm of conscious awareness, instead coordinating physical activities like standing and breathing. But now neuroscientists have discovered that it plays an important role in the reward response — one of the main drives that motivate and shape human behaviour.
Not only does this open up new research possibilities for the little region that has for centuries been primarily linked motor skills and sensory input, but it suggests that the neurons that make up much of the cerebellum — called granule cells — are functioning in ways we never anticipated.