Summary: Researchers at the University of California discovered a key way that cancer manipulates the genetic code using DNA methylation that has important implications for the treatment of cancers. [This article first appeared on the website LongevityFacts.com. Author: Brady Hartman. ]
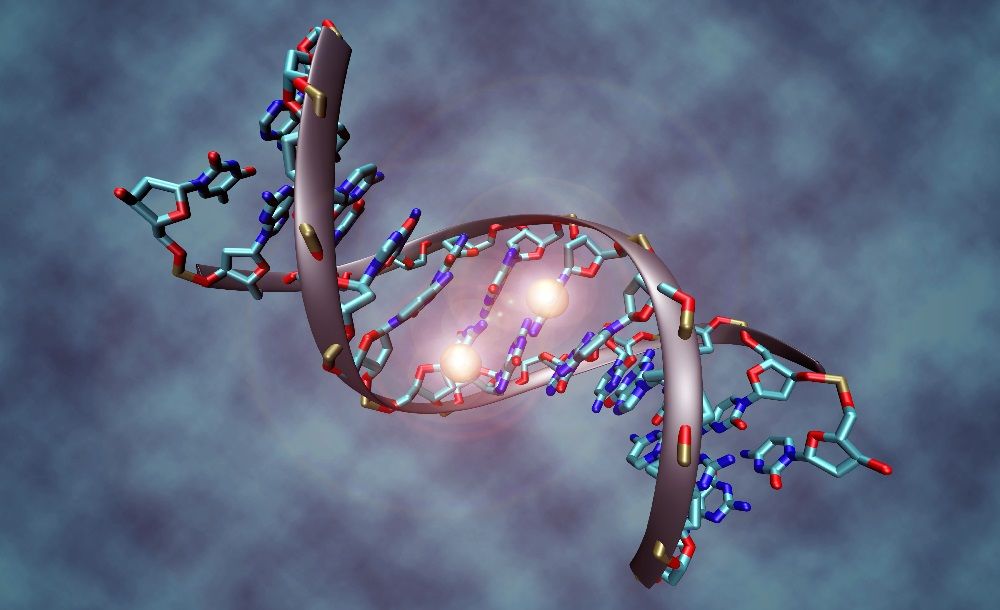
Up until now, scientists haven’t fully understood how DNA methylation causes changes in our genetic code that enable cancer to thrive.
Now, a team led by associate professor Jikui Song at the University of California Riverside have deciphered the crystal structure of an enzyme that plays a crucial role in DNA methylation that allows tumors to survive and grow.