A novel way to target proteins in cells could lead to undruggable diseases being treatable.
Researchers at the university of Dundee have shown that it is possible to target and destroy specific proteins within cells using a new directed protein missile system. This is very interesting as it raises the possibility of targeting aberrant proteins present in diseases that currently have no drug that affects them.
This opens the door to treating a range of diseases as well as potentially being useful in directly targeting proteins involved in the aging process. Before we take a look at the research let’s recap on why proteins are important, what they do and how they relate to aging and diseases.
So what are proteins?
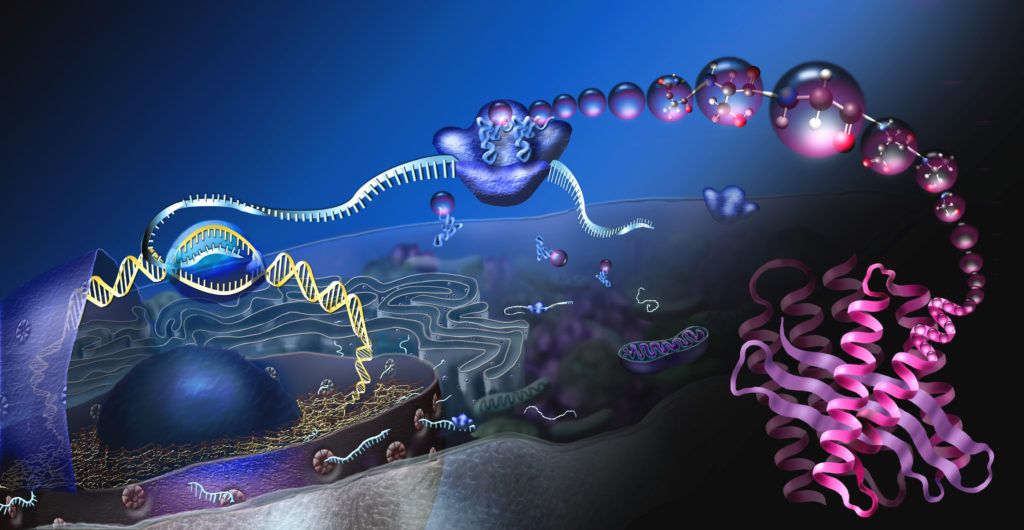
Proteins are often called the building blocks of life and they are critical to the operation of our cells and therefore to our lives. Proteins are produced by the cell and perform a huge variety of functions such as, activating the immune response against pathogens, regulating metabolism and cellular functions. They do the majority of the work in cells and are required for maintaining the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs.
Read more